Topic 1 The nature and variety of organisms
Characteristics of a living organism
Movement | Organisms moving towords or away from things |
Respiration | Release of energy from their food source |
Sensitivity | Reacting to changes around there environment |
Growth | Growth of cells, tissues, age , becoming adult ect… |
Reproduction | Producing an offspring |
Excretion | Getting rid of waste, Carbon dioxide, Urine ect… |
Nutrition | Nutrition needed to provide energy for respiration ect… |
Level Of organisms
Organelle - Cells - Tissue - Organ - Organ system - living organism
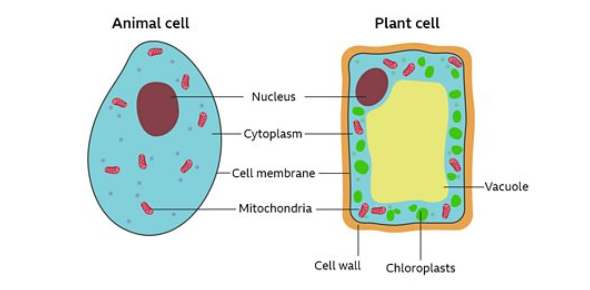
Organelles found in plant and animal cells
Nucleus | Contains genetic materials |
Cell membrane | Controls what comes in and out of the cell through diffusion |
Cytoplasm | Where chemical reactions take place and enzymes break down ect… |
Mitocondria | Aerobic respiration and production of energy through it. |
Ribosomes | Where proteins are made |
Organelles Found in plant cells only
Chloroplast | Has Chlorophyll making it green and its where photosynthesis takes place |
Cell wall | Supports the cells structure |
Vacuole | Contains cell sap which provides the cell with extra support |
Specialized Cells and stem cells
Specialized cells:
These cells do specific functions like how red blood cells carry oxygen throughout the body
Embryonic stem cells:
They can turn into any type of cell
CELL DIFFERENTIATION is the process in where a cell changes to become a specialized cell
They developed diffrent organelles for diffrent functions
Stem cells are found in early human embryo, They can differentiate into any kind of specialized cell. they can also divide to become multiple undifferentiated cells
Adults also have stem cells but they are only found in bone marrow and can only differentiate into cerin things like red blood cells.
Stem cells Cure diseases
Stem cells from a healthy person is transferred into another person to replace faulty cells
Embryo cells cane make insulin wich is used to cure or help diabetes and paralyzed patinates ect…
There is also a risk of transferring a viruses contaminated cell wich causes the other person to get even more sick.
Against stem cell research
Feels like human embryo shouldnt be taken for experiments becuase they have a “Potential life”
Some belive curing a sick patient is more important then rights of an embryo
Embryos used for research are often “Unwanted” and if they are not used they would have otherwise been destroyed
Some belive scientists should research how to help people without having to use and embryo
Eukaryotic
Type | Description | Example |
Plant | Multicellular Chloroplast for photosynthesis Carbohydrates stored as starch | Mazie Peas Beans |
Animal | Multicellular No Chloroplast so no Photosynthesis Nervous coordination Carbohydrates from glycogen | Human Mosquitoes |
Fungi | Single cell (Mainly) Hyphae body No photosynthesis Cell wall made of Chitin Carbohydrates as glucagon Saprotrophic nutrition - (Enzyme break food so it can digest) | Yeast Mucor |
Prokaryotic Organism
Protoctista | Single cell Some photosynthesizes | Chlorella |
Bacteria | Single cell No nucleus Some photosynthesis Feed off other organisms | Lactobacillus |
Viruses | Particles Reproduce inside living organism Diffrent shapes and sizes No cellular structure Have proteins around there genetic material | Influenza |
Some organisms are pathogens
Enzymes
A catalysts is a substance wich increases the speed of a reaction without being changed or used up. Enzymes are biosocial catalysts
You can increase speed of reactions through increase of temperature But it can cause damage to cells when to large
So enzymes are created to prevent damage of cells with temperature increase
Enzymes are made of proteins made of amino acids and each have a unique shape
Enzymes are specific
Chemical reactions involve splitting or joining
Every enzyme has an active site to join in with the substrate
Optimal temperature of enzymes is 37’C
When temperature is higher then optimal it begins to dem=nature meaning it dosent work anymore because substrate and active site do not lock and key (Fit togther)
Diffusion and Osmosis
Diffusion
Net movement of particle from area of high concentration to low concentration down the concentration gradient
Osmosis
Net movement of water molecules across a partly permeable membrane from a region of high concentration to a region of ow concentration.
Water Particles can move both ways in and out the cell membrane
Lots of water = Solution i more dilute
Less of water = Solution is less dilute
Active Transport
Movement of Particles AGAINST the concentration gradient. from low concentration to an area of high concentration using energy released during respiration.
Factors effecting movement of substance (Diffusion, osmosis and APT)
Surface area - Large surface area = faster transportation
Distance - Short distance = Faster transportation
Temperature - Gain more energy as temperature increases = Faster transportation
Concentration - Big concentration diffrence = Faster Transportation