L1: Motherboard Expansion Slots - CompTIA A+ 220-1101 - 3.4
Components of a Motherboard
Main Components:
CPU (Central Processing Unit)
Memory (RAM)
Storage
Expansion Slots
Communication: All components need to communicate via a bus system.
Buses and Communication Paths
Communication Paths: Series of connections allowing interaction between CPU and memory.
Visible Traces: Traces can be seen at the bottom of the motherboard showing communication paths.
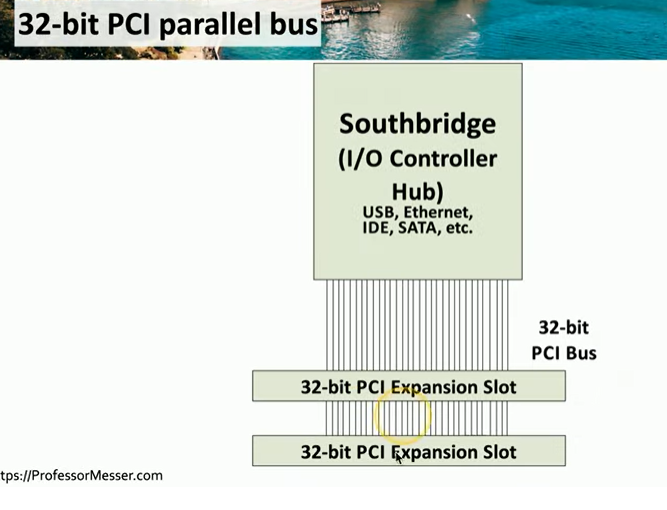
PCI Slots and Standards
PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect):
Established in 1994.
Supports 32-bit and 64-bit bus sizes.
Uses parallel communication.

Expansion Slots:
Older computers may have PCI slots.
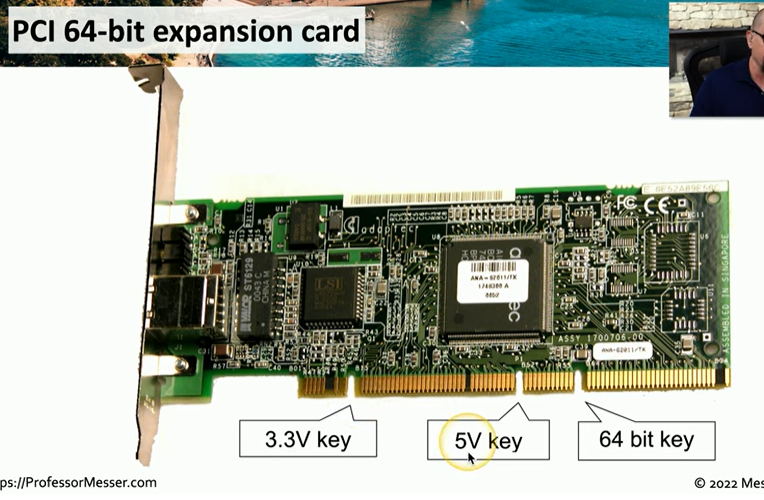
PCI expansion cards come with different widths and voltage options (3.3V and 5V).
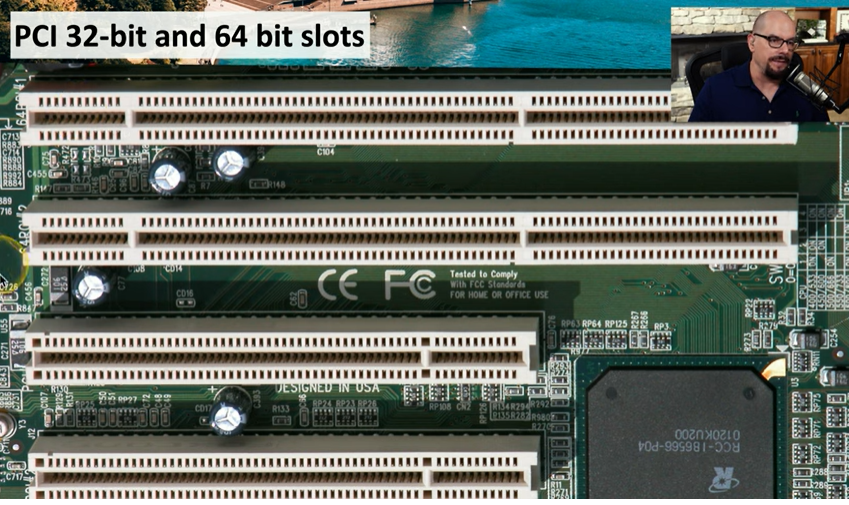
Physical Characteristics of PCI Slots
32-bit vs. 64-bit PCI Slots:
64-bit PCI slots are larger and can transfer twice the data of 32-bit slots.
Voltage Compatibility: Cards carry indicators for voltage capability.
