Cell
All living things are made up of cells, some are only made up of one cell and others of many cells.
There are 2 types of organisms based on how many cells they have; unicellular, and multicellular
Definition:
Cells are the building blocks of life and they are the most basic structural and functional units of our life. They form the tissues, organs, and organ systems in organism’s
If the average adult human has around 37.2 trillion cells
Cells are called the building blocks of life because they are the basic structural and functional units of an organism.
Robert Hooke named the cells after tiny boxes that monks lived in, after he cut thin slices from cork and looked at them under a microscope. They were named cells in the year 1665
Animal Cells
Nucleus
Carries the genes
Regulates cell’s activity
Nucleolus
Constructs ribosomes
Golgi Apparatus
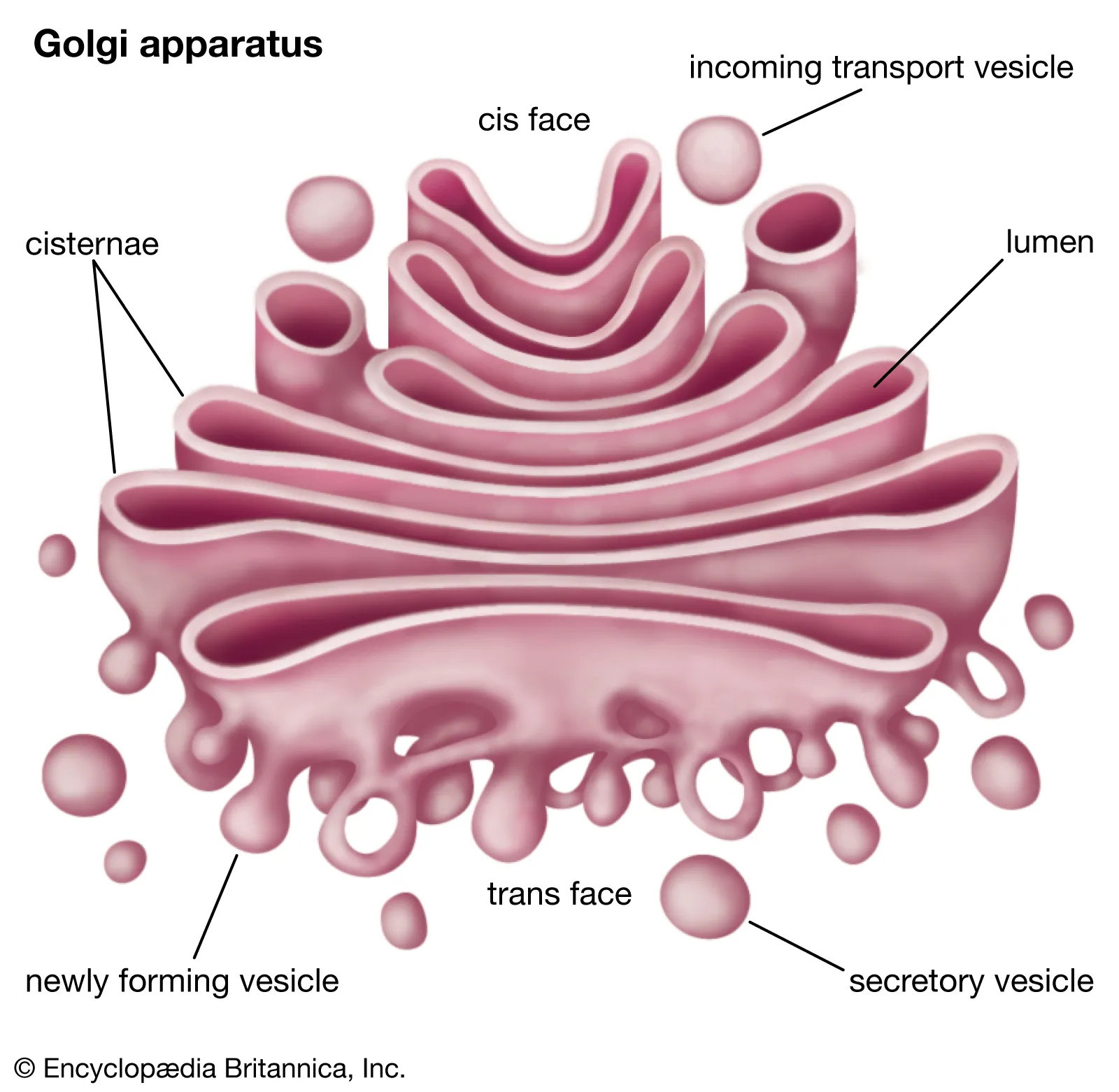
