Economics
economics - how individuals make choices to satisfy unlimited wants
established by Adam Smith
cost-benefit analysis - people rationally compare the pros and cons of actions and choose based on benefit
economic analysis
observe
describe
measure
theory
Types of Economics
Types of Studies:
Positive Economics
use cause-and-effect to predict events
Normative Economics
judgements based off what should be
cannot be proved false or true
Pareto Efficiency
efficiency of resource allocation
resource allocation - assigning tasks/resources to a certain business
exists so that people may benefit
Two Economic Fields:
Microeconomics
Macroeconomics
Microeconomics
-Examines the economy on an individual level
agents - individual consumers, groups of consumers, producers
supply and demand
how agents behave and interact
determines prices and distribution of products
Supply and Demand:
Demand:
the amount buyers are willing to purchase
main determinant - price
law of demand: inverse relationship between price and demand
demand schedule: lists the price and corresponding quality of products
dependent variable = demand
independent = price
market demand curve = sum of individual demand curves
quantity that every customer demands at each price
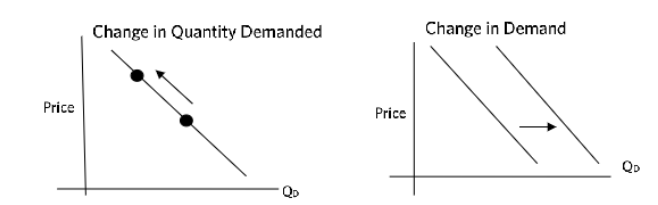
shifts in demand curve:
External Factors - Consumer Income, Prices of Related Goods, Consumer Preference, Consumer Expectations, Consumer Numbers
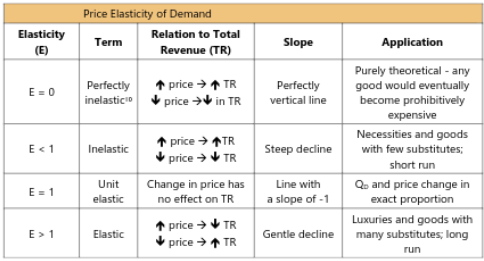
Elasticity of demand curve = demand curve shape
factors: substitutes (good), necessity (lower than luxury), time horizon (direct relationship), market size (inverse relationship)
decreases along demand curve

Supply:
amount sellers are willing to produce
most determinant = price
law of supply: direct relationship between supply and products
supply schedule: lists price and corresponding products
market supply curve = sum of all quantities at supplier prices
movement - change in quantity supplied
shift - change in supply [inward(left) = decrease, outward(right) = increase]
factors: Production Costs, Technological Process, Price Expectations, Number of Suppliers
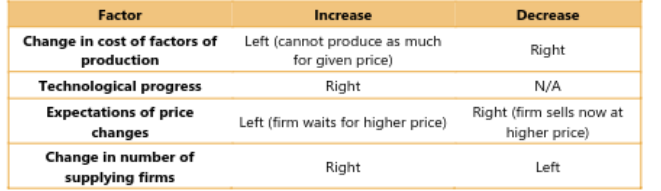
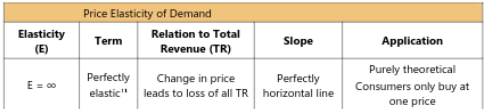
Elasticity
supply and price relationship sensitivity
factors: difficulty of transportation, time, production decisions of firms
f = final
i = initial
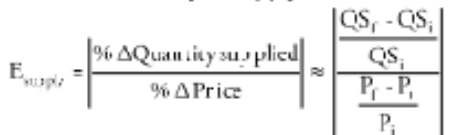
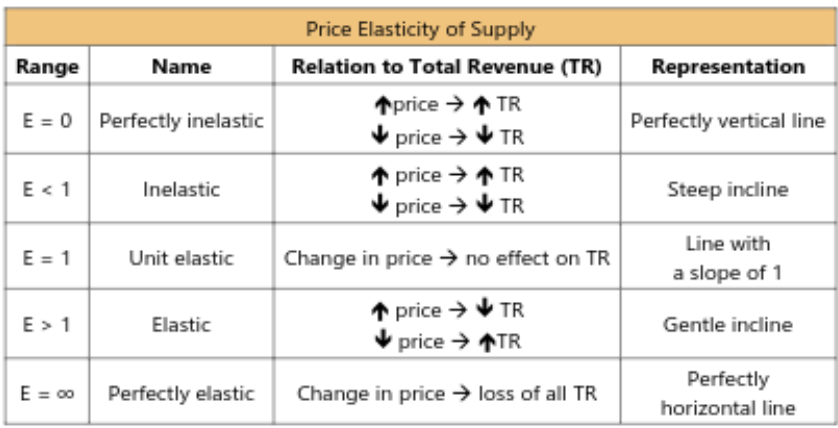
good elasticity = increase in price = small decrease in product quantity
Revenue = price x quantity
Unit Elasticity: price increase = equivalent quantity decrease
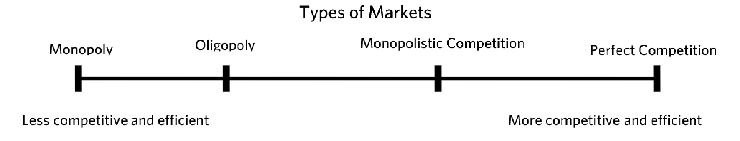
Markets:
Market - all buyers and sellers of a certain product
formal (stock exchange) & informal (gas station) markets
interdependent: relying/trading with strangers for supplies
Production Possibilities Frontier - summarizes an economy’s possible products
moving along curve = substituting 1 good for another
linear curve- constant opportunity cost
most resources are best for 1 good; or else efficiency decreases
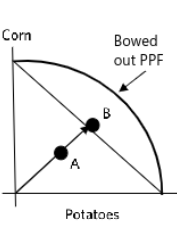
//////
Absolute Advantage
produces good more efficiently/ ability to produce more of a good or service
