Dissection 5 - The Orbit
Dissection Guide
Osteology and Surface Anatomy
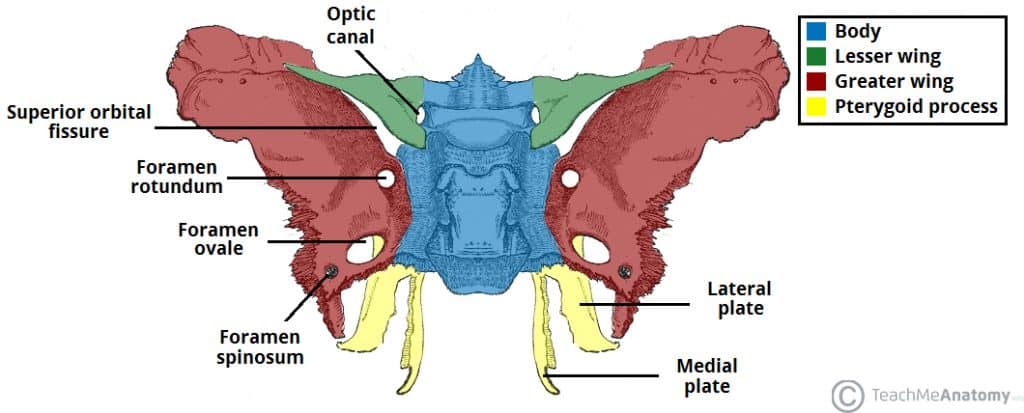
Roof of the orbit = orbital plate of frontal bone + lesser wing of sphenoid bone + floor of anterior cranial fossa
Floor of orbit = Maxilla and zygomatic
Foramina of the orbit: Optic canal, superior orbital fissure, inferior orbital fissure, supraorbital notch/foramen, infraorbital groove, infraorbital foramen, nasolacrimal canal
Conjunctivitis
Pink eye
From dilated blood vessels in the sclera surrounding the pupil and iris
Dissection - Superior → Inferior
Layer 1: Roof of the orbit
Layer 2: Periorbital membrane
Layer 3: Frontal n. (branch of CN V1)
Branches into supraorbital and supratrochelar n.
Layer 4: Levator palpebral superioris (innervated by CN III)
Layer 5: Superior rectus muscle (innervated by CN III)
Layer 6: Superior ophthalmic v.
Dissection - Lateral and medial
Medial
Superior oblique m. parallels medial wall and goes through fibrocartilaginous trochlea
Innervated by CN IV (pierces lateral aspect of m.)
Medial rectus
Layer 2: Nasociliary n. (branching in the plane between superior oblique and more inferior than medial rectus)
Lateral
Lateral rectus
Lacrimal n. course laterally toward lacrimal gland
Abducens n. enter medial side of lateral rectus (just anterior to apex of orbit)
Note that all rectus muscles originate from the common tendenous (annular) ring that encircles the optic n.
Optic a. is usually tortuous (allow mobility of the eye) and seen entering via the optic canal
Unilateral dissection
Long ciliary n. branches off nasociliary n. on top of the or medial to optic n.
SS to cornea and conjunctiva and sympathetics to dilator pupillae
Short ciliary n. lateral or superior to optic n. can be traced through the ciliary ganglion
Lacrimal gland
SS from CN V1 (lacrimal n.)
Preganglionic parasympathetics synapse at the pterygopalatine ganglion (before hitchhiking on V2 and V1)
Anterior orbit
Lacrimal caruncle: medial angle of the eye
Inferior oblique and inferior rectus can be seen from the front (incise lower eyelid)
Nasolacrimal canal → Drains inferiorly into inferior nasal meatus
Venous Drainage of the Eye
Primary drainage of the eye
Superior and inferior ophthalmic v. → Cavernous sinus posteriorly (primary)
Pterygoidplexus of veins (infratemporal fossa) inferiorly
Facial v. (anteriorly)
Possible venous blood pathways around the eye
Supraorbital v. → Merge with angular v. → Superior ophthalmic v. → Cavernous sinus
Supratrochlear v. → Angular v. → Facial v.
