Chapter 6 - Motivating employees
^^Why work?^^
- Money → To pay for necessities & some luxuries
- security → A sense of security. E.g. knowing that you aren’t likely to lose your job & will have a constant pay
- Job satisfaction → Enjoyment is derived from feeling that you’ve done a good job
- Esteem need (self-importance) → Feeling important, feeling that the job you do is important
- Social Needs (affiliation) → Feeling that you are part of a group or org, meeting people & making friends at work
^^Benefits of a well-motivated workforce^^
- High output per worker → helps keep costs low & increase profits
- Willingness to accept change → e.g. new modes of work & new machinery
- Two-way communication → e.g. Suggestions for improving quality
- Low labor turnover → a loyal workforce → reduces the costs if re-recruiting
- Low rates of absenteeism
- Low rates of strike action → Avoiding damage to customer relations
Well-motivated workers → high productivity → increased output → higher profits
^^unhappy workers^^ → don’t work very effectively → low output → ^^lower/no profit^^
Maslow’s hierarchy
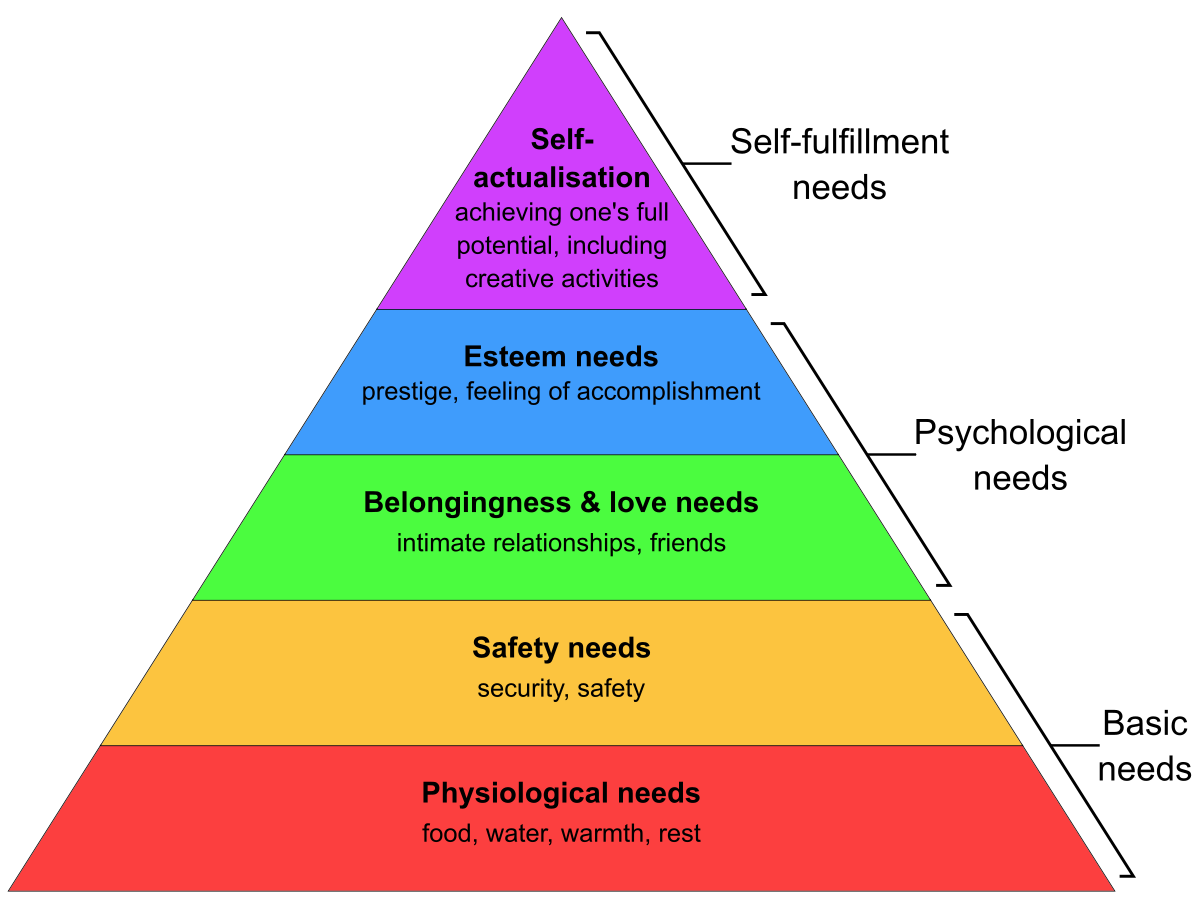
Physiological needs → Wages high enough to meet weekly bill, food, rest, recreation & shelter
Safety needs → Job security, protection against danger & poverty & receive fair treatment
Social needs (belongingness & love needs) → Friendship, a sense of belonging ti a team & work colleagues who support you at work
Esteem needs → having status & recognitions, achievement, independence & being given recognition for a well done
Self-actualization → being promoted & given more responsibility, succeeding to your full potential, feeling that you have done a good job not just fir financial & personal reward
- Higher levels of the hierarchy must be available to employees → Money alone will not be the single route to increased productivity
- Each level in the hierarchy must be achieved before an employee can be motivated by the next level → However, some levels don’t exist for uncertain individuals
- Managers must identify the level of the hierarchy that a particular job provides & then look for ways of allowing to benefit from the next level up the hierarchy
Motivation theories
- When people work for themselves, e.g. entrepreneur, they tend to work hard & effectively as they see the directs benefits of their work
- However, when a person works for someone else, they don’t work as effectively. Management has to then encourage the workforce to contribute fully to the success of the business
Frederick Taylor’s theory
His theory was based around the assumption that all workers are motivated by personal gain:
@@“If workers are paid more, they will work more effectively”@@
He broke down the workers’ tasks & calculated how much output they can produce in a day. If the employees met this goal then they would be paid more money
This theory doesn’t always work as :
- Treats employees like machines
- Pay cab be increased bur if workers are unsatisfied, their effectivity & productivity will not increase
- Employees are motivated by many various factors & not just money
- This can’t work if an employee’s output cannot be measured
Herzberg’s theory
→ According to Herzberg, humans have 2 sets of needs :
| Motivators - Needs that help in psychological growth | ^^‘Hygiene’ ( or ‘maintenance’) factors - basic needs^^ |
|---|---|
| Achievement | Status |
| Recognition | Security |
| personal growth/ development | Work conditions |
| Advancement / promotion | Company policies & administration |
| work itself | Relationship with supervisors |
| Relationship with subordinates | |
| Salary |
‘Hygiene’ factors must be satisfied, otherwise they can act as demotivators. They aren’t motivators as once satisfied, the effects of them wear off.
