week 8: Examination of Youngs
Veterinary Pediatrics (finished)
1. Examination of Mother 👩⚕
History: Check for diseases and vaccination records.
Clinical Examination: Conduct a thorough physical assessment.
2. Environment and Nutrition 🌡🥕
Temperature
Humidity: Control humidity levels.
Air Condition: Ensure proper ventilation.
Colostrum: Provide early colostrum for immunity.
Ration: Ensure appropriate diet.
3. Clinical Examination of Newborns 👶
Body Development:
Posture
Body Condition
Size - Weight
Vitality (Behavior):
Consciousness
Reflexes (suckling reflexes is checked by finger)
Perception (how they respond to stimuli - sight, sound, touch)
Basic Signs of Normal Vitality in Calves
Standing up and walking within the first hour.
Suckling reflex within the first hour.
First defecation within 6-8 hours.
Piglets should:
weight more than 1 kg, lower weight is considered hypotrophic.
Right after birth, piglets need to be dried, attached to teat of sow → placed in thermbox after (prevent hypothermia)
shortening of canine teeth - in cases of possible mastitis
apply iron preparations in range from 3-5 days after birth, castrated without anaesthesia up to 7 days after birth.
Puppies:
Cannot regulate body temp., deaf, blind, dependent on mother - post-natal period, lasting 14 days → needed to ensure temp. of 27-29 degrees.
Right after birth → ensure attached to teat, colostrum
puppies eyes open between 10 - 14 days of age.
Timing of Significant Events in Pediatric Development
Event | Age at Occurrence |
|---|---|
Umbilical cord dries and falls off | 2 to 3 days |
Eyelids open | 5 to 14 days |
External ear canals open | 6 to 14 days |
Extensor dominance | 5 days |
Capable of crawling | 7 to 14 days |
Capable of walking, urinating, defecating spontaneously | 14 to 21 days |
Hematocrit / RBC number stabilize near that of adult | 8 weeks |
Renal function nears that of adult | 8 weeks |
Hepatic function nears that of adult | 5 months |
size abnormalities can happen - hypertrophy (spontaneous birth is not possible, animals are thus needed to be born by caesarean section. Opposite is hypotrophy, born with lower weight than normal.
Care after birth → amniotic sacs removed, airways need to be cleared to prevent hypoxia or asphyxia. Then treat navel, shorten it, disinfect.
Navel (Umbilicus) ⚓
Umbilical cord is torn during delivery (or bitten off) in large animals.
Bleeding stops physiologically within 3-4 minutes.
Complications:
If umbilical cord is torn, cut close to abdomen → complications can occur, in case of bleeding → cord is ligated. In arterial bleeding, light red blood, spurts out rapid.
Another problem can be urination through urachus (umbilical)→ obstruction of urinary tract of newborn, not enough treatment of navel, swelling
Respiration 🫁
Asphyxia: Can be caused by insufficient development of lung tissue (alveolar walls).
Heart ❤
Murmurs: May indicate conditions such as VSD (Ventricular Septal Defect), PDA (Patent Ductus Arteriosus), or mitral/pulmonic stenosis.
Body Openings 🚪
Atresia ani: Absence of the anus.
Atresia ani et recti: Absence of the anus and rectum.
Anus vaginalis (rectovagina): Abnormal opening between the rectum and vagina.
Anus vesicalis: Abnormal opening between the anus and bladder.
Inherited and Congenital Disorders 🧬
A) Inherited
Umbilical Hernia
B) Congenital
Disorders developed during pregnancy.
Hydrocephalus: Accumulation of fluid in the brain.
Various Origins
Infections: Such as oculocerebral syndrome in cattle.
Nutritional: Like goitre (iodine deficiency).
Poisonings: Caused by mycotoxins.
Physical: Due to irradiation or temperature extremes.
Clinical Examination of Young Animals 🩺
Navel
Joints & Muscle
Liver
Tendons
Heart
Eyes
Digestive Organs
Kidney
Thyroid Gland and Thymus
CNS
Bad Habits
Umbilicus 👶
Umbilical cord dries up until 14 days.