Arranges important protein to the destination
Ribosomes
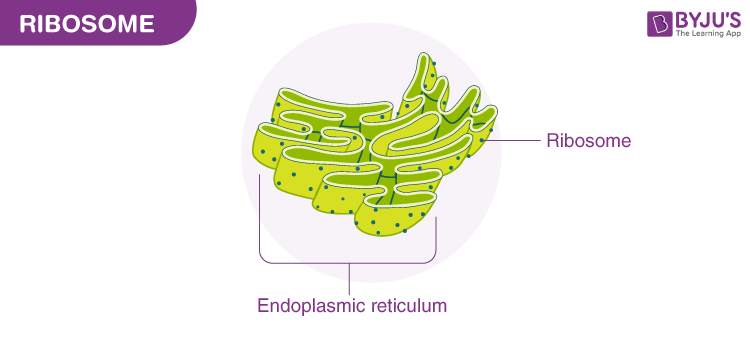
Constructs protein from amino acids
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum

Attached to ribosomes
Produces protein needed for the cell to function
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
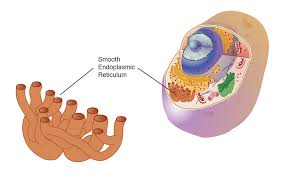
No ribosomes attached
Makes lipids in the cell
Helps detoxify harmful substances found in cell
Mitochondria
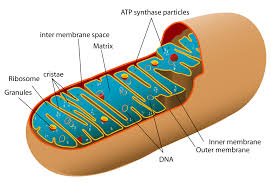
Cells powerhouse
Produces energy
Lysosome
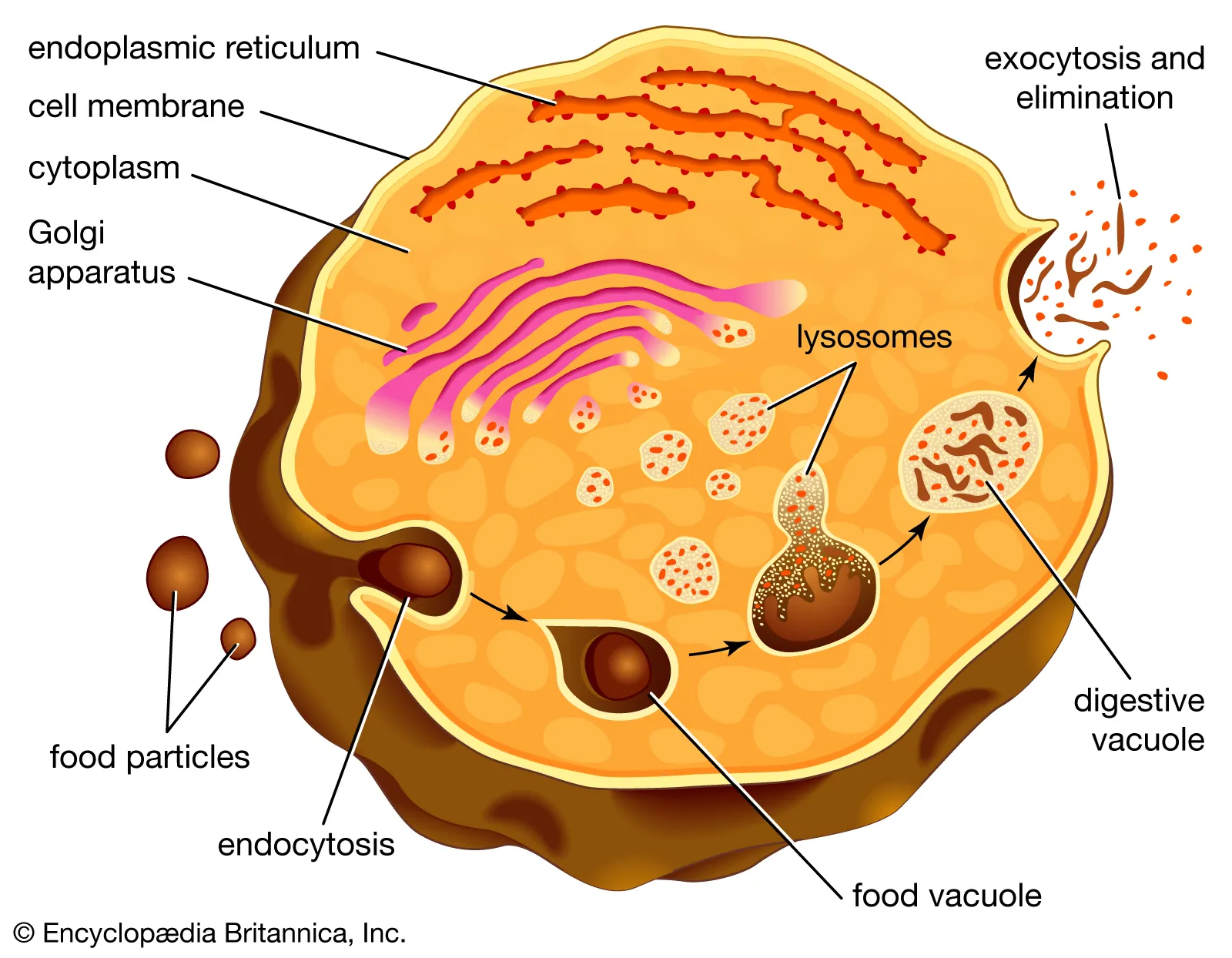
Breaks down large molecules
Centriole
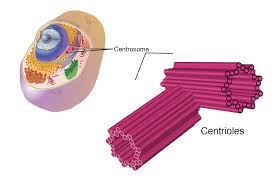
Helps cell division
Cytoplasm
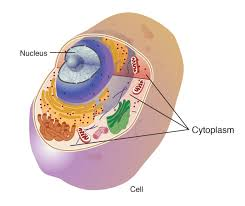
Holding all the organelles together
Protects organelle from damage
Cell Membrane

Protecting the cell
Regulates transport of materials (enter/exit)
Plant Cells
Cell Wall
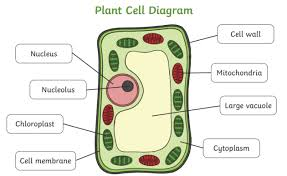
Provide structural strength and support
Prevents osmotic bursting
Cell membrane
Protecting the cell
Regulates transport of materials (enter/exit)
Nucleus
Carries the genes
Regulates cell’s activity
Nucleolus
Constructs ribosomes
Cytoplasm
Holding all the organelles together
Protects organelle from damage
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Attached to ribosomes
Produces protein needed for the cell to function
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
No ribosomes attached
Makes lipids in the cell
Helps detoxify harmful substances found in cell
Golgi Apparatus
Arranges important protein to the destination
Mitochondria
Cells powerhouse
Produces energy
Chloroplast
Contains chlorophyll
Place where photosynthesis takes place
Vacuole
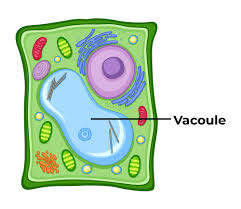
Stores nutrients and water
Helps maintain water balance