Unit 1: One Dimensional Motion
Lesson 2 - Distance, displacement, and coordinate systems:
- Key Terms:
| [[Word[[ | [[Defination[[ |
|---|---|
| Coordinate Systems | Defines position and direction for positive and negative number |
| Position | Location of an object relative to originSymbol “x“ refer to postion |
| Displacement | Chnage in position of an object /\ x for displacement/\ = change |
| Distance | Totale amount the object has moved Always a non-negative numberA scalar quantity with unit of distance |
| Reference Frame | Point of view from which measurement can be made All frames of references are equally valid |
- Equations
| <<Formula<< | <<Symbol Meaning<< |
|---|---|
| /\x = x(f) - x(i) | /\x = displacementx(f) = final positionx(i) = inital position |
Lesson 3 - Average Velocity and Speed:
- Equation
| <<Formula<< | <<Defination of Symbols<< |
|---|---|
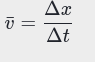 |  |
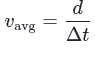 |  |
- Key Points:
- Avg. speed doesn ot equal the magnitude of avg. velocity
- Speed is a scalar quantity, and avg. velocity is a vector quantity
- Avg. velocity = direction and can be negative number when displacement is in negative direction
- Avg. speed ~~=~~ direction; can only be positive or zero
Lesson 4 - Velocity and speed from graph
- Key Terms
| Instantaneous Velocity | Velocity at a given moment in timeSI units = m/s |
|---|---|
| Instantaneous Speed | Speed at a given moment in time Equal to the megnitude of the Intantaneous VelocitySI unites = m/s |
- Equations
| <<Formula<< | <<Defination of Symbols<< |
|---|---|
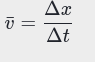 |  |
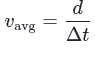 |  |
Lesson 5 - Average and instantaneous acceleration
What is velocity vs. time graph?
- Veritical axis represents the velocity of the object
What does the slope represent on a velocity graph?
- Slope = acceleration of the object
- rise/run = v2-v1/t2-t1 = /\v / /\t
What does the aera under a velocity graph represent?
- area under curve represent = displacement of object
- /\x = v/\t
Key Terms
| <<Words<< | <<Defination<< |
|---|---|
| Avg. Acceleration | Rate at which velocity changes over a specified time intervalSI = m/s^2Vector Quantity |
| Instantaneous acceleration | Rate at which velocity changes at a speific intant at time SI = m/s^2Vector Quantity |
- Equation
| <<Formula<< | <<Symbol Defination<< |
|---|---|
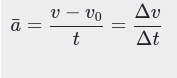 |  |
Lesson 6 - Motion with constant Acceleration
- Key Terms
| <<Word<< | <<Defination<< |
|---|---|
| Kinematic Variable | Variable that describes the moition of an object over time Includes displacement “/\X”time interval “t”intial velocity “Vi”final velocity “Vf”acceleration “a” |
| Kinematic Formula | formula that describe the relationships between Kinematic variable when accelaration is constant |
- Equations
| <<Formula<< |
|---|
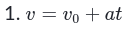 |
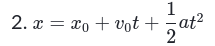 |
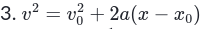 |
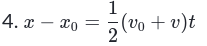 |
Symbols

Assumptions
- Acceleration is constant over the time interval
When using kinematic formulas
- Choosing best kinematic formulas
- figure out which variable you are not given & asked to find
- Finsing the known variable
- Somtimes a known variable will not be explicity given in a problem, but neither implied with codeword
- “start from rest“ = Vi = 0
- “dropped“ = Vi = 0
- “Comes to a stop” = Vf = 0
- g = 9.8 m/s^2 = acceleration due to gravity on all objects in free fall on Earth
Lesson 7 - Objects in freefall
- Key terms:
| <<Word<< | <<Definition<< |
|---|---|
| Acceleration due of gravity | In the absence of air resistance, all objects fall with constant acceleration “g“ toward the surface of the Earth. On the surface of Earth, defined ad g = 9.8 m/s^2 |
Annalyzing motion for objects in freefall
- special cade with constant acceleration
- Accelaration due to gravity is always constant and downward
- True even when object thrown upward or has zero velocity
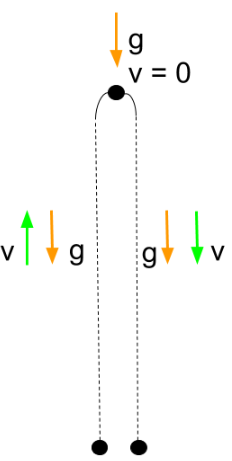
Example
- A ball thrown up in the air
- Ball’s velocity is initally upwards
- Gravity pulls ball towards earth surface with constant acceleration ““g“
- Magnitude of velocity decreases as ball approches maxximum height
- At highest point
- Ball velocity is zero
- Magnitude of the ball increases again as it falls back to the earth surface