Comparative Advantage
ability to produce at lower opportunity costs
parties with different comparative advantages will benefit
Equilibrium:
point where all the forces in a system are balanced and stable
Market equilibrium = when supply and demand are equal
price taker - any buyer/seller
Perfectly Competitive Market -
Homogeneous/Standardized product
Large Number of buyers and sellers
Transparent market price info
No entry barriers
near equilibrium, allocates sources well, benefits consumers
consumer surplus: extra consumer benefit
producer surplus: market price exceeds opportunity cost
total market surplus: total participant benefits
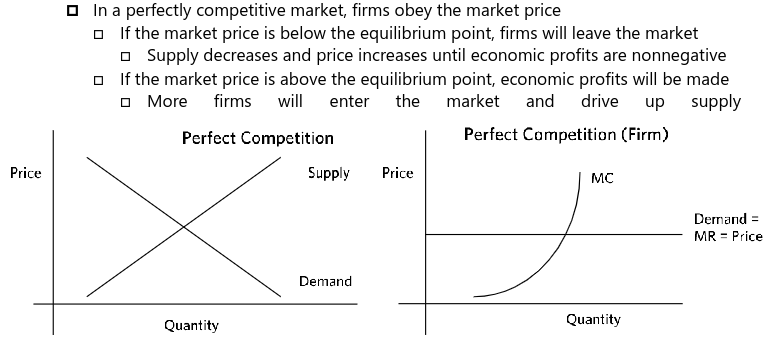
marginal revenue = revenue from selling a unit
primary commodity markets
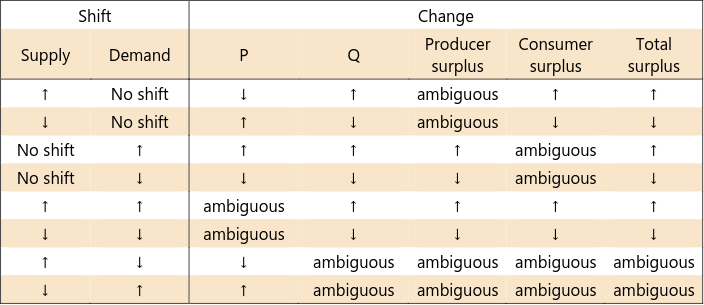
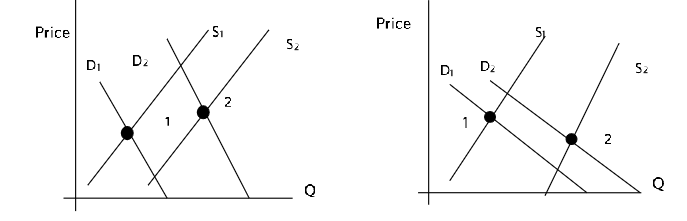
Changes in Market Equilibrium
Firms:
Economic actors that combine labor, capitol equipment, and raw materials to produce goods with max profits
Total Revenue = output quantity x price
Total costs - expenses
Accounting costs/profit: monetary costs/profit
Accounting Revenue = accounting profit - explicit cost
Economic costs/profit: monetary and opportunity costs/profit
economic profit = monetary profit - opportunity costs
Economic Revenue = economic profit - explicit costs - implicit costs
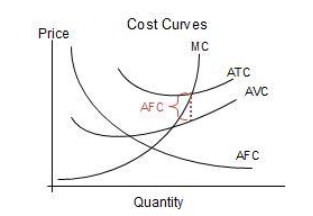
Fixed Costs - must be paid regardless
Variable Costs - paid based on amounts produced
marginal cost - cost from producing an extra unit
Average cost - total production cost of each output
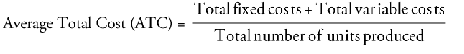
Average Fixed Cost (AFC)
Marginal Cost (MC)
Average Variable Cost (AVC)
Average Total Cost (ATC)
Failures:
When Competitive Markets fail to produce socially desired outcomes
Externalities - costs or benefits of uninvolved 3rd parties
Negative: harm on others
Positive
Internalizing externalities - paying directly to market (taxes, fines)
helpful to the individual
Coase Theorem by Ronald Coase
private parties should be able to solve inefficiencies of externalities
not really effective
Quoata - numerical limit on quantity
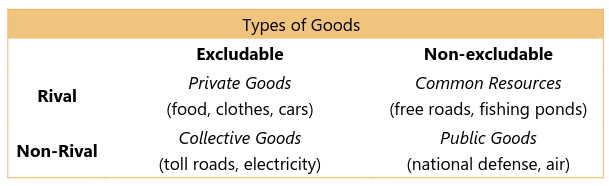
Rivalry in property rights and public goods
Imperfect competition
few suppliers
monopolies → scarcity → contrived scarcity
Legilsation
something something idk
Oligopoly
a market with some interdependent firms
produce both different and homogeneous products
common
ex. Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) - oil
collusion - non-competitive/secret (sometimes illegal) agreement between rivals to disrupt market equilibrium
cartel - groups involved
Monopolistically Competitive
most common
ex. restaurants, clothing, service
competition through advertising, branding (but not prices)
Influences on Microeconomic Markets
lowkey common sense (taxes, gov, business)
Macroecomics
-Studies economics on a national level
Aggregation: combines multiple factors into 1 variable
2 Main Concerins:
Long-term
Short-term
Money and Inflation:
Money is:
A medium of exchange
A unit of account
A storage of value
Wealth = all value in economy
highly liquid: currency, stocks
