Chapter 13 - Serous Fluid
Physiology
- The closed cavities of the body - the pleural, pericardial and peritoneal cavities - are each lined by two membranes referred to as the serous membranes.
- One membrane lines the cavity wall (parietal membrane).
- The other covers the organs within the cavity (visceral membrane).
- The fluid between the membranes is called serous fluid, which provides lubrication between the parietal and visceral membranes.
- Normally, only a small amount of serous fluid is present, because production and reabsorption take place at a constant rate.
- Production and reabsorption are subject to hydrostatic and colloidal (oncotic) pressures from the capillaries that serve the cavities and the capillary permeability.
- Under normal conditions, colloidal pressure from serum proteins is the same in the capillaries on both sides of the membrane.
- The hydrostatic pressure in the parietal and visceral capillaries causes fluid to enter between the membranes.
- A slightly unequal pressure in the parietal and visceral capillaries creates a small excess of fluid that is reabsorbed by the lymphatic capillaries.
- Serous fluids are formed as ultrafiltrates of plasma, with no additional material contributed by the mesothelial cells that line the membranes.
- The filtration of the plasma ultrafiltrate results in increased oncotic pressure in the capillaries that favors reabsorption of fluid back into the capillaries.
- This produces a continuous exchange of serous fluid and maintains the normal volume of fluid beween the membranes.
Specimen Collection and Handling
- Collection is done by needle aspiration, namely thoracentesis (pleural), pericardiocentesis (pericardial), and paracentesis (peritoneal).
- Abundant fluid (greater than 100 mL) is usually collected.
- An ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) tube is used for cell counts and differential counts.
- Sterile heparinized evacuated tubes are used for microbiology and cytology.
- For better recovery of microorganisms and abnormal cells, concentration of large amounts of fluid is performed by centrifugation.
- Chemistry tests can be run on clotted specimens in plain tubes or on heparinized tubes.
- Blood specimens should be obtained at the time of collection for comparison with chemical tests.
- Specimens for pH must be maintained anaerobically in ice.
Transudates and Exudates
- Effusions that form because of a systemic disorder that disrupts the balance in the regulation of fluid filtration and reabsorption are called transudates.
- Testing transudate fluids is usually not necessary.
- Effusions that form because of conditions that directly involve the membranes of the particular cavity are called exudates.
- Differentiation is done by determining the fluid-to-blood ratios for protein and lactic dehydrogenase.
| Transudate | Exudate |
|---|
| Appearance | clear | cloudy |
| Fluid-Serum Protein Ratio | <0.5 | >0.5 |
| Fluid-Serum LDH Ratio | <0.6 | >0.6 |
| WBC Count | <1000/μL | >1000/μL |
| RBC Count | <100,000/μL | >100,000/μL |
| Spontaneous Clotting | No | Possible |
| Pleural Fluid Cholesterol | <45-60 mg/dL | >45-60 mg/dL |
| Pleural Fluid-Serum Cholesterol Ratio | <0.3 | >0.3 |
| Pleural Fluid-Bilirubin Ratio | <0.6 | >0.6 |
| Serum-Ascites Albumin Gradient | >1.1 | <1.1 |
Pleural Fluid
- Pleural fluid is obtained from the pleural cavity, located between the parietal pleural membrane lining the chest wall and the visceral pleural membrane covering the lungs.
Appearance
| Appearance | Clinical Significance |
|---|
| clear, pale yellow | normal |
| turbid, white | bacterial infection, tuberculosis, immunologic disorder |
| bloody | hemathorax (traumatic injury, appears streaked and uneven), hemorrhagic effusion, pulmonary embolis, tuberculosis, membrane damage |
| milky, white | chylous material (thoracic duct leakage) |
| milky, green tinge | pseudochylous material (chronic inflammation) |
| brown | rupture of amoebic liver abscess |
| black | Aspergillus |
| viscous | malignant mesothelioma (increased hyaluronic acid) |
- To differentate between hemothorax and hemorrhagic exudate, the fluid hematocrit is more than 50% of the whole blood hematocrit.
- Effusion occurrs from the inpour of blood from the injury.
