1.8 - CompTIA A+ Core 2
1.8a - macOS Overview: Professor Messer
Installation and uninstallation of applications
File Types
.dmg: Apple Disk Image file - these files are commonly used for distributing software and can be opened by double-clicking, which mounts the image as a virtual disk in Finder (similar to a virtual disk).
. pkg: Installer package - used to distribute software, and executed via an installer script.
.app: Application bundle - contains the necessary files to use an application. Files are viewed via “View Package Contents” in Finder. When end-users double-click to access this application, the system unpacks the files within the .app bundle, allowing the software to launch and function as intended.
App Store
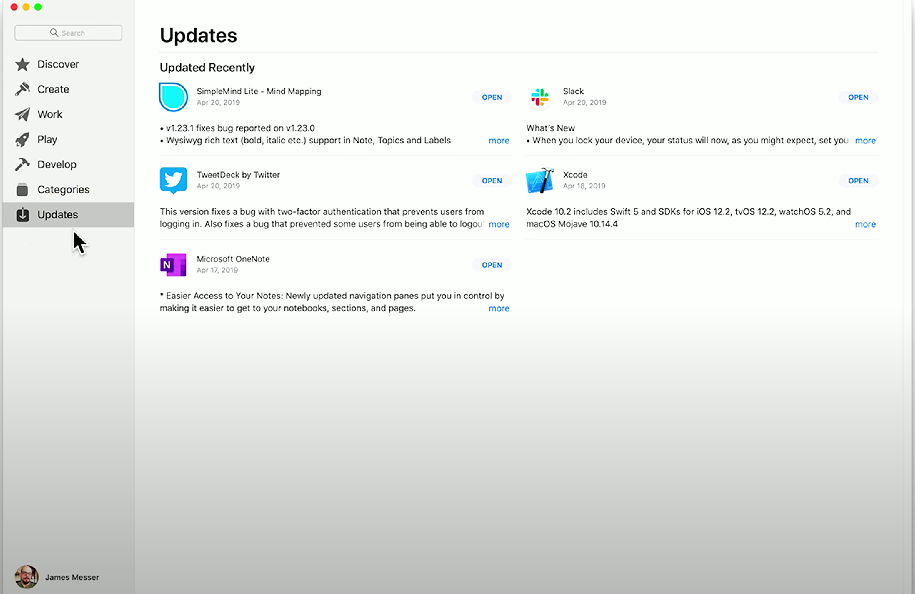
App Store: macOS app that provides centralized updates and patches for macOS applications. Applications can be automatically updated or updated manually.
Uninstallation process
Uninstallation process for macOS: Move the .app file to the Trash - this contains all the application’s files and removes the application. Some applications have a dedicated uninstall program, usually included in the Applications folder (/Applications).
System folders
/Applications

/Applications: macOS folder that houses all the applications you’ve installed on macOS (similar toC:\Program FilesWindows). Applications are displayed as bundles/folders - deleting the folder deletes the application and all its data.
/Users
/Users: macOS folder that stores documents created by each user. Folders for a particular user match the person’s username.
/Library
/Library: macOS folder that supports files, scripts, and applications for system-wide functionality and software installations.
/Users/Library
~/Library: macOS folder that provides the same functionality as the/Libraryfolder, but stores files for a specific user. The tilde (~) refers to the user’s home directory (i.e.,/Users/Professor/Library). This data shouldn’t be directly accessed (hidden), but can be accessed for troubleshooting purposes.
/System
/System: Stores operating system files - similar to the \Windows directory.
Apple ID and corporate restrictions
Apple ID: Account used to sync data and digital purchases across Apple devices - an application purchased on one device is available to multiple Apple Devices owned by the user.
Apple ID (corporate): Companies manage Apple IDs via Apple Business Manager, which integrates with Active Directory and Mobile Device Manager (MDM) software, assigns apps, and moves digital content to selected users.
