Climate Change
The Earth is warming.
What influences Earth’s Temperature?
Solar radiation
Every 11 years, the sun's core flips, producing more radiation.
Milankovitch cycles: 3 parts - Eccentricity, Obliquity, Precession
Eccentricity-
Changes every 95,000 years.
Elipse, Earth is farther away from the sun.
Orbit Shape
Obliquity-
Every 42,000 years.
Earth’s tilt.
Precession-
21,000 years
Different star consolation
Earth’s wobble
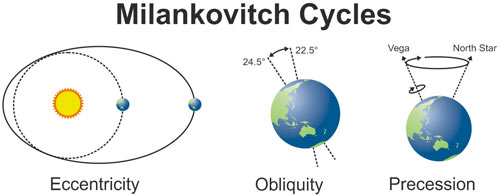
*Responsible for the ice ages.
The Greenhouse Effect: Trapping heat trying to escape.
CH4
N2O
O2 and O3
CO2
H2O
Sources:
Agriculture
Factories
Cars
Cows
Fossil Fuels
Burning forests
Decomposing organic matter
Sinks:
Rain
Trees
Oceans
Occur to Slowly for Climate Change
Eruptions and Asteroids- Temporary cool behaviors.
Asteroids- break apart, hitting molecules in the air, and stay in the atmosphere for decades.
Eruptions- They hardly occur but release chemicals as it does.
Plate tectonics and Ocean current.
Effects of Climate Change
Why is the ocean rising?
Thermal Expansion: The ocean is getting warmer, causing sea levels to rise.
Warmer ocean= more energy (strength for hurricanes)
Loss of cold habitat
Melted Ice: Ice on the surface melting into the ocean. (Glaciers)
Problems with sea level rising-
Destruction of property
Loss of natural habitats
Flooding from surges farther inland
Saltwater intrusion
Loss of islands
Coral bleaching: Relationship with algae. Algae are kicked out when coral is stressed, water pH changes, etc., therefore turning white/ dying.
Ocean acidification: Co2- carbon dioxide is being absorbed into the ocean more than needed, resulting in less carbonate ions needed to help corals build their skeletons.
Increase in average temperature: longer hot days, shorter cold days,/
Changes in precipitation (water falling in a solid or liquid state): Extreme one-day precipitation events.
Problems:
Flash flooding.
More wildfires.
Extended, shrinking, or shift ranges.
Changes in seasonal timing
Global Policies
Kyoto Protocol 1997
93 countries signed/agreed
Developed countries reduce admissions
Developing countries excused
Goal to achieve below 15
Developing countries: Focus on getting individuals to higher living.
Copenhagen Accord 2009
111 countries agreed
Set new targets for 2020
Reduction based on a year
Paris Agreement 2015
All countries set goals to reduce emissions
Money was given to developing countries
The goal is to keep the temperature below 2 degrees Celsius increase.
Why is Climate Change Difficult to Deal with?
Ozone depletion- easily fixed because it was man-made chemicals that were banned.
Climate change: Natural sources (fossil fuels) everywhere. Need to develop technology to replace it.
Lobbyist: Talk to representatives about influencing or denying laws. Legal bribing- buying votes.
The Misinformation Campaign: companies lying. propaganda.
Thinktank: a group of smart people coming up with ideas.
Algae: Certain algae produce oil, taking out carbon. Still in the works.
Methods to Reduce
Carbon tax: Products containing more carbon/greenhouse gases to produce = more tax on product. Tax break.
Cap and Trade: The government puts “caps” on companies to limit carbon/greenhouse gas emissions. In return, companies earn credits. Credits = more emissions. Can sell their credits to other companies.
Federal Policies
Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 Tax Credits
30% cost for solar on houses
1,200 for insulations
7,500 for new electric vehicle
4,000-8,000 for heat pumps/efficient appliances
GDP: Gross Domestic Product
Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (California)
15.6b- transportation including E.V. charging and electric buses
2.3b- clean energy, building, and manufacturing
1.5b- climate change reliance
State Polices
2045, California wants to be carbon neutral.
Carbon capture: capturing carbon and storing it somewhere it cannot escape.