- A chronic membrane disease effusion contains both blood and increased pleural fluid, resulting in a much lower hematocrit.
- To differentiate between chylous and pseudochylous effusions, the following are observed:
| Chylous | Pseudochylous |
|---|
| Cells Seen | predominantly lymphocytes | mixed cells |
| Cholesterol Crystals | absent | present |
| Triglycerides | >110 mg/dL | <55 mg/dL |
| Sudan III stain | strongly positive | negative or weakly positive |
Hematology Tests
| Cell | Appearance | Clinical Significance | Picture |
|---|
| neutrophils | | increased in bacterial infection, pancreatitis and pulmonary infarction | 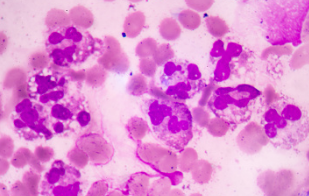 |
| lymphocytes | prominent nucleoli, cleaved nuclei, may be seen with LE cells | increased in tuberculosis, viral infections, malignancy and autoimmune disorders | 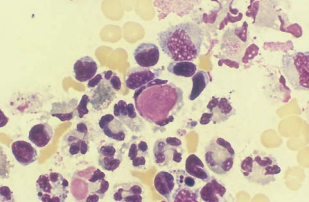 |
| eosinophils | | increased in pneumothorax and hemothorax, allergic reactions and parasitic infections | 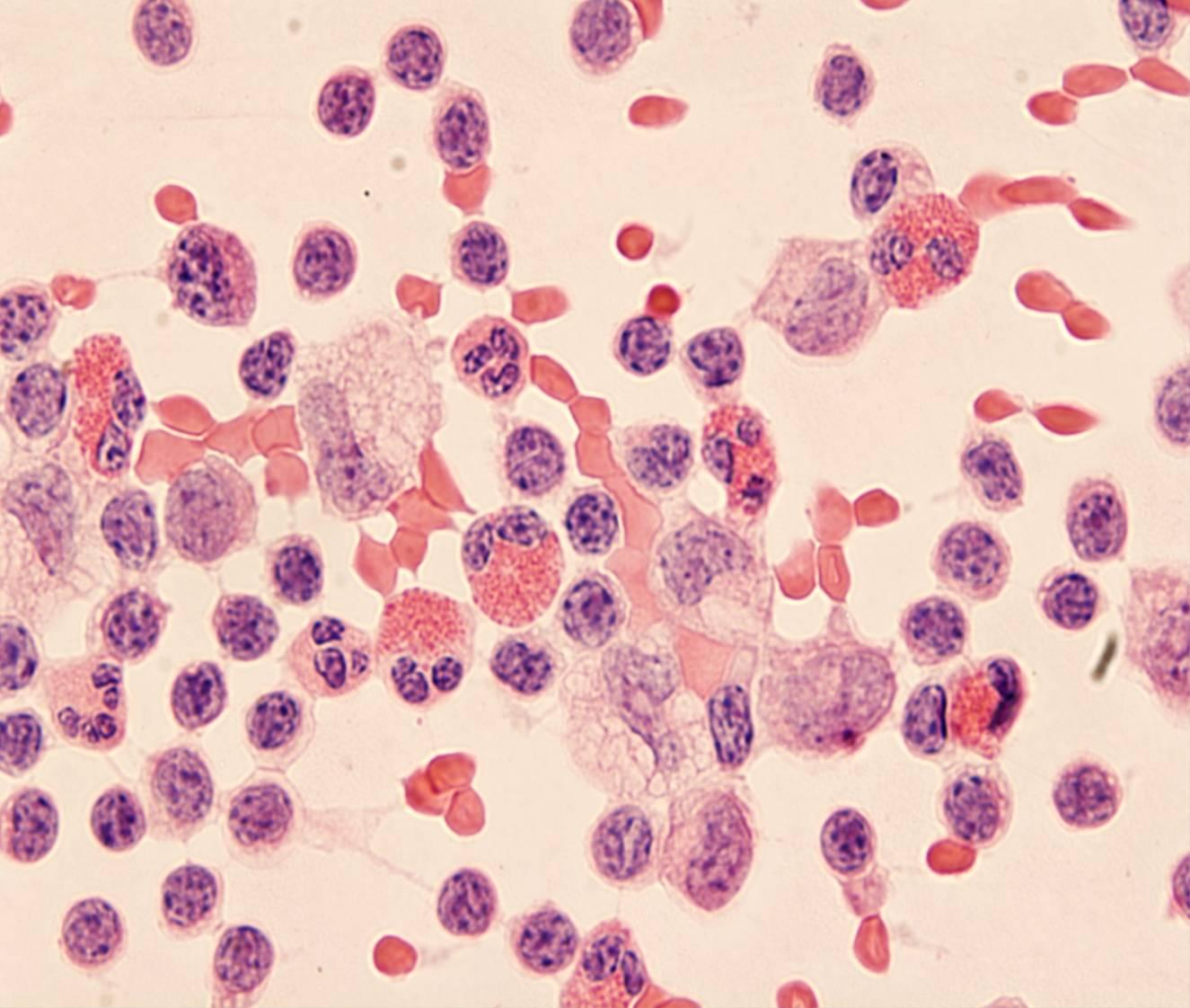 |
| mesothelial cells | pleomorphic; resemble lymphocytes, plasma cells and malignant cells; single round cell with abundant blue cytoplasm and round uniform dark purple nucleus (normal), or clustered multinucleated cells with varying amounts of cytoplasm, eccentric nuclei, and prominent nucleoli (“reactive”) | increased in pneumonia and malignancy, decreased in tuberculosis | 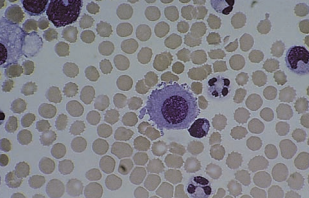 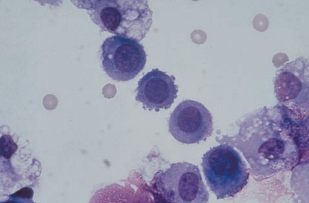 |