Best practices
Backups
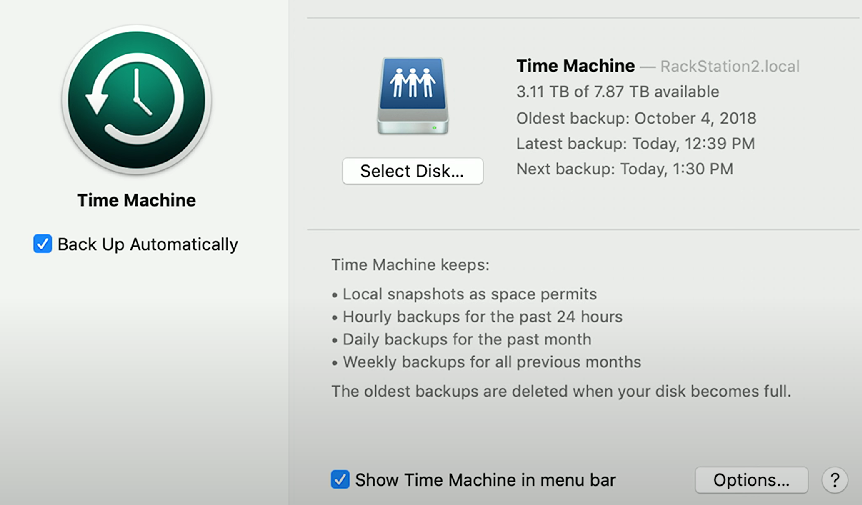
Time Machine: macOS app that provides hourly backups of files (for the past 24 hours), daily backups (in the past month), and weekly backups (for previous months). Time Machine deletes backups when the data is complete, starting from the oldest backups.
Antivirus
macOS does not include a dedicated antivirus or anti-malware application. However, many 3rd party options are available.
Most viruses target Windows. However, an increasing number of viruses are designed to harm macOS. The likelihood of malware creation (related to macOS) is linked to the high user base of Windows compared to macOS.
If you’re using third-party software, update AV signatures regularly (hourly/daily).
Updates/patches
Accessible via System Settings → General → Software Updates
Separate from the App Store - it is designed for the operating system.
Users can install beta updates (unreleased updates from Apple) - not a good best practice, but valuable for lab testing.
Rapid Security Response (RSR)
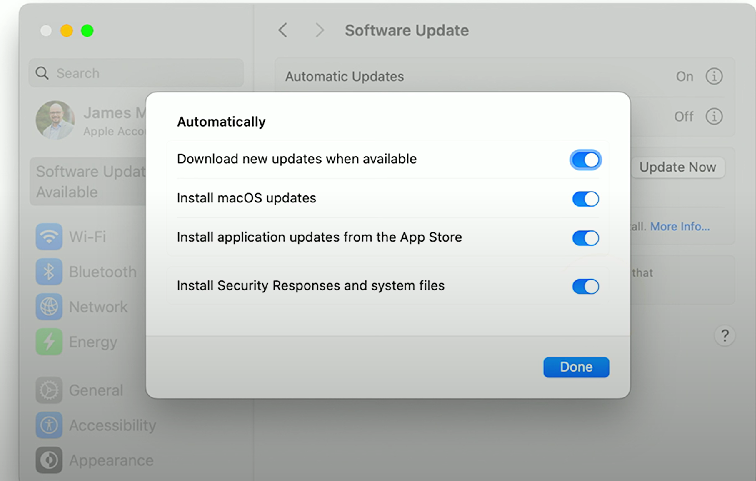
Rapid Security Response (RSR): macOS/iOS/iPadOS patches to combat zero-day exploits. It can be turned on or off in System settings. After these are installed, the macOS version number includes a letter (e.g., macOS 13.3.1 (a)).
1.8b - macOS System Preferences: Professor Messer
System Settings
System Preferences: macOS version of the Windows Control Panel - allows access to most customization and personalization options for the operating system.
