QUALITY
WHAT IS QUALITY?
Quality is ensuring that a good of service meets the needs and requirements of the customers, it can also be described as the features of a product or service that satisfy customer wants.
WHY IS QUALITY IMPORTANT?
A quality product needs to be fit for purpose. If a product is of good quality , it helps raise customers confidence regarding a business and its products , thus helping to gain a competitive advantage over rivals. It also encourages repeat purchase as quality products help retain customers , which will increase the businesses market share overtime.
Quality control : the process of making sure that the quality of a product meets specified quality performance criterias.
WHAT IS QUALITY ASSURANCE?
Quality assurance is a system of setting agreed standards for every stage of production. It is essentially a commitment by a business to maintain quality throughout the organisation. the basic idea is to stop problems before they occur in order to prevent the production of faulty products.
SHORT OVERVIEW :
Quality issues are identified early so products may be reworked rather than rejected
The cause of defects is the focus so future quality issues may be prevented ; if the business knows of possible errors that can occur during production , it can be prevented in the future
can help improve brand image as products will be of good quality
However ,
Staff training and a skilled workforce is required so labour costs may be increased ; time is going to be spent on training the workforce to identify problems during production so less time might be spent on increasing output
Reworking may lengthen the production process ; lead time may increase
WHAT ARE QUALITY CIRCLES?
Quality circles is a small group of employees who voluntarily meet up on a regular basis to identify , examine and solve problems related to their work to improve the quality of output.
SHORT OVERVIEW:
it helps to motivate workers as they think their opinions are considered by the business and they feel more involved in decision making
Relevant and focused solutions are likely as workers are familiar with processes ; suggestions from workers who are directly involved in the production process , since they are familiar with the process they may have better ideas regarding how to improve the quality or reduce issues
the idea is to prevent defects from arising in the first place by looking for possible problems before production
can help lower costs as no resources will go to waste
However,
members must receive appropriate training in problem solving and identification of problems
management must be supportive of the teams and fund them appropriately , quality circles will not work where managers are resistant to change
taking opinions from workers can be time consuming
output is lost since time is spent on meetings instead
WHAT IS TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT ( TQM )
Total quality management is a quality management approach that aims to involve every employee in the quality assurance process. it involves organisation wise approaches to quality improvements in people , products , process and philosophy.
the business is designed so that the manufacturing process is organised to be investigated at every stage.
SHORT OVERVIEW:
it improves the motivation of employees since they are involved in decision making ; Empowerment & Delegation – Employees are given authority to make decisions regarding quality improvements in their tasks.
A culture of constant improvement exists within the business
competitive advantage as it puts customers needs at the centre of the production process
cost effective as TQM eliminates the need for inspections and the cost of reworking mistakes and defective outputs
in the long term , quality is higher and costs are reduced
However,
It requires a change in attitude and commitment from all staff members , which can be difficult to achieve
staff training , management training and development costs are involved
Risk of Bureaucracy – Excessive focus on procedures and documentation can slow down operations.
WHAT IS KAIZEN?
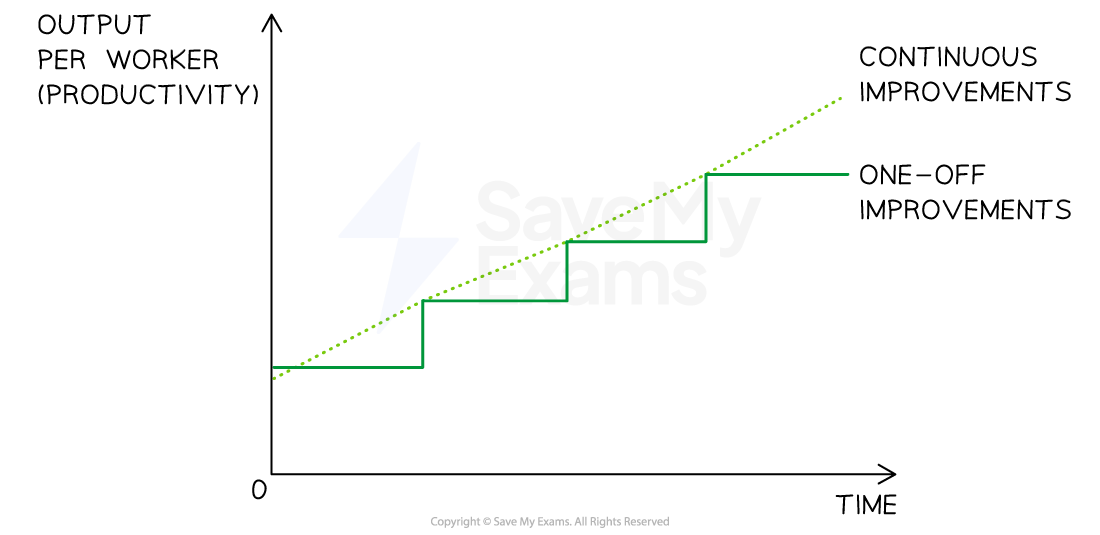
Kaizen is a continuous improvement philosophy that focuses on making small, incremental changes to processes, products, or services to enhance efficiency, quality, and productivity rather than making dramatic changes.
SHORT OVERVIEW :
Continuous Improvement – Encourages ongoing small changes that lead to significant long-term improvements.
as the changes arent too great , employees are less resistant to change
Changes are small and ongoing rather than significant one-off’s and are constantly reviewed to ensure that the desired positive impact on productivity is achieved
Uses Existing Resources – Employees identify inefficiencies and suggest improvements using current tools and processes, reducing the need for new investments ; more cost effective than investing in huge amounts of capital to get better technology to improve quality
However,
Slow Results – Small, incremental changes take time to show significant impact. So while quality will improve, it will take a considerable amount of time
Requires Full Commitment – Success depends on the involvement of all employees and management.
Time-Consuming Approval Processes – If every small change needs managerial approval, it can delay implementation and frustrate employees.
Elements of Kaizen commonly include
Total Quality Management
Just in Time stock management
Teamwork and quality circles
Zero defects in manufacturing
High levels of automation
High levels of cooperation between workers and management
THE IMPLEMENTATION OF CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT : PDCA
Plan : business must identify where the improvement is needed. data must be gathered and used to develop a plan that will aid in improvement
Do : once the plan has been finalised it needs to be carried out
Check : check if there as been any improvements after the implementation
Action : if the plan is successful it needs to be introduced to every aspect of the business
WHAT IS LEAN PRODUCTION?
Lean production is a manufacturing and management approach that focuses on minimizing waste by getting things right the first time whilst maximizing quality.
The seven sources of waste are :
defective products
overproduction
excessive inventories
unnecessary transportation
over proessing
waiting time
excess movement by workings
Methods of waste minimization include : JIT , kaizen , benchmarking and TQM