Topic 1.2 - Elements of Life
^^Organic Chemistry^^: The study of compounds with covalently bonded carbon
^^Organic compounds^^: Compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen
- Carbon has four valence electrons, which allows it to form diverse molecules because it still has 4 electrons remaining in its outer shell.
Single, double, or triple covalent bonds can be formed with carbon
- A single carbon can form up to four bonds
- Allows for long chains to be formed by linking carbon molecules together
Most commonly formed with hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen
Type and number of bonds carbon forms affects the length of the carbon chain and the shape of the molecule.
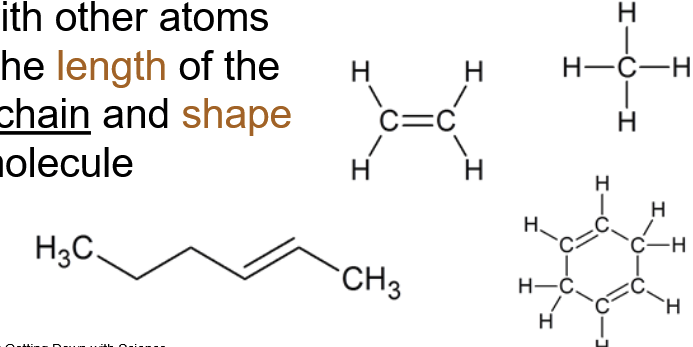
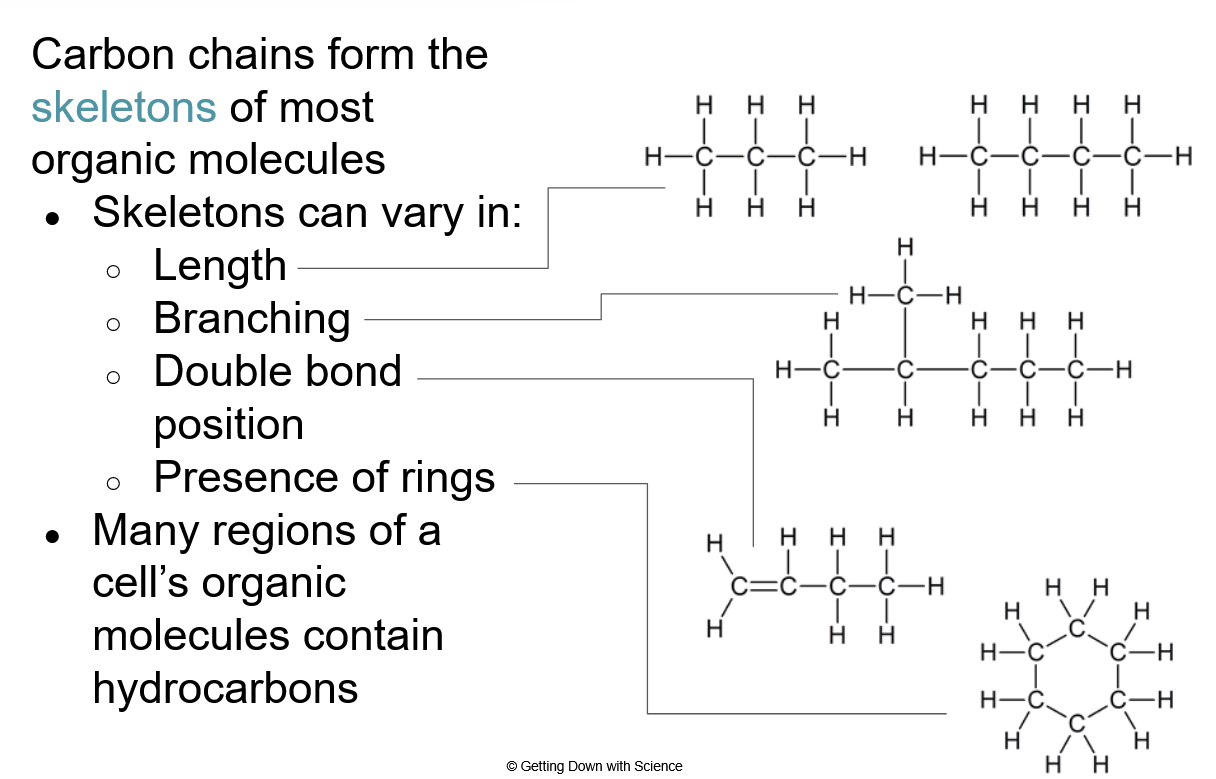
^^Hydrocarbons^^: Organic molecules consisting only of carbon and hydrogen
- Framework/skeletons for more complex molecules
They vary in length, branching, double bond positions, and presence of rings.
^^Functional groups^^: Chemical groups attached to the skeleton that participate in chemical reactions.