
Handout page 13

Nitrogenous bases - Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C), Thymine (T), and Uracil ( U)
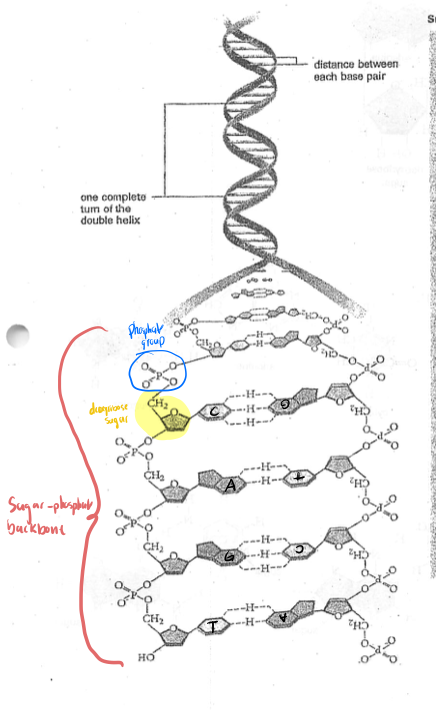
What is the linkage between the separate nucleotide phosphates? - the linkage between the (?) is a phosphodiester bond
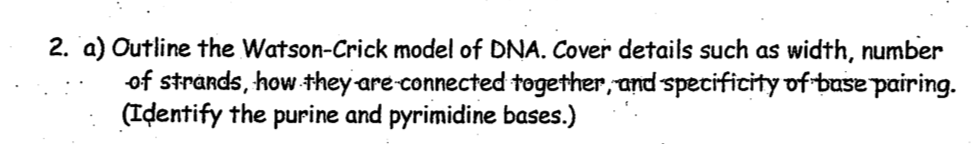
Watson- Crick model of DNA
Width of DNA (Watson-crick) - 2nm ( nanometer)
What are the purines? - These are double-ringed structures. Ex. A and G
What are the pyrimidines ? - These are single-ringed structures. Ex. T and C

What is the length of helix that completes 360 turn and how many bases per turn? - 3.4nm and 10 (?)

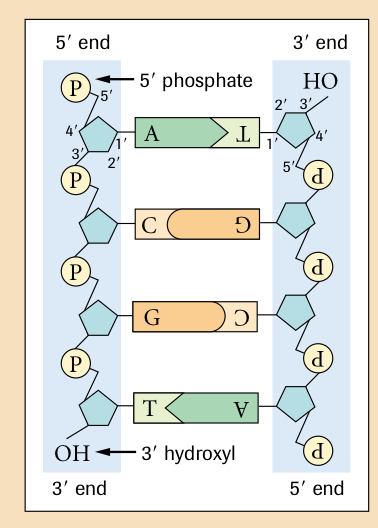
Define “ antiparallel strands” - Parallel but running in opposite directions; the 5’ end of the one strand of DNA aligns with the 3’ end of the other strand in a double helix
two strands of DNA run antiparallel (define) - one strand runs in the 5’ tp 3’ direction and the other runs 3’ to 5’ direction

What does 3’ mean? - This depicts the deoxyribose has a hydroxyl group on the 3’ carbon
What doe 5’ mean? - this depicts the phosphate group is attached to the 5’ carbon
Name the functional groups located at the 3’ and 5’ ends of a DNA strand? Hydroxyl group and phosphate group ( respectively to Question)
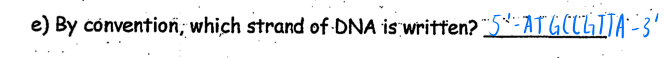
By convention which strand of DNA is written? - by convention only 5’to 3’ strand
How is 5’ to 3’ strand written ? - 5’- ATGCCGTTA -3’
Who is the the scientist that assisted Watson and Crick with their model? - Rosalind Franklin assisted (? 2 people)
What work of Rosalind Franklin assisted Watson and Crick? - Using their x-ray cystallography talents, they were able to produce a clear x-ray diffraction pattern that suggested that DNA is helical in nature and DNA is a constant at 2nm.

How did Watson and Crick decide on the specific base pairing of DNA? - Since only purines and pyrimidines combined will get you 2nm then it has to be AT and GC

You can copy based on complementary strands.


Nitrogenous bases - Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C), Thymine (T), and Uracil ( U)
What is the linkage between the separate nucleotide phosphates? - the linkage between the (?) is a phosphodiester bond

Watson- Crick model of DNA
Width of DNA (Watson-crick) - 2nm ( nanometer)
What are the purines? - These are double-ringed structures. Ex. A and G
What are the pyrimidines ? - These are single-ringed structures. Ex. T and C

What is the length of helix that completes 360 turn and how many bases per turn? - 3.4nm and 10 (?)


Define “ antiparallel strands” - Parallel but running in opposite directions; the 5’ end of the one strand of DNA aligns with the 3’ end of the other strand in a double helix
two strands of DNA run antiparallel (define) - one strand runs in the 5’ tp 3’ direction and the other runs 3’ to 5’ direction

What does 3’ mean? - This depicts the deoxyribose has a hydroxyl group on the 3’ carbon
What doe 5’ mean? - this depicts the phosphate group is attached to the 5’ carbon
Name the functional groups located at the 3’ and 5’ ends of a DNA strand? Hydroxyl group and phosphate group ( respectively to Question)
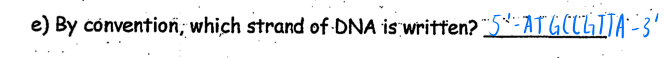
By convention which strand of DNA is written? - by convention only 5’to 3’ strand
How is 5’ to 3’ strand written ? - 5’- ATGCCGTTA -3’
Who is the the scientist that assisted Watson and Crick with their model? - Rosalind Franklin assisted (? 2 people)
What work of Rosalind Franklin assisted Watson and Crick? - Using their x-ray cystallography talents, they were able to produce a clear x-ray diffraction pattern that suggested that DNA is helical in nature and DNA is a constant at 2nm.

How did Watson and Crick decide on the specific base pairing of DNA? - Since only purines and pyrimidines combined will get you 2nm then it has to be AT and GC

You can copy based on complementary strands.