| plasma cells | seen in the absence of mesothelial cels | decreased in tuberculosis | 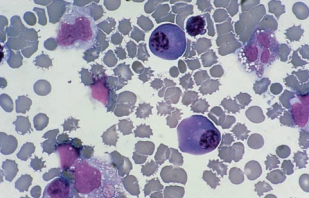 |
| malignant cells | nuclear and cytoplasmic irregularities, hyperchromatic nucleoli, cellular clumps with cytoplasmic molding (community borders), increased nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratios | primary adenocarcinoma, small-cell carcinoma, metastatic carcinoma | 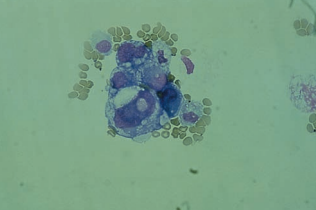 |
Chemistry Tests
| Parameter | Important Values | Clinical SIgnificance |
|---|
| glucose | <60 mg/dL | tuberculosis, rheumatoid inflammation, and purulent infections |
| lactate | elevated | bacterial infection |
| pH | <7.0 | need for chest-tube drainage and antibiotics (pneumonia) |
| <6.0 | esophageal rupture and influx of gastric fluid |
| 0.30 degrees lower than the blood pH | acidosis |
| adenosine deaminase (ADA) | >40 U/L | tuberculosis and malignancy |
| amylase | elevated | pancreatitis, esophageal rupture and malignancy |
Microbiologic and Serologic Tests
- Microorganisms primarily seen include Staphylococcus aureus, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Enterobacteriaceae and anaerobes.
- Antinuclear antibody (ANA) and rheumatoid factor (RF) tests are usually performed to differentiate effusions of immunologic origin from noninflammatory processes.
- Detection of the tumor markers carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), CA 125 (metastatic uterine cancer), CA15.3 and CA 549 (breast cancer), and CYFRA 21-1 (lung cancer) provide valuable diagnostic information in effusions of malignant origin.
