Reflection and Refraction
Reflection and Refraction
Mirrors Have Shiny Surfaces Which Reflect Light
1) A light wave is also known as a light a Light rays reflect off miss and 2) Mirrors have a very smooth shiny surface. The shiny surface
allows each light ray to reflect off it at the smal giving clear reflection. This is specular efection
3) Rough surfaces look dull, because the light is reflected back in lots of different directions (sceffered). This is diffuse.reflection (or diffuttering) 4) Learn the LAW OF REFLECTION:
ANGLE OF INCIDENCE ANGLE OF REFLECTION ANGLE I ANGLE
5) The angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are always measured between the light ray and the normal.
6) The normal is a line at a right angle (90°) to the surface.
Incident
This saray diagram Make sure you
draw straight lines and get the angles
Not shiny
fuse analer and a protractor)
Refraction is When Light Bends as it Crosses a Boundary
1) Light will travel through transparent (see-through) material. but it won't go through anything opaque (not see-through).
2) Any substance that light (or another wave, e.g. sound) travels through is called a medium- 3) When light travels from one transparent medium to another, it bends or refracts.
LEARN THESE
REAL GOOD:
The plural of
medium is media
When light goes from a LESS dense medium to a MORE dense medium: light bends TOWARDS THE NORMAL
When light goes from a MORE dense medium to a LESS dense medium: light bends AWAY FROM THE NORMAL
Light hitting a glass block is like a car hitting sand
1) Light hits the glass at an angle,
slows down and bends.
2) It's a bit like a car hitting sand at an angle. The right wheels get slowed down first and this turns the car to the right TOWARDS the normal.
3) Leaving the sand, the right wheel speeds up first and this turns the car to the left- AWAY from the normal.
4) If both wheels hit the sand together they slow down together, so the car goes straight through, WITHOUT TURNING.
E) Light does exactly the same when it hits the glass block straight on.
Example: air to glass-
Example: plass to sir.
Incident ray Normal
2
Ray bends towards the normal
Glass
1
This wheel slows first Car's direction
Normal
Refracted ray
Incident ray at 90° to glass
5
Glass
Not refracted
changes This wheel speeds up
This wheel continues to move fast The car travels slower on sand then farmac
8
Car's direction changes
3
0000
Wheels all slow, or speed up st the same time
4
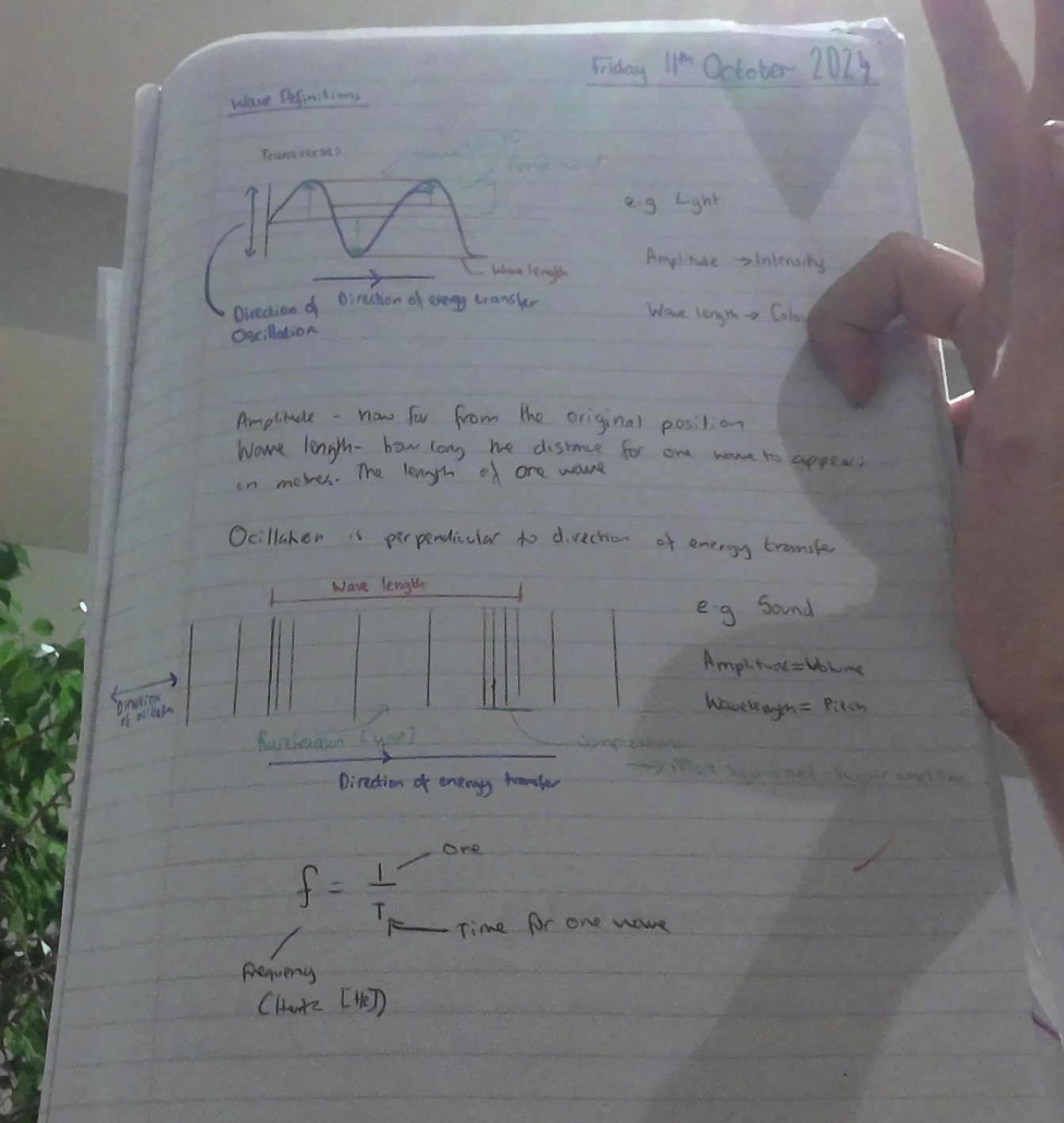

f=v/Lamda
Lamda=v/f
v=f x v