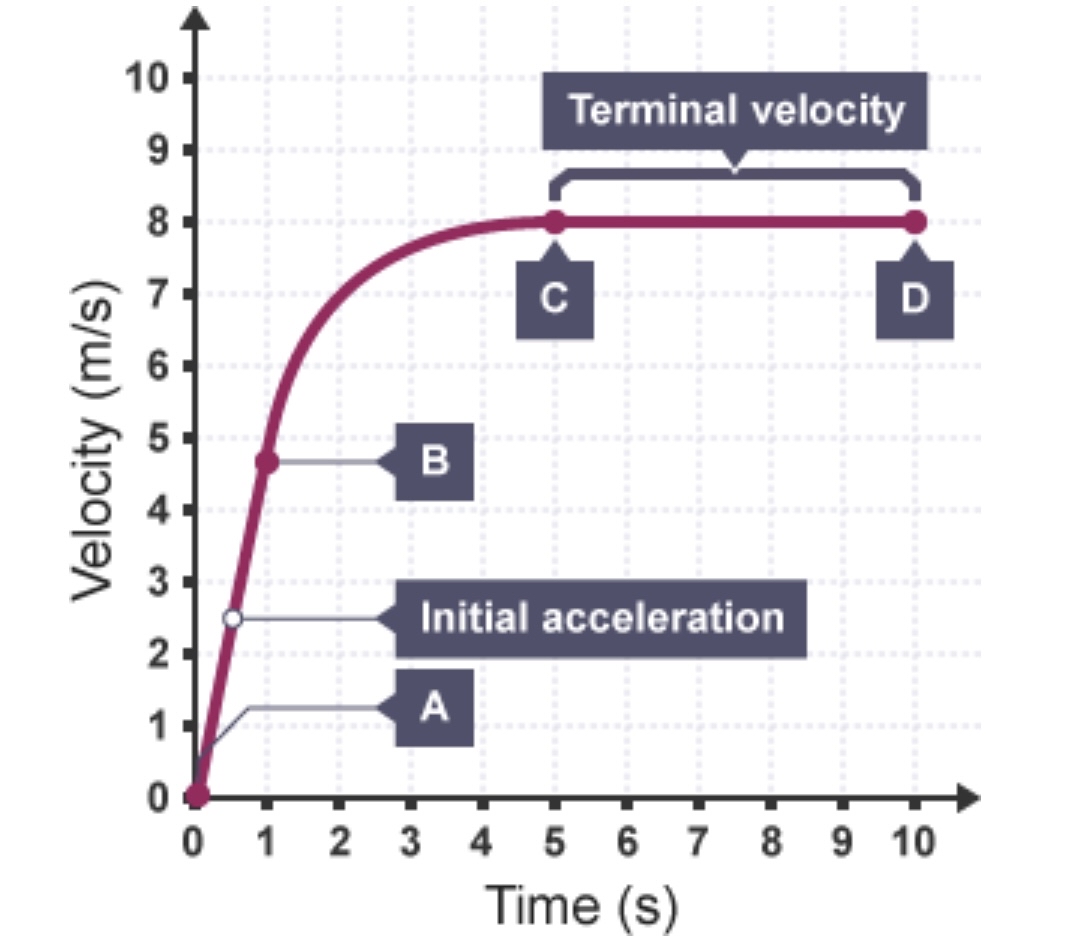
b) Terminal velocity
c) motion of objects falling in a uniform gravitational field in the presence of drag
di) terminal velocity
when an object travels through a fluid it will eventually reach terminal velocity
terminal velocity = the constant speed an object experiences under drag through a fluid
the instant it begins to fall
v = 0
D = 0
a = g
F = mg
falling → before it reaches terminal velocity
v = increasing
D = increasing
a < g → decreasing
a = F / m
F = mg - D
falling → once it reaches terminal velocity
v = constant
D = mg
a = 0
F = 0