Pericardial Fluid
- The presence of an effusion is suspected when cardiac compression (tamponade) is noted during the physician’s examination.
- Normally, only a small amount (10 to 50 mL) of fluid is found between the pericardial serous membranes.
Appearance
| Appearance | Clinical Significance |
|---|
| clear, pale yellow | normal or transudate |
| turbid | infection, malignancy |
| blood-streaked | malignancy |
| grossly bloody | accidental cardiac puncture, misuse of anticoagulant medications |
| milky | chylous or pseudochylous |
Laboratory Tests
- WBC counts greater than 1000 WBCs/μL is indicative of bacterial endocarditis.
- When endocarditis is suspected, bacterial cultures and Gram staining is done.
- Infections are frequently caused by previous respiratory infections including Haemophilus, Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, Adenovirus and Coxsackievirus.
- Malignant cells are frequently found in cases of metastatic lung or breast carcinoma, supported by positive detection of carcinoembryonic antigens.
- Acid-fast stains and chemical tests for ADA are done in cases of AIDS infection.
Ascitic Fluid/Peritoneal Fluid
- Ascites refers to the accumulation of fluid between the peritoneal membranes, and the fluid is commonly referred to as ascitic fluid rather than peritoneal fluid.
- Normal saline is sometimes introduced into the peritoneal cavity to act as a lavage for the detection of abdominal injuries that have not yet resulted in the accumulation of fluid.
- Peritoneal lavage is a sensitive test for the detection of intra-abdominal bleeding in blunt trauma cases, and results of the RBC count can be used along with radiographic procedures to aid in determining the need for surgery.
Appearance
| Appearance | Clinical Significance |
|---|
| clear, pale yellow | normal |
| turbid | bacterial or fungal infection |
| green or dark brown | presence of bile |
| blood-streaked | trauma, tuberculosis, intestinal disorders or malignancy |
Transudates and Exudates
Differentiation between ascitic fluid transudates and exudates is more difficult than for pleural and pericardial effusions.
The serum-ascites albumin gradient (SAAG) is recommended over the fluid:serum total protein and LD ratios for the detection of transudates of hepatic origin.
Fluid and serum albumin levels are measured concurrently, and the fluid albumin level is then subtracted from the serum albumin level.
A difference (gradient) of 1.1 or greater suggests a transudate effusion of hepatic origin, and lower gradients are associated with exudative effusions.

Cellular Examination
- Cells present in ascitic fluid include leukocytes, abundant mesothelial cells and macrophages, including lipophages.
- RBC counts greater than 100,000/μL are indicative of blunt trauma injuries.
- Normal WBC counts are less than 350 cells/μL, and the count increases with bacterial peritonitis and cirrhosis.
- An absolute neutrophil count greater than 250 cells/μL or greater than 50% of the total WBC count is indicative of infection.
- Lymphocytes are the predominant cell in tuberculosis.
- Microorganisms including bacteria, yeast and Toxoplasma gondii may also be present.
- Malignant cells of ovarian, prostatic and colonic origin often containing mucin-filled vacuoles are frequently seen.
- Psammoma bodies containing concentric striations of collagen-like material can be seen in benign conditions and are also associated with ovarian and thyroid malignancies.
- The presence of mucin-16 (CA 125) antigen with a negative CEA suggests the source is from the ovaries, fallopian tubes or endometrium.
Chemical Testing
| Parameter | Important Values | Clinical Significance |
|---|
| glucose | decreased below serum levels | bacterial and tubercular peritonitis or malignancy |
| amylase | increased | pancreatitis or gastrointestinal perforations |
| alkaline phosphatase | increased | intestinal perforation |
| blood urea nitrogen, creatinine | | ruptured bladder or accidental puncture of the bladder during the paracentesis |
Microbiologic Testing
- Bacterial cultures and Gram staining for both aerobes and anaerobes are performed when bacterial peritonitis is suspected.
- Inoculation of fluid into blood culture bottles at the bedside increases the recovery of anaerobic organisms.
- Acid-fast stains, adenosine deaminase and cultures for tuberculosis may also be requested.







