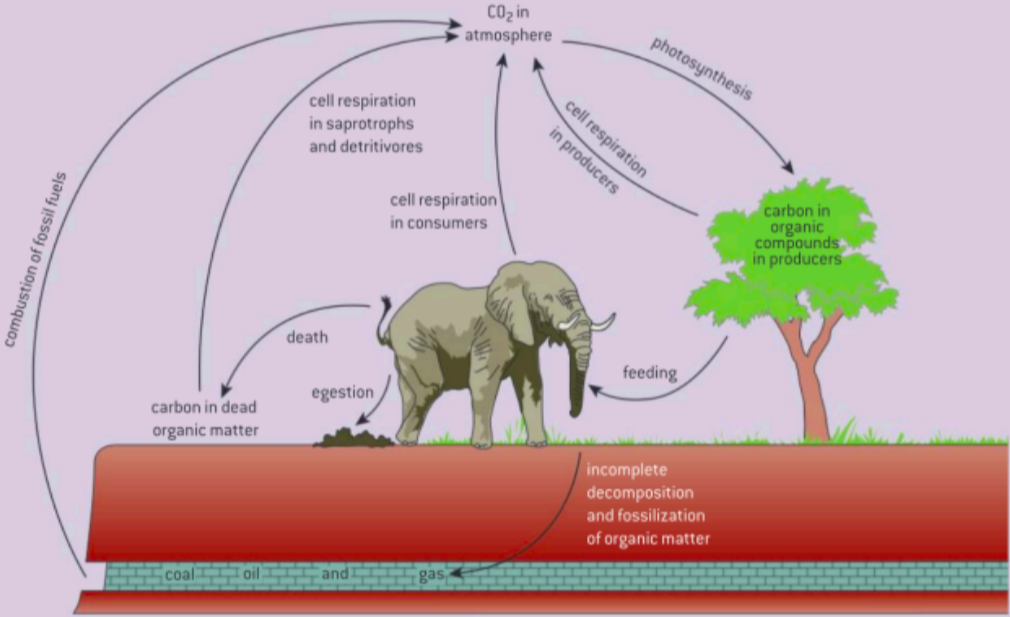
4.3 The Carbon Cycle
Light from sun is initial energy source for most communities
Ecosystem - a community and its abiotic environment
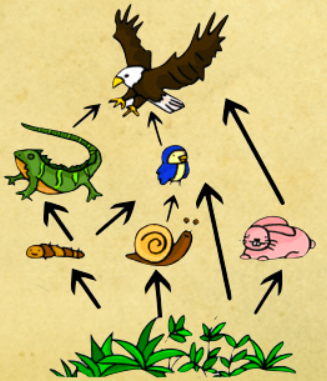
Community - a group of organisms living and interacting with each other in an area
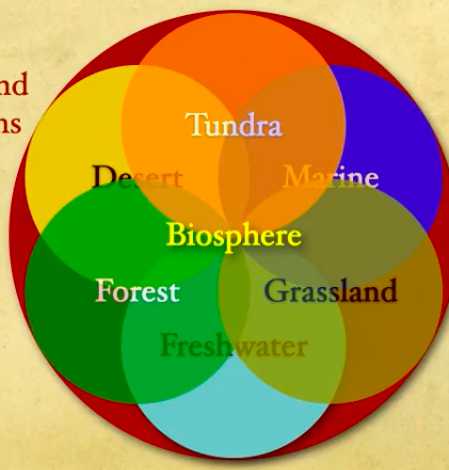
 Biosphere - made up of interrelated and interdependent ecosystems
Biosphere - made up of interrelated and interdependent ecosystems
Energy can enter and leave an ecosystem, but nutrients must be recycled
It is important to understand how major nutrients are cycled through an ecosystem
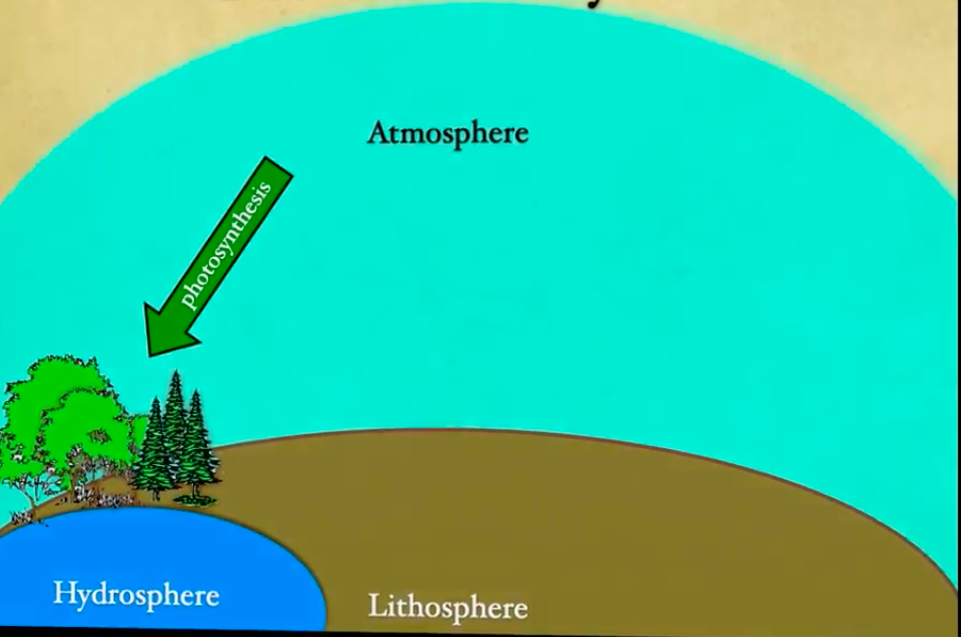
There is an interaction of living organisms and biosphere through processes of photosynthesis, respiration, fossilization, and combustion.
Photosynthesis
atmospheric CO2 is used to produce organic compounds in autotrophs (mostly plants and algae).
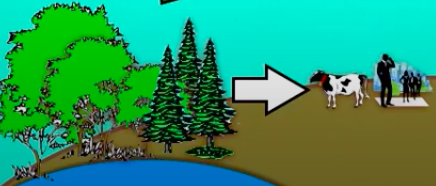
Consumption
Heterotrophs consume these compounds and incorporate them into their bodies.
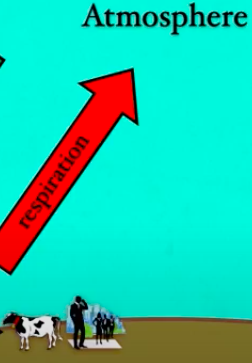
 Respiration+Decomposition
Respiration+Decomposition
Respiration releases carbon compounds back into the atmosphere. When organisms die some of the carbon compounds are fossilized and therefore sequestered (stored) in the earth.
Combustion
When fossil fuels and other organic materials are burned, carbon compounds are released into the atmosphere.
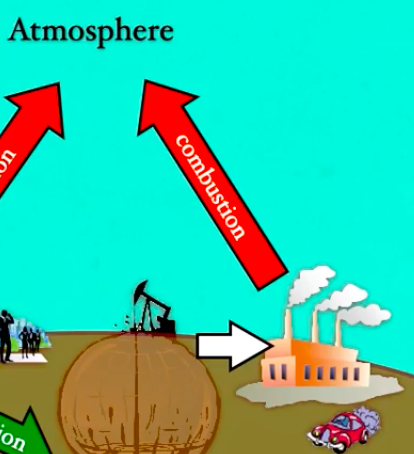
Image to Memorize for Carbon Cycle