Creating a Constitution
A New Nation
The war for American Independence ended in 1783.
Many predicted that the new nation would collapse.
Leaders in the United States avoided the nation’s collapse by creating an entirely new system of government. They wrote the Constitution of the United States.
The Articles of Confederation
At first, the United States operated under the Articles of Confederation.
No Man in the United States is, or can be more deeply impressed with the necessity of a reform in our present Confederation than myself
Congress lacked the power to:
raise money
regulate trade
conduct foreign affairs
Changing the Articles required the approval of all thirteen states.
New Compromises
A Grand Convention
National leaders became concerned that the Articles of Confederation were not working.
Shay’s Rebellion provided the final push to revise the Articles
The Grand Convention was called for in May 1787.
The Grand Convention became the Constitutional Convention.

Big Decisions in Philadelphia
The delegates had to decide whether:
Congress should be made up of one house or two
every state should have the same number of representatives
representation should be based on a state’s population
The Virginia Plan
The delegates proposed two plans for a Congress.
The first was the Virginia Plan, which:
proposed representation based on population
proposed a bicameral (two-house) Congress.
was supported by large and growing states
The New Jersey Plan
The second plan was the New Jersey Plan, which:
proposed a unicameral (one-house) Congress
proposed that every state have the same number of representatives
was supposed by small states
The First Compromise
The issue of representation in Congress was the most difficult challenge.

The House of Representatives
The Great Compromise said that representation in the House of Representatives would be based on population.
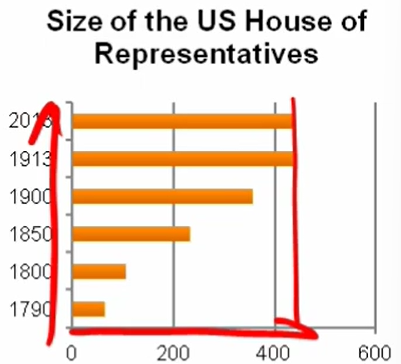
At first, the House had 64 members
Today, it has 435 members
The Importance of a Number
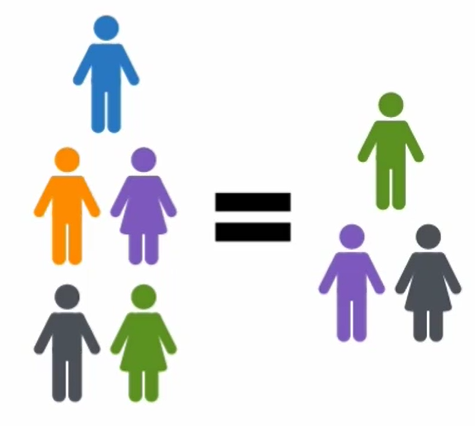
Another issue was how enslaved people should be counted in the population.
Southerners:
1 enslaved person = 1 person
Northerners:
1 enslaved person = 0 persons
If enslaved people were counted, Southern states had larger populations.
The Three-Fifths Compromise
With the question of the structure of Congress settled, the delegates moved on to another difficult question:
How should enslaved people be counted?
According to the Three-Fifths Compromise, each would be counted as three-fifths of a person.
Commerce and Slave Trade Compromise
Northern States | Southern States |
Give Congress the commerce power | Don’t give Congress the commerce power |
Allow Congress to regulate the slave trade | Don’t allow Congress to regulate the slave trade |
The Commerce and Slave Trade Compromise:
Congress would have the commerce power
Congress would not be allowed to regulate the slave trade until 1808
New Government
Government Structure
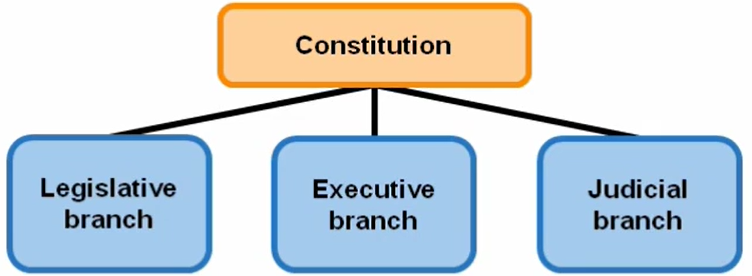
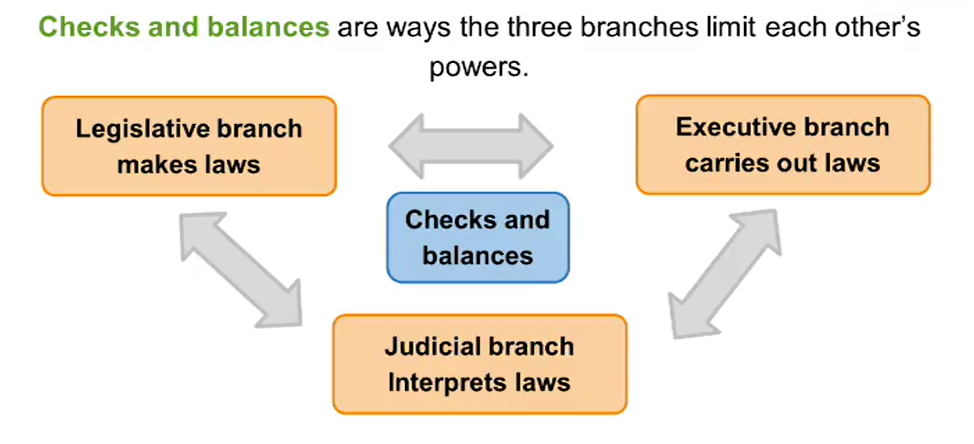
The Constitution organizes the federal government into three branches.
