memory: ap psych unit 3
memory: the persistence of learning over time through encoding, storage, retrieval of info
encoding: processing info into memory system
ex. extracting meaning
storage: process of retaining info over time
retrieval: process of getting info out of memory storage
parallel processing: processing of many aspects of a problem simultaneously; natural mode of info processing
→ this is different from step-by-step process of computers
ex. enter lunchroom, at once process info about people you see, sounds of voices, smell of food
sensory memory: very brief immediate recording of sensory info in memory system
short term memory: memory that holds a few items briefly before info is either stored or forgotten
ex. seven digits of phone number while dialing
long term memory: relatively permanent + limitless storehouse of memory system
→ includes knowledge, skills, experiences
- episodic memories = personally experienced events (what u had for breakfast)
- semantic memories = general factual knowledge (what temp at which water boils)
- procedural memories = relate to skills of habits (how to brush teeth)
external events→sensory input→sensory memory→encoding→short-term memory→encoding→long term memory storage(← retrieving)
working memory: newer understanding of short term memory focusing on auditory/visual info + info retreived from long term memory
- auditory rehearsal ex. mentally repeating password long enough to enter it online
- visual-spatial info ex. mentally rearranging furniture in room
31.3 How do explicit/implicit memories differ?
types of long term memories:
explicit memories: memory of facts + experiences that one is consciously aware
ex. memory of playing on a particular golf course
- processed in hippocampus
- facts, personally experienced events
implicit memories: memories of which one is not conscious
ex. how to tie one’s shoe but not be able to describe how to do it
- processed by cerebellum
- skills(motor + cognitive), classical+operant conditioning effects(pavlov)
- implicit memories are processed automatically!
explicit = effortful processing → encoding that requires attention + conscious effort
implicit = automatic processing → unconscious encoding of info (well learned info)
31-4 What info do we automatically process?
implicit memories + automatic processing
ex. conditioned association linking doctors office w shot, find yourself with sweaty palms
with implicit memories, you automatically process info about
- space ex. encode place on page while studying, retrieve info by visualizing location of info on that page
- time ex. while going about day, unintentionally note sequence of events, lose an item and retrace your steps
- frequency ex. keep track of how many times things happen, suddenly realize you’ve run into someone 3 times
explicit memories + effortful processing
learning to read is not automatic → effortful
but w experience+practice, reading becomes automatic
31-5 how does sensory memory work?
sensory memory - records momentary images of scenes, echoes of sounds
iconic memory (EYEconic) - george sperling’s recall of letters
- for few tenths of second we can register photographic memory of a scene
- but if time in between seeing visual and repeating it gets longer, visual screen clears, new imaged replaced over old one
echoic memory
- momentary sensory memory of auditory stimuli
→ if attention is elsewhere, sounds/word can be recalled within 3 or 4 secs
ex. distracted in class, teacher asks “what did i just say”, you can recover the last few words from your minds echo chamber
31-6 what is the capacity of our short term and working memory
short term memory- limited to about 18 secs unless info is rehearsed
- about 7 numbers, 6 letters, or 5 words can be maintained in short term memory if nothing distracts us
amount of info that is encoded can be increased if organized into chunks of meaningful, well practiced info
31-7 what are some effortful processing strategies that can help us remember new info?
george miller - stated that short term memory could hold 7 chunks of information
chunking
chunking/organizing items info familiar manageable units helps us remember more easily
ex. phone numbers are separated by the area code, then 3 digits, then 4
mnemonics
memory aids, especially those techniques that use vivid imagery and organizational devices
- peg method
ex. acrostic, acronyms
hierarchies
composed of broad concepts divided and subdivided into narrower concepts/facts
- organizes concepts
spacing effect (space out learning)
tendency for distributed study/practice to be better for longterm storage than through cramming
- those who learn quickly, forget quickly
- spreading learning over time
testing effect
enhanced memory after retrieving rather than simply rereading info
ex. better to practice questions and force retrieval of concepts rather than reread info from textbook
shallow processing
- use of only surface features to encode info, basic encoding
→ physical/visual info abt something
→ only auditory
ex. memorizing list by reading them aloud, not understanding
deep processing
- encodes semantically (factual, meaning) based on meaning of words
- the more meaningful (deeper) the processing, the better we recall it
32-2 what roles do the frontal lobes and hippocampus play in memory processing?