Examination: Inspection & Palpation
Disorders
Inflammation:
Omphalitis: Inflammation of the external navel.
Omphalophlebitis: Inflammation of the umbilical veins.
Omphaloarteritis: Inflammation of the umbilical arteries.
Urachitis (cystitis): Inflammation of the urachus/bladder.
Hernia: Protrusion of tissue through the umbilical opening.
Digestive Organs 🍎
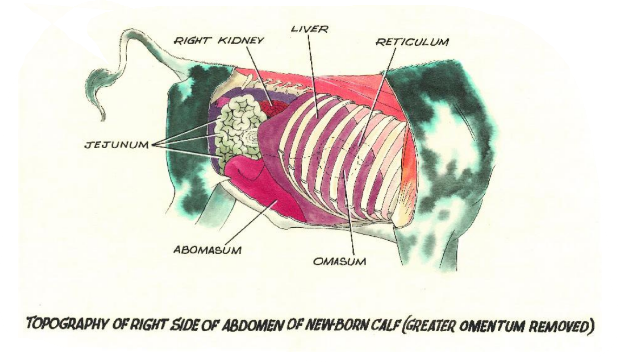
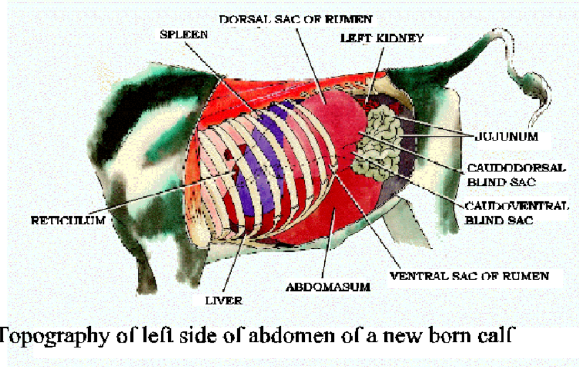
Rumen/Abomasum
At 2 weeks, the rumen/abomasum ratio is 0.5:1, while in adults, it's 9:1.
First ruminal contraction occurs in the 3rd week.
Disorders
Ruminal Drinking: Abnormal fluid accumulation in the rumen.
Tympany: Bloat (abomasal/gastric, ruminal, or intestinal).
Diarrhea
Organ/structure to examine: | Topography: |
Liver: | 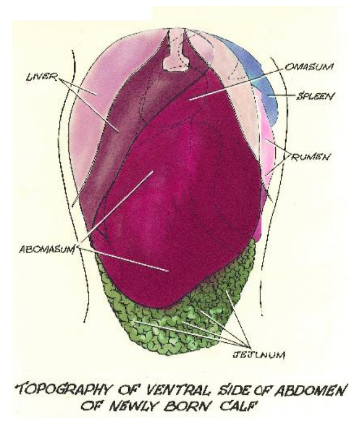 |
Ventral side of abdomen: | 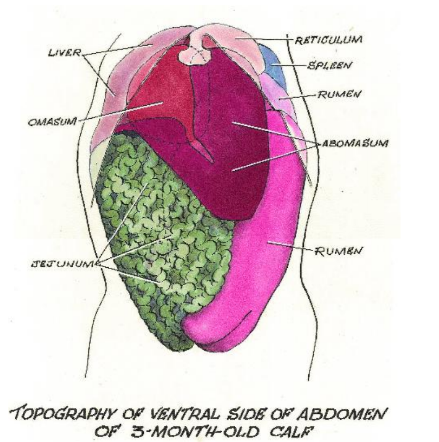 |
Thyroid gland: | 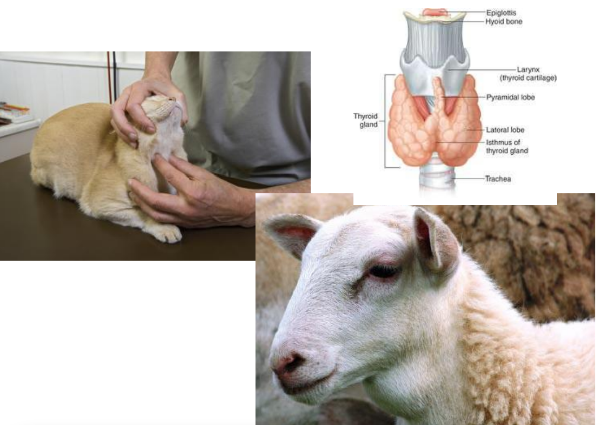 |
Thymus: | 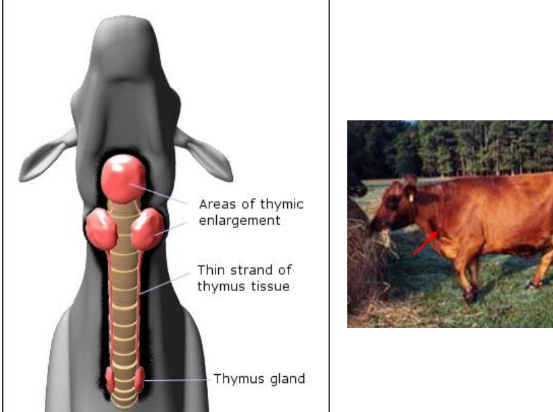 |
Joints & Muscle 💪
Polyarthritis: Often due to omphalophlebitis.
Myopathy: Muscle disease.
Bad Habits 😥
Learned abnormal behaviors, usually seen in groups of animals.y
Animal: | Bad behaviours/Stereotypies: |
Puppies |
|
Horse |
|
Calves |
|
Pigs |
|
Practical way - order according to book/practical.
General assessment first, posture, condition, size-weight, behaviour (vitality).
navel (inspection and palpation)
check for inflammation, hernias or bleeding, dried cord by 14 days
if hernia - into abdomen, pus content, firm-elastic, enlargement, increased temperature
Respiration
assess breathing
inspection, percussion, auscultation
respiration and type
upper: inspection, palpation
lower: percussion, auscultation
percussive sound that is resonant
detect pain, dullness in a pathological condition
auscultation evaluates breathing sounds and presence of abnormal sounds like crackles, wheezing, rubbing etc.