Displays
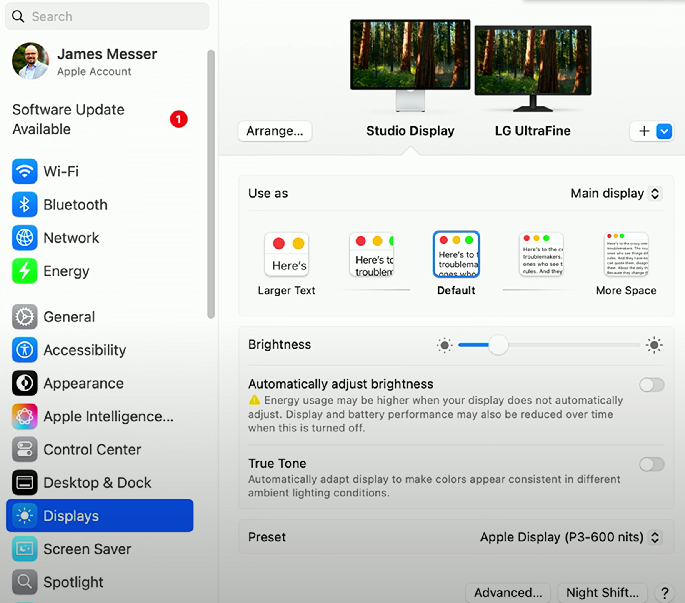
Displays: Controls what is shown on monitors/displays. Provides settings for resolution, text display, brightness, and colors.
Networks
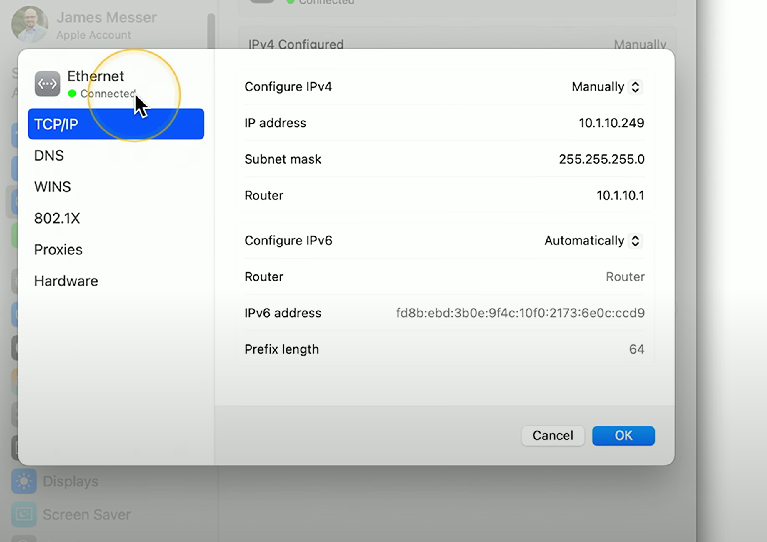
Networks: Allows configuration for wired/wireless network interfaces, IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, and detailed network settings (DNS, DHCP, 802.1X, etc.)
Printers & Scanners
Printers & Scanners: macOS settings allow users to add/remove printers, share printers/scanners, configure print permissions, and view ink/toner levels.
Privacy & Security
Privacy & Security: Limits application access to private data and protects user credentials.
Accessibility
Accessibility: Provides tools and features that assist users with disabilities, ensuring everyone has equal access to the operating system and its applications, such as VoiceOver, Zoom, and other assistive technologies.
It also limits third-party applications - no one can control the keyboard/mouse without permission.
Time Machine
Time Machine: A built-in backup feature for macOS that automatically backs up the entire system, allowing users to easily restore files and applications from previous versions.
Configuration settings can be accessed within System Preferences: General → Time Machine
1.8c - macOS Features: Professor Messer
Features
Multiple desktops (Spaces)
Spaces: macOS feature for creating multiple desktops - accessible via Mission Control. Allows users to organize workflow by splitting applications between desktops.