frontal lobe for working memory processing
- left frontal lobe = activates recalling password + holding it in working memory
- right frontal lobe = activates visual party scene
hippocampus - neural center located in limbic system, helps process explicit memories for storage
→ save button for explicit memories
- damage to hippocampus = affects recalls of explicit memories
left hippocampus damage = troube remembering verbal, no trouble w visual recall
right hippocampus damage = opposite as left damage
LEFT = VERBAL; RIGHT = VISUAL
32-3 what roles do the cerebellum and basal ganglia play in memory processing?
cerebellum - forming+storing implicit memories created by classical conditioning
damaged cerebellum = cannot develop conditioned reflexes
basal ganglia - involved in motor movement
- formation of procedural memories for skills
ex. learning how to ride bike
32-4 how do emotions affect our memory processing?
amygdala triggers hippocampus to process memory deeper than normal
- exaggerated stress response until more experience overwrites it
flashbulb memories: a clear memory of an emotionally significant moment or event
ex. people could recall exactly where they were during news of 9/11 attack
32-5 how do changes at the synapse level affect our memory processing?
sea slug experiment
- classically conditioned slug to reflexively withdraw its gills when squirted w water
→ learning occured, more serotonin
long term potentiation: increase in strength of synapses between neurons through electrical stimulation = basis for memory, learning
ex. mice that lacked an enzyme needed for LTP couldnt learn way out of maze
32-6 how is memory measured?
recall - retrieving info that was learned at earlier time
recognition - identifying items previously learned
relearning - learning smth more quickly when u learn a second or later time
ebbinghaus forgetting curve
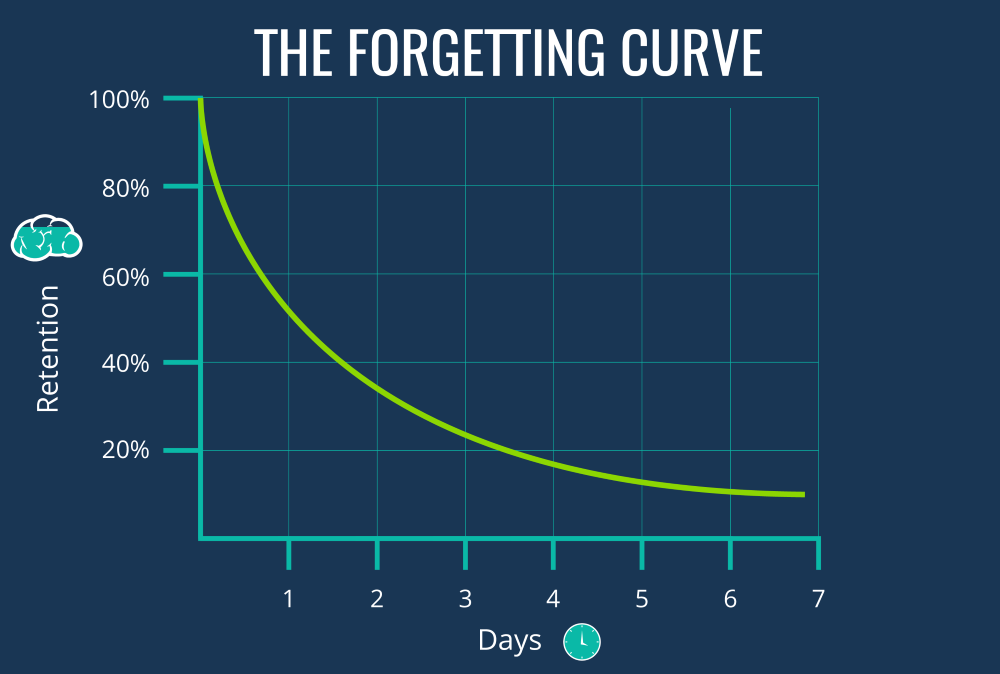
rate human memory deteriorates over time without rehearsal
32-7 how do external cues, internal emotions, order of appearance influence memeory retrieval?
priming: unconscious activation of particular associations in memory
ex. seeing/hearing the word rabbit primes the word hare, even though we might not remember seeing or hearing the word rabbit
→memoryless memory
context dependent memory
putting youtself back in context where you experienced smth, primes memory retrieval
ex. need to sharpen pencil, walk into another room, forget why you were there, walk back to desk, realizes why you went
33-1 why do we forget?