Superior ophthalmic v. → Cavernous sinus
Inferior ophthalmic v. → Pterygoid plexus
Inferior ophthalmic v. → Superior ophthalmic v. → Cavernous sinus
Infraorbital v. → Pterygoid plexus
Possible venous blood pathways of external orbit
Supraorbital v. → Merge with Angular v. → Superior ophthalmic v. → Cavernous sinus
Infraorbital v. → Through inferior orbital fissure → Pterygoid plexus
Lacrimal v. → Superior ophthalmic v. → Cavernous sinus
Bolded Terms
Abducent N.
CN VI
Pierces through middle of cavernous sinus → Superior orbital fissure → Lateral rectus
Pierces medial side of lateral rectus
Annular ring
Tendons ring around optic n. where all 4 rectus muscles originate from
Anterior cranial fossa
Floor of it contribute to roof of orbit
Ciliary ganglion
Nasciliary n. → Ciliary ganglion → Short ciliary n. → Eye
Where para/pre from CN III synapse
Conjunctiva
Transparent membrane covering the inner portion of the eyelid and sclera
Cribiform plate
Part of ethmoid plate on the medial side of the orbit
Frontal n.
Most medial and superficial branch of the ophthalmic division of CN V
Lays on top of levator palpebrae and branches into supraorbital and supratrochlear n.
Infraorbital groove
Path for infraorbital n. (CN V2) to travel through on the floor of the orbit before exiting through the infraorbital foramen
Infraorbital foramen
Infraorbital VAN (branch of V2) passes through
Inferior orbital fissure
Zygomatic nerve, infraorbital vein, artery, and nerve
Inferior oblique m.
Involved in elevation and ABduction
Innervated by CN III
Inferior rectus m.
Involved in Depression and ADDuction
Innervated by CN III
Iris
Lacrimal caruncle
On the medial potion of the eye, can be seen anteriorly
Lacrimal gland
On the lateral upper corner
SS innervation by CN V1 (lacrimal n.)
Parasympathetics by CN VII
Lacrimal n.
Most lateral branch of CN V1
Lateral rectus m.
ABduction
Innervated by CN VI
Lesser wing of sphenoid
Levator palpebrae superioris
Must superior muscle right below the frontal n.
Innervated by CN III
Long ciliary n.
Branch of nasociliary n.
Path for sympathetic innervation of dilator pupillae
Maxilla
Contributes to the floor of the orbit
Medial rectus m.
ADDuction
Innervated by CN III
Nasociliary n.
Most medial branch of CN V1
Branches into long ciliary and ciliary ganglion → Short ciliary n.
Nasolacrimal canal
Nasolacrimal canal → Drains inferiorly into inferior nasal meatus
Oculomotor n.
CN III
Ophthalmic a.
Branch of ICA that enters orbit with CN II
Optic canal
CN II and opthalmic a. enter orbit
Optic n.
CN II
Orobicularis oculi
M. of facial expression that allows for forceful blinking
Orbital plate of the frontal
Contributes to the roof of the orbit
Periorbital membrane
Lays just below the bony roof of the orbit
Pupil
Sclera
Short ciliary n.
Branches from the ciliary ganglion
Superior oblique m.
Goes through trochlea before attaching to eye
Depression and ABduction
Innervated by CN IV
Superior ophthalmic v.
Superior ophthalmic v. → Cavernous sinus
Superior orbital fissure
CN III, IV, V1 and VI enter orbit
Superior ophthalmic v. exits orbit to join cavernous sinus
Superior rectus m.
Just deep to levator palpebrae
Elevation and ADDuction
Innervated by CN III
Supraorbital n.
Branch of frontal n. that innervates lateral forehead
Supraorbital notch/foramen
Where suprorbital VAN exits
Supratrochlear n.
Branch of frontal n. that innervates medial forehead
Trochlea
Fibrocartilagenous sling that supraorbital n. passes before attaching to eye
Trochlear n.
CN IV
Zygomatic
Forms lateral wall of orbit