Methods of motivation - financial rewards
- Wages = payment for work, paid weekly
- Often paid every week (can be in cash or directly in bank)
- Workers get paid regularly. This tends to be paid to manual workers
- Overtime is also paid. Overtime = an incentive to work additional hours
==The drawbacks :==
- Must be calculated every week & are time taking. Wages clerks are also hired to calculate wages, which also costs extra money
- Time rate = Payment based on hours worked
- Easy to calculate
==The drawbacks :==
- Hours worked are recorded on a time-sheet, this system is time taking
- Good & bad workers are paid the same
- Supervisors are needed to make sure the workers keep working & produce good quality products, which also costs extra-money
A clocking-in system is required to determine hours worked, this system is expensive
→ Time Rate is used for services & when it is difficult to determine the output per worker
- Piece rate = payment depending on the quantity of products made
- A basic rate is paid + extra money, depending in the amount of products
- This system can also be used as a bonus system, when the actual output has exceeded the target output
- Encourages workers to work faster
- Only possible when the performance of an individual / team can be easily measured
==The drawbacks :==
- Employees ignore quality & focus solely on quantity
- Quality control system is required & it is expensive
- bad products could tarnish the reputation of the business
- Workers who produce quality products will earn lesser than those who rush ( & don’t produce good quality) → causing friction between the employees
- If machinery is breaks down, employees won’t be able to make products, therefore they must be paid a minimum fixed amount
- Salary = Payment for work, paid monthly
- Paid monthly & straight into the bank account
- Calculated as : Money per year for the job performed, the divided by 12
- Easy to calculate & has to be calculated once per month ( & not 4 times per month like with wages)
==The drawbacks :==
- Workers might prefer weekly pay
- No payment for extra-time worked → Demotivating for employees
- Bonuses + an additional amount of money paid above basic pay as a reward
- A lump sum paid to workers when worked well. Can be given at the end of the year or at intervals during the year
- Not necessary → Can be paid to just 1 or few selected workers or even all
- Has a positive motivating effect on workers as they feel ‘recognized’ & ‘special’
==The drawbacks:==
- Can become ‘expected’ → Employees are disappointed & unhappy if not received
- Bad feelings amongst workers can be caused if paid only to one or selected few
- Commissions = payment relating to the number of sales paid
- Paid to sales staff → similar to piece rate but for sales staff
- Sales may increase
- Paid in addition to existing salary
==The drawbacks :==
- If customers are persuaded into buying unwanted goods, sales may fall in the long run as they get a bad reputation
- very stressful for workers → Bad month = lower pay
- Too much competition between workers
- Profit sharing = a system in which a proportion of the company’s profit is paid to employees
- Received in addition to basic salary
- Should motivate workers to work hard
- Rest of the profits are paid as dividends or retained by the business
- Often used in the service sector, where it is difficult to recognize an individual employees work
==The drawbacks :==
- If loss making or little profit making, then no profit share is possible, disappointing employees
- Calculated on basis of existing salary → higher paid workers get higher profit share, leaving lower paid workers unhappy
Fringe benefits
→ In addition to financial reward, business may give other employee benefits, These vary according to the seniority of the posting. E.g. :
- Chauffeur driven car
- Discounts on the business’ products
- Healthcare paid for
- Children’s education fees
- free accommodation
- Share options (where company shares are given to employees)
- Generous expense accounts (for food & clothing)
- Pension paid for by the business
- Free trips abroad / holidays
Non-financial motivating factors
Job rotation
- Job rotation involves workers swapping around & doing each specific task for a limited time & then changing around again.
- Though, this doesn’t make the job more satisfying, or interesting, it helps covering for absentees.
Job enrichment
- Job enrichment involves looking at jobs and adding tasks that require more skill and/or responsibility
Autonomous work groups or teamworking
- Teamworking involves using groups of worker & allocating specific tasks & responsibilities to them
- They are allowed to choose, within the team, their tasks. This increased involvement in their work, and having the freedom of choice, increases job satisfaction
- Working as a group helps boost morale as well as giving a a greater sense of belonging to the company
Training
- Workers can feel a great sense of achievement if they successfully gain & apply new work-based skill. Then they could now be given more challenging & rewarding work to perform.
- Workers can also feel selected by the management for training courses and this can make them feel that their good work has been recognized
Opportunities for promotion
- Many businesses prefer to fill posts of responsibility with existing workforce, rather than recruiting new managers.
- This internal recruitment offers opportunities for advancement to existing workers.
- The business benefits by promoting employees to managerial postings , as they already know how the business operates at base-level.
- By promoting employees, the business gains a motivated manager, and motivated workers who wish to be promoted.
- Promoted employees feel recognized & have higher status, which gives job satisfaction & motivation the employee.