Velocity-Time Graphs
Velocity-time graphs
- Velocity means speed in a certain direction
- A velocity-time graph is sometimes called a speed-time graph
- You need to be able to interpret a velocity-time graph
- Use the two golden rules on the right to answer questions involving speed, time and acceleration
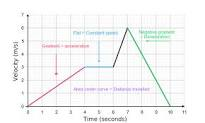
Golden rules
- The gradient of a velocity-time graph tells you the acceleration
- The most common units of acceleration are m/s(2)
- Acceleration = change in velocity / change in time
- The area underneath a velocity-time graph tells you the distance travelled
- If you have to estimate the area under a curve use the techniques shown later
Problem solved
The easiest way to solve this problem is to sketch a velocity-time graph of a journey
The graph doesn’t have to be to scale, but make sure you label the axes and mark any important points
Constant deceleration means that this section of the velocity-time graph will be a straight line
To calculate the total distance travelled you need to work out the total area underneath the graph
Divide it into sections, work out the area of each section, and then add them together