Ch 1
Lecture 8/26
Management is about Organizations
The key is organizations’ “very productive way of getting things done”
Division of Labor
Leverage resources
Social creatures
Superior Performance is not automatic
Organizations come with challenges
Individual, Team, and Firm Levels
People are complex
Motivations
Personalities
Decision-Making
Understanding Organisations (Individual, Team, and Firm)
Why are the degrees we offer useful?
They work in any organization
Analysts, consultants, and managers all require a broad understanding of the organizational structure
Lecture 8/28
What is Management?
The pursuit of organizational goals efficiently and effectively by connecting people to
Purpose
other people
the right resources to achieve competitive advantage (doing something better, results and performance)
Organizational Goals Provide
Purpose and Direction
Set goals and you determine how to achieve them
Arrange tasks/people and motivate people to achieve those goals
Goals lead to better performance
Control
compare performance with goals
Effectiveness
Doing the Right Things
make the right decisions and carry them out to achieve
Efficiency
Doing Things Right
to use resources (people, money, raw materials) without waste, using the minimum amount possible
Connecting People to Purpose
Helping employees/team members understand how their efforts are worthwhile and connected to the organization
Creating a sense that employees have a role in the organization
Connecting People to Resources
Giving employees tools so they can be as productive as possible
Machinery, education, tools to manage information, technology, their time
Connecting People to People
Helping employees create and maintain internal and external networks that add value to their work and ultimately value to the organization
Competitive Advantage
Weak firms die in competitive markets
Need to maximize finite resources
Beyond Managing for Competitive Advantage
Sustainability
Economic development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
Ethical Standards
Ethics and profits do not always go hand in hand (e.g., minimum wage, pollution, working conditions abroad VS. profits)
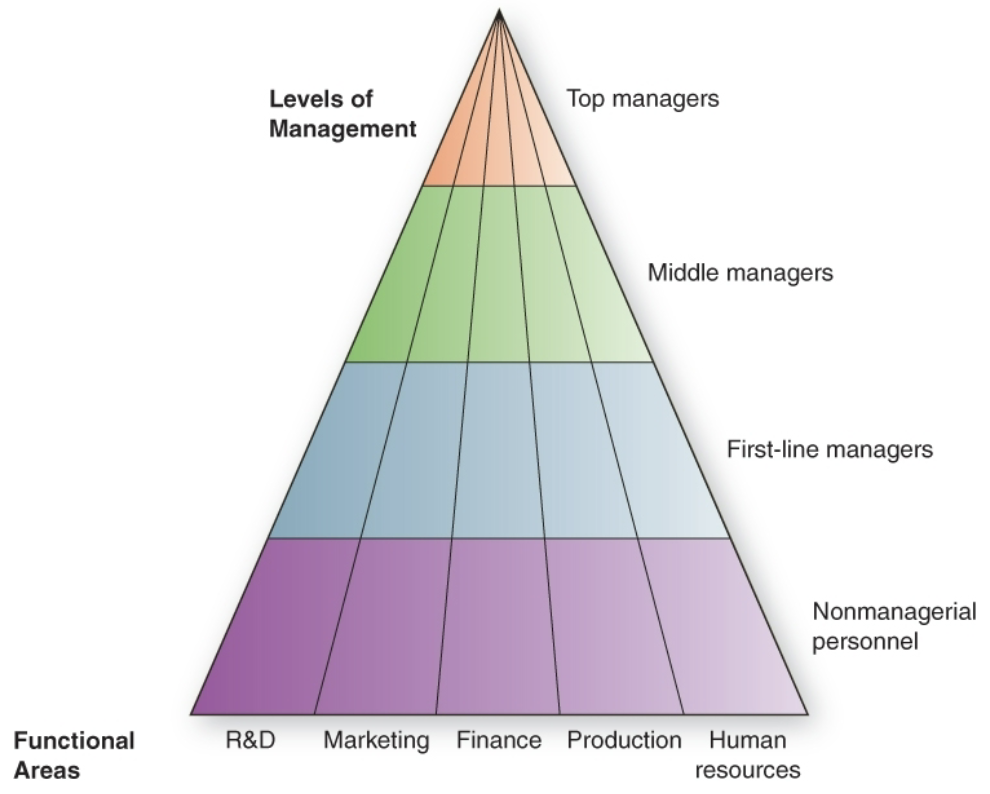
Levels and Areas of Management
Top Managers
make long-term decisions about the overall direction of the organization and establish the objectives, policies, and strategies for it
Middle Managers
implement the policies and plans of top managers and supervise and coordinate the activities of the first-line managers below them
Front-Line Managers
make short-term operating decisions, direct the daily tasks of non-managerial personnel
Team Leader
a manager who is responsible for facilitating team activities toward achieving key results
Functional Manager
responsible for just one organizational activity
General Manager
responsible for several organizational activities
Skills Managers Need
Technical skills
the job-specific knowledge needed to perform well in a specialized field
Conceptual skills
the ability to think analytically, visualize an organization as a whole, and understand how the parts work together
Human / Soft skills
the ability to work well in cooperation with other people to get things done
the ability to motivate, inspire trust, and communicate with others
Three Types of Managerial Roles
Interpersonal roles
managers interact with people inside and outside their work units figureheads, leaders, liaison
Informational roles
managers receive and communicate information
monitor, disseminator, spokesperson
Decisional roles
managers use the information to make decisions to solve problems or take advantage of opportunities entrepreneurs, disturbance handlers, resource allocators, negotiator
What is Entrepreneurship?
Entrepreneurship
process of taking risks to try to create a new empire
Entrepreneur
someone who sees a new opportunity for a product or service and launches a business to try to realize it