HM:
- brain to surgery to stop seizures, unable to form new conscious memories
anterograde amnesia: able to recall the past, but inability to form new memories
retrograde amnesia: cannot recall the past but can form new memories
storage decay:
hermann ebbinghaus - measured how much he retained when relearning each list
→forgetting curve
- showed that first few days after learning list, could not remember list when relearning, but as time went on, it became constant
/
proactive interference: the disruptive effect of prior learning on recall of new info
ex. well rehearsed password may interfere with retrievel of newly learned code
- forward acting = left to right = old info disrupts new info
retroactive interference:new info disrupting recall of old info
- backward acting = right to left = new info disrupts old info
repression : basic defense mechanism that repress painful memories to protect self and minimize anxiety
33-2 how do misinfo, imagination, and source amnesia influence our memory construction?
misinformation effect: incorporating misleading info into ones memory of an event
ex. elizabeth loftus tested about how fast were the cars going when they smashed/hit each other?
smashed gave a high speed + recalled seeing broken glass
source amnesia: using wrong source with an event we have experienced, heard about, read about, imagined
ex. remember smth when you were younger because you heard so many stories about it but it is not actually true
34-1 what is cognition, and what are the functions of concepts?
cognition = all mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, communicating
prototype: mental image, best example of a category
ex. a robin matches our bird prototype more than penguin being a bird
convergent thinking: narrows available problem solutions to determine single best solution
- intelligence tests, multiple choice qs
- injury to left parietal lobe damages this ability
divergent thinking: expands number of possible solutions (creative thinking)
- injury to frontal lobes can destroy imagination
35-1 what cognitive strategies assist out problem solving and what obstacles hinder it?
heuristics: simple thinking strategy that allows us to make judgements, speedy, but more error
ex. walking faster if someone has a hood in dark alley
insight : sudden realization of solution, not strategy based, aha moment
confirmation bias: tendency to searvh for info that supports our preconceptions, ignoring contradicting info
mental set : tendency to approach problem in a particular way that was successful in the past
ex. pattern is first letter of numbers, but next pattern is first letter of the months
representativeness heuristic: likelihood of things in terms of how well they represent particular prototypes, may lead us to ignore other relevant info
ex. someone wearing a suit and briefcase we may believe they are a lawyer because of stereotype
availability heuristic: likelihood of events based on how often they are in our memory, if they come easily to mind, they are common
- casino encourages gambling by signaling small wins w bells and lights, big losses are soundless
belief preserverance: clinging to ones initial belief after basis on which they were formed has been discredited
framing: the way an issue is posed, affect decisions
ex. telling patient 90% survive, telling them 10% die from surgery
36-1 components of a language
phonemes = smallest distinctive sound units
ex. chat has ch, a, t
morphemes = smallest units that carry meaning
ex. pre- in preview
-ed in adapted
bat, gentle
36-2 milestones in language development
start at 4 months, babbling stage
at 10 months, babbling can identify househould language
around 1 years old, one-word stage
2 years old, two-word stage
uses telegraphic speech = early speech in which child speaks like telegram “go car” with only nouns and verbs
aphasia: damage to broca’s area/wernicke’s area, impairment of language
damage to LEFT hemisphere
linguistic determinism:
whorf’s hypothesis that language determines the way we think
ex. different personality profiles when taking same test in two languages
60-2 arguments for/against considering intelligence as mental ability?
general intelligence (g factor)- influences how well someone performs on cognitive tests
→ spearman
factor analysis - method used to identify underlying factors that explain relationship between large numbers and variables
savant syndrome: condition in which person limited in mental ability is exceptional in a specific skill like drawing, computation
sternberg’s 3 intelligences (triarchic theory)
1. analytical intelligence
2. creative intelligence
3. practical intelligence”
intelligence related to brain anatomy?
correlations about +.33 between brain size and intelligence score
61-1. historical of intelligence testing
mental age (binet)- level of performance associated w a certain age
IQ = measured by mental age/real age x 100, average iq is 100
achievement tests: measure what you have learned
ex. standardized state tests, end of unit tests
aptitude tests: test to determine future performance
ex. college entrance exam
wechsler adult intelligence scale: most widely used intelligence test, containig verbal + perofrmance
reliability: yields consistent results
validity: test measures what is it supposed to, predicts what it promised
content validity: how well test measures concept, theme
predictive validity: success w which test predicts behavior it is designed to predict
flynn effect: improvement in performance on tests of intelligence over decades
crystallized intelligence: accumulated knowledge as reflected in vocab + analogies, tends to increase with age
fluid intelligence: our ability to reason speedily + abstractly; tends to decrease with age
*we lose recall memory + processing speed as we age, but gain vocab knowledge
intellectual disability: condition of limited mental ability, iq of 70 or lower
down syndrome: extra chromosome 21