not liquid: real estate, land
Commodity Money - made of material with intrinsic worth (ex. gold)
Fiat Money - value from gov order
Demand Deposits - money stored in accounts (withdrawn at anytime)
Time Deposits - money stored in accounts (cannot be withdrawn whenever)
Money Market Accounts - money stored with restrictions
Monetary Base, M0 - narrowest possible definition of money supply
M0 - all currency held by general public
M1 - very liquid forms of money
M2 - M1 + saving accounts, money market funds, and deposits
Price level and Inflation
Inflation - currency value decreased
sustained rise in general price level
reduces money’s value and purchasing power
CPI - Consumer Price Index
measures inflation
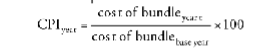
Price Level - price relative to a base; average of current prices of goods and services for the entire economy
Aggregate Price Level = price level for the entire economy
price level rises —> more expensive
Money Market in the Long Run
Long Run - time it takes for the Demand money = Supply money
value of money depends on supply and demand
Quantity Money Theory/ Equation of Exchange = MV = PY
amount of money spent = amount of money used
M = money stock/supply
V = money velocity (frequency of money transactions in some time)
P = current average price level
Y = output of goods and services
Financial Institutions
coordinates the economy’s saving and investment decisions
financial markets - a place people can save money by giving to investors
investments - buying new capital equipment
Debt Finance - bond insurance
Bond - obligation to bond holder
Date of Maturity - date when payment + interest is due
longer maturity period = greater risk of price change
Principle - original bond value
large corporations will sell bonds to the public for funds
Default - risk of bond buyer if borrower goes bankrupt
Borrower: Seller
Equity Finance - stock sales
Stocks - share of onwership of a firm
National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotation System (NASDAQ)
New York Stock Exchange (NYSE)
prices depends on supply and demand
Dividends - shareholders receive this if the company does well
Financial Intermediaries
Intermediary - 3rd party used for connection (ex. banks)
Mutual Funds - allow shareholders with little money to buy stocks/bonds
The Federal Reserve
Amount of Money in the US = public interactions, commercial banks, and the Federal Reserve System (Fed)
Fed Central Banks
12 regional banks per central bank
ran by 7 board of governors
Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC)

Fractional Reserve Banking
fractions keep a deposit of loans/deposits
bank run - when depositors rush to deposit in a bank
monetary policies increase/decrease the effective money supply
Contractionary policy - decreases money supply
Expansionary policy - increases money supply
Supply and Investment in aggregate
identity - an equation that is always true
something gdp agghghghgh
GDP (Gross Domestic Product)
interest in economic output
market value of all final goods and services
Simon Kuznets - developed modern concept of GDP (1934)
GDP = expenditures = C + I + G + NX
C = Household Consumption
I = Firm Investment