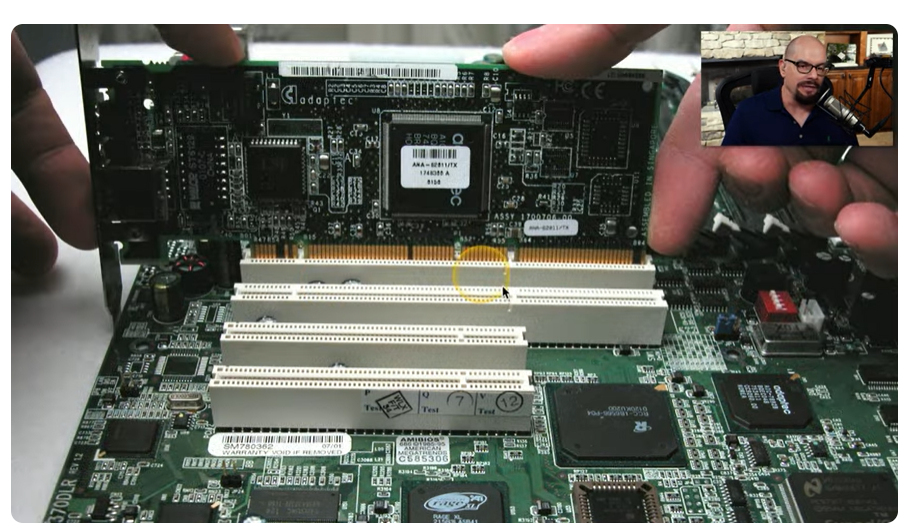
Installing PCI Cards
Mounting Process:
Insert PCI card into the correct slot, ensuring copper contacts are aligned.
Secure the card using a screw connection.

Transition to PCI Express (PCIe)
Overview of PCIe:
Replaces PCI with a serial connection instead of parallel.
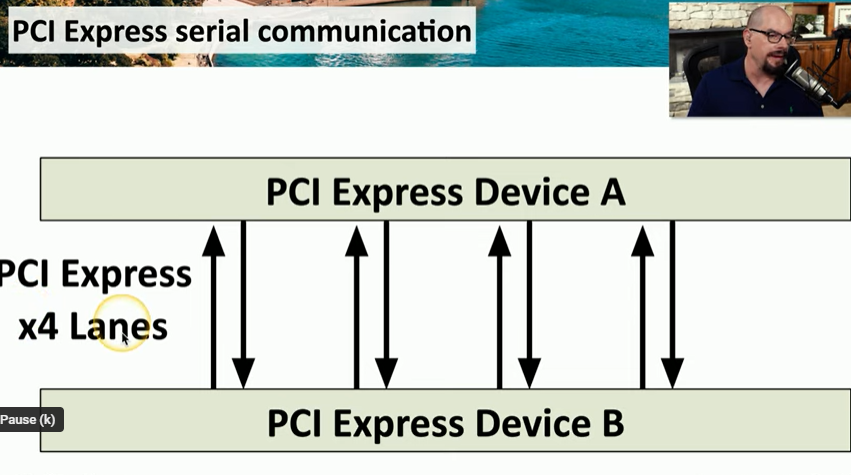
Features lanes used for communication (x1, x2, x4, x8, x16).
Bandwidth Capacity: More lanes provide higher data transfer capabilities.
PCI Express Characteristics
Communication Paths: Each PCIe lane has a bidirectional path for data.
Expansion Slots: Different sizes accommodate various data transfer needs.
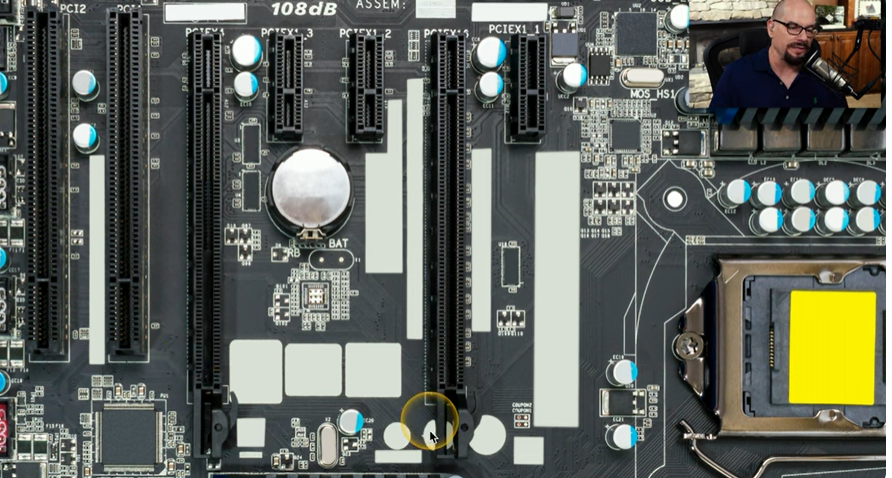
Combined Motherboard Support
Motherboard Design: Supports both PCI and PCIe slots for flexibility in expansion options.
Installation Process for PCIe Cards:
Align the card with the slot's hook first, then gently push down.
If misaligned, remove and reinsert.
Secure in place once properly installed.