2.4) Population Dynamics
Explain factors that account for contemporary and historical trends in population growth & decline
What factors determine a population’s growth and decline?
- Fertility
a) Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
b) Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
- Mortality
a) Life expectancy
b) Crude Death Rate (CDR)
c) Infant Mortality rate (IMR)
- Migration
Fertility
a) Crude Birth rate (CBR)
- The number of live births occurring in one year per 1,000 poeple
b) Total Ferility Rate (TFR)
- AVerage number of children who would be born per woman during her childbearing years
- Globally TFR has been significantly decreasing over time
Mortality
a) Life Expectancy
- The number of years the average person will live
- This has been steadily increasing over time, which has contributed to population growth
b) Crude Death Rate (CDR)
- The number of deaths occurring in one year per 1,000 people
c) Infant Mortality Rate (IMR)
- The number of children who die before one year of age
- Typically when IMR goes down, life expectancy goes up which leads to higher population growth
How do geographers calculate population growth & decline?
a) Natural Increase Rate (NIR) or Natural rate of Increase (RNI)
Does not account for migration
Can be a negative #, indicating population decrease
Usually expressed/ represented in a percentage
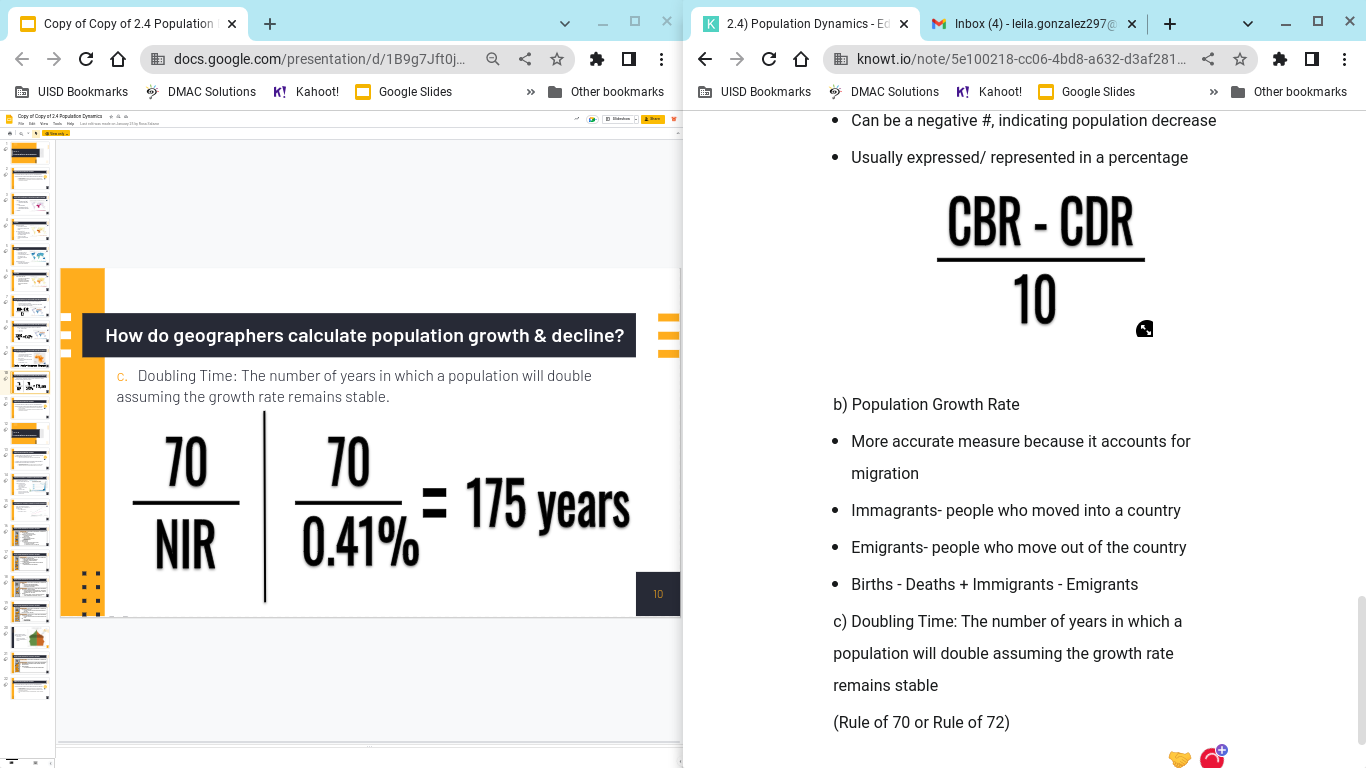
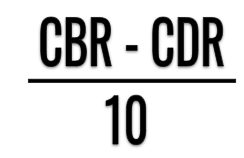 b) Population Growth Rate
b) Population Growth RateMore accurate measure because it accounts for migration
Immagrants- people who moved into a country
Emigrants- people who move out of the country
Births - Deaths + Immigrants - Emigrants
c) Doubling Time: The number of years in which a population will double assuming the growth rate remains stable
(Rule of 70 or Rule of 72)
 Explain factors that account for contemporary and historical trends in population growth and decline
Explain factors that account for contemporary and historical trends in population growth and decline
Explain how the changing role of females has demographic consequences in different parts of the world
Historical Trends in Population Growth and decline
- Throughout most of history, population growth was very low
- Starting around 1750
- Agricultural revolution
- Industrial revolution
- Rapid Urbanization
- Rapid Urbanization
- Advances in healthcare and Sanitation
- First 1 billion in 1804
- Since then, doubling time has decreased as population growth increased rapidly
Contemporary Trends in Population Growth and Decline
- Today, most population growth is happening in LDCs- specifically in Aisa and Africa
- NIR in Niger = 3.8%
- NIR in Spain= -0.11%
What causes population to grow and decline
Population Growth- High TFR, CBR or life expectancy// Low CDR & IMR
ECONOMIC
- Agricultural societies
- Need children to labor on the farm
- Advancements in food production and nutrition
- Mechanization of Agriculture
- Farming efficiency
- Advancements in sanitation
- Less water contamination and disease
- Water treatment plants
- Garbage pickup
- Economic prosperity
- Access to healthcare
- Core countries provide better healthcare services
- Prevention and Cure of disease
- Women have access to pre & and post-natal care
Population Decline - High CDR and IMR // Low TFR, CBR, or life expectancy
- Industrial and post-industrial society
- Women more involved in workforce
- Urbanization → small living quarters
- Economic hardship
- Children are expensive, provision of food and resources
- Access to healthcare
- Women have access to contraceptives
SOCIAL
- Religion
- Traditional cultures encourage big families
- Restriction of contraceptive use and abortion
- Earlier Marriages = more children
- Role of Women - Education & Workforce
- Cultural expectations have changed in many MDC’s → more women in the workforce/ education → postpone having children → reduction is childbearing years → less children
- Healthcare
- How to care for babies → lower IMR, CDR, higher life expectancy
- Access & understanding of contraception → lower TFR
POLITICAL
Pro-Natalist Population Policies
- Government encourages families through propaganda and incentives to have children
Shift from war to peace → Baby Boom
Anti-Natalist Population policies
- Government discourages families through propaganda, disincentives, and policies.
War
Higher mortality rate,
shortages of supplies
increase in migration
NATURAL
- Natural disasters (earthquakes, flooding, tsunamis, hurricanes)
- Famine and Drought
- Spread of disease
- 60% of Europe died in the 1300s due to Bubonic Plague