G = Government purchases
NX = Foregin Net Exports
real GDP - calculated by converting prices to the baseline year; to remove inflation;
average labor per capita
nominal GDP - calculated in prices of current year
depends on quantity of goods and services
larger economies should have greater GDPs (typically)
Human capita: skills acquired
Economic Growth
19th century - great US and European economic growth
circular flow model - relationship between sectors of the economy
factor market - where firms buy factors of production
factors of production - labor, capital, etc.
business secotr = firms
Unemployment
Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS):
measures monthly unemployment rate
3 Types of Unemployment
Structural Unemployment
from change in consumer tastes, or technology
Cyclical Unemployment
business cycle
Frictional Unemployment
from time between changing jobs
effect on output
output group = potential - actual output gap
Aruthur Okun - noted output and cyclical unemployment relationship
Okun’s Law - if the unemployment rate changes by 1%, the output gap changes by 2%
Short-Run Fluctuations:
the Aggregate Demand Curve
Aggregate Demand (AD)
the 4 components of GDP (C + I + G + NX)
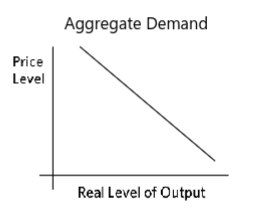
price level decrease = decrease in product prices
wealth effect
similar to income effect
price decrease →income increase →customers buy more
interest effect
price increase →more expensive →more borrowing money →increase rates go up
foreign exchange effect
cheaper domestic goods →consumers want more
Shifts of the Aggregate Demand Curve
changing local and foreign consumption = curve shifts
firm investment altered = curve shifts
direct relationship
consumer opinion
gov taxes
short-run aggregate supply curve (SRAS)
potential goods in the short-run
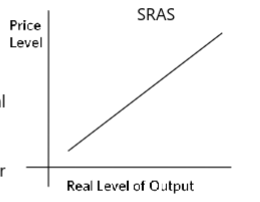
depends on long-run potential output and price level expectations
Shift in the Aggregate Supply Curve
change in price levels
Business Cycle
The Keynesian Model
developed by John Maynard Keynes
so like idc
Fiscal policy
allows gov to impact the overall economy
Expansionary Fiscal Policy - expand gov spending and lower taxes
Contractionary Fiscal Policy - decrease gov spending and raise taxes
Climate Change
Climate Commons: shared atmosphere for a stable climate
Economic Concepts and Climate: Theory and Practice
Externalities - irregularities in otherwise regularly-functioning markets (ex. public places)
Uni-directional/1 Way - externalities that only affect one party
Reciprocal - both parties affected
Collective Action = Expectations + Norms + Institutions
common property - belong to whole group
discount rate: interest rate used to determine the value of future cash flows
time value of money
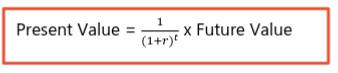
people are myopic
myopic: short-sighted
Topics similar to Social Science Section
disagreements between countries, leaders, and organizations
more money-based contributions
Policy Responses
Do Nothing
Unilateralism
geoengineering
a single country taking action without consulting others
Negotiations
int treaties and cooperation
Multileralism
global organizations
alliance between countires
 Knowt
Knowt