Mission Control
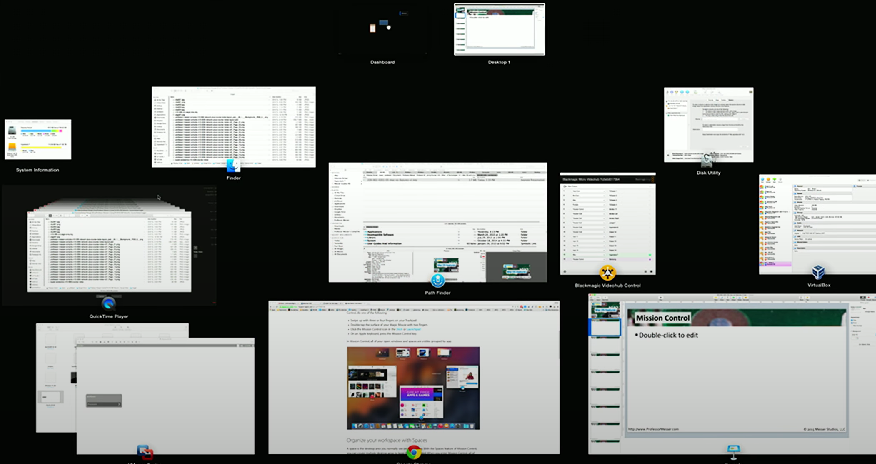
Mission Control: A macOS feature that allows users to view all running applications in a single viewable area. Accessible by swiping upwards with three fingers (trackpad) or
Ctrl + Up arrow (↑)
Keychain
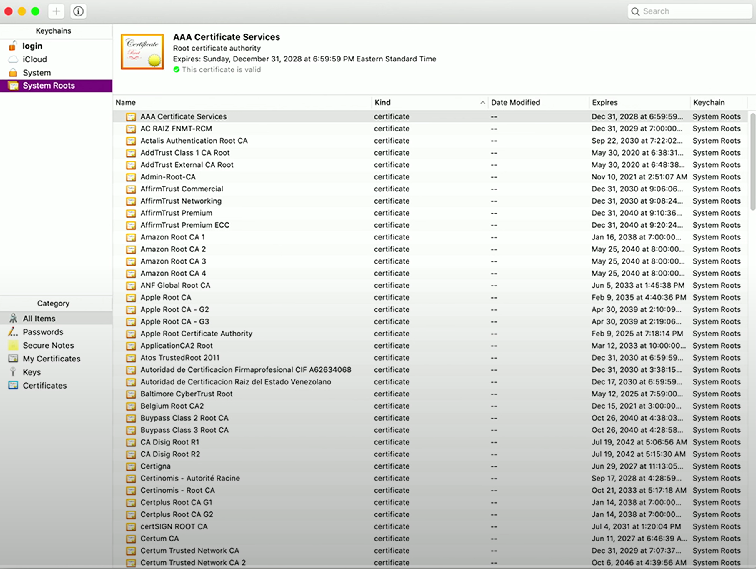
Keychain: Integrated macOS feature that allows storage of secure passwords, notes, and digital certificates. Passwords and secure notes are encrypted and can only be decrypted with the user’s password.
Spotlight

Spotlight: macOS search utility that allows users to find apps, files, and images. Accessible via the Magnifying glass in the upper right corner, or
Cmd + Space. Users can define search categories (i.e., what Spotlight can/can’t look through) in System Preferences → Spotlight.
iCloud
iCloud: Apple cloud storage service integrating files, passwords, notes, messages, etc. across multiple Apple OSs.
iMessage: Service responsible for sending messages between different Apple OSs - iMessage is the service, Messages is the app.
FaceTime: Apple’s audio/video conferencing app.
Drive: Apple’s file storage service, allowing users to store and sync files and documents across devices within the Apple ecosystem.
Gestures
Gestures: Allows users to use specific movements on a trackpad to trigger actions (e.g., swiping down with three fingers = Mission Control).