Article 1: The Legislative Branch
Article 1 established the legislative branch - Congress.
This branch creates laws.
Congress is made up of two houses, the Senate and the House of Representatives.
Senators serve six-year terms
Members of the House serve two-year terms
Article 2: The Executive Branch
Article 2 established the executive branch - the presidency.
The president represents the nation and creates policies.
The president’s responsibilities include:
taking care that “the Laws be faithfully executed”
serving as the head of state and commander-in-chief of the armed forces
appointing the heads of federal agencies
Article 3: The Judicial Branch
Article 3 established the judicial branch - the courts
This branch interprets the laws created by Congress and the actions of the President.
It is made up of a system of courts that includes:
One Supreme Court
Other courts created by Congress
All criminal trials must be decided by a jury of citizens.
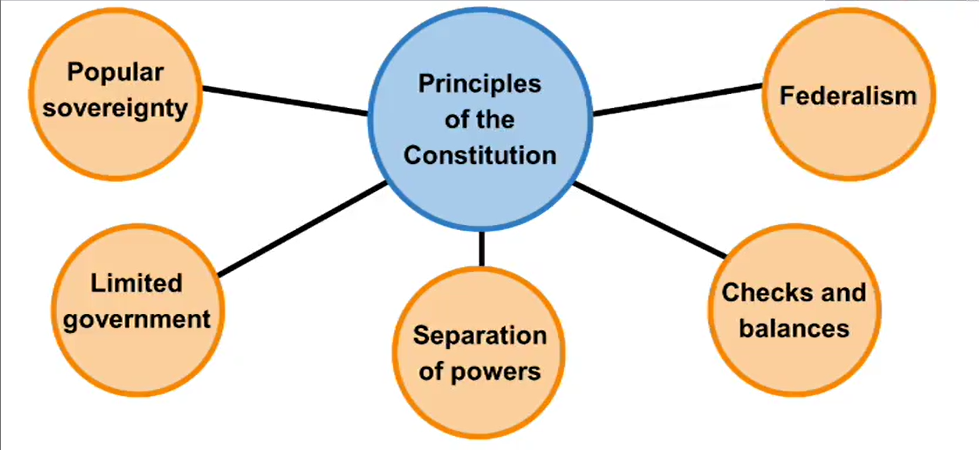
New Principles
Popular Sovereignty in the Preamble
The government receives its power from the people.
This is called popular sovereignty.
The people give the government power by voting for their representatives
Limited Government
The principle of limited government is that a government can only do what its people give it authority to do.
The people would give the government authority by ratifying the Constitution
The framers hoped to prevent tyranny by following this principle.
The Principle of Separation of Powers
Legislative Branch | Executive Branch | Judicial Branch |
Creates Law | Enforce Laws | Interprets Laws |
Collects taxes and regulates interstate commerce | Serves as commander-in-chief of the armed forces | Decides how the Constitution should be applied to new laws and situations |
The Constitution grants different powers to each branch of government.
Checks and Balances
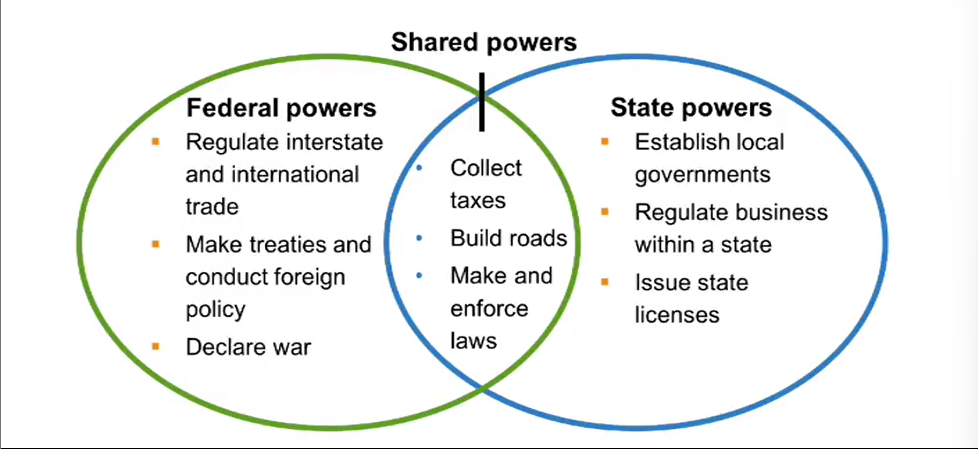
Federalism
 Knowt
Knowt