Heart
listen for murmurs
Liver
projects below the costal arch in young animals
palpation: clearly feel caudal edge of liver
in 8 month old calves, liver does not reach behind costal arch.
Kidney
inspection: evaluate enlargement
palpation: surface (nodular, smooth), size, consistency, pain
Digestive system
Abomasum: primarily investivated in case of newborn calves and calves on milk diet.
Palpation, percussion, auscultation between xhiphoid cartilage and rumen
normal: cannot differentiate abomasum from intestines
palpation + percussion: contents, consistency, pain
auscultation: peristaltic sounds under physiological conditions
pathological:
dilatation, right-sided, left-sided dislocation, dilated → balloon-shaped formation filled with air is felt. A metallic percussion sound and splashing is heard in the given area.
reflux of contents of the abomasum into the rumen → in case of dislocation, phyto and trichobezoars.
Rumen: in calves - probing, palpation, auscultation
ratio of rumen and abomasum in calf on dairy nutrition: 0.5-1.
examine filling, consistency, pain
ruminal drinking, tympany, diarrhea
Thyroid gland
inspection, palpation
located on ventral side of neck
neurological examination
inspection, palpation, percussion
assess consciousness (response to stimuli), disorders (paresis, paralysis, convulsions), sensitivity, cutaneous and limb reflexes (patellar, triceps, perineal, panicular)
Locomotor system
inspection, palpation of muscles, bones, joints, tendons
inspect while animal is standing up, walking, monitor activity, notice muscle tone, myotrophy, bone formation, tendons and joints.
palpation for detection of pain.
in case of swelling - we evaluate mobility of joint, consistency, fluctuation and temperature.
Bad habits - Stereotypies
behavior patterns assessed
As respiration and heart was right after navel in practical, but respiration was after kidney in book.