Can be enabled/disbaled/configured via System Preferences → Trackpad
Finder
Finder: Centralized macOS file management frontend - offers launching, deleting, and renaming files, along with file servers, remote storage, and screen sharing.
Dock
Dock: The Dock provides quick access to frequently used applications, documents, and minimized windows, allowing for easy navigation and organization of workspace.
Continuity
Continuity: A feature that allows seamless integration between macOS and iOS devices, enabling users to start a task on one device and continue it on another, enhancing productivity and convenience. Feature provided via iCloud.
Can be used to share resoruces across operating systems (e.g., using an iPhone as a Mac webcam, Airdropping files).
Disk Utility
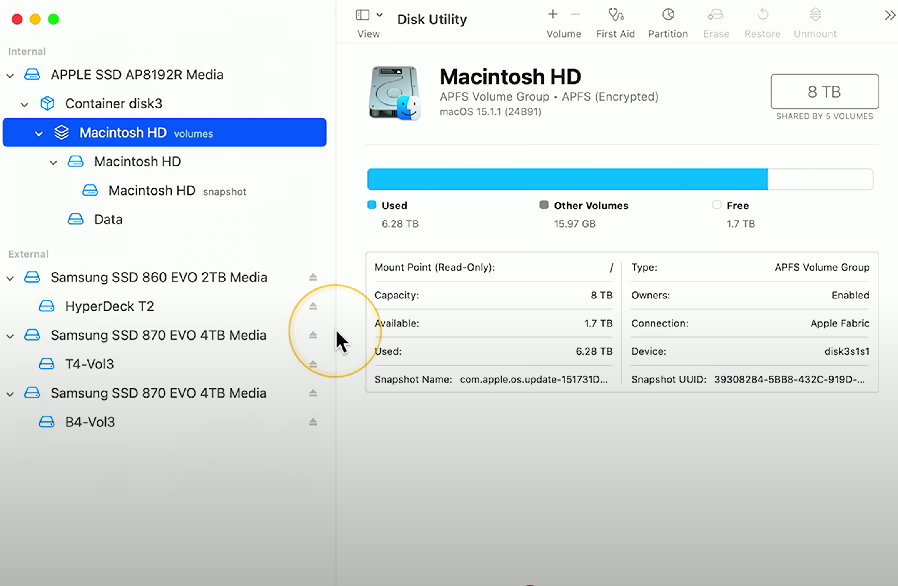
Disk Utility: A management utility for storage disks in macOS - allows modifications for file systems, partitioning disks, erasing disks, and creating/cloning disk images.
FileVault
FileVault: Provides full disk encryption (FDE) for macOS. Decryption requires a local key or iCloud authentication. Configuration is managed via System Preferences → Privacy & Security → FileVault
Terminal
Terminal: Command-line for macOS - allows for OS management without a GUI. Allows running scripts, managing files, or OS/application configuration.
Force Quit
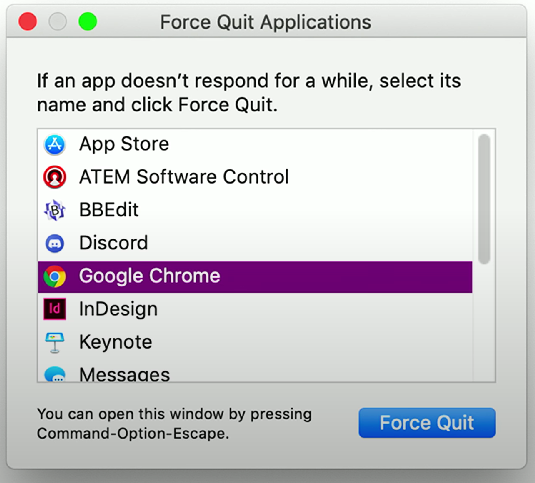
Force Quit: A feature that enables users to terminate unresponsive applications by using the keyboard shortcut
Command + Option + Escapeor through the Apple menu.