Chemistry - 1st Semester Final Review - 2024.docx
Chemistry - 1st Semester Final Review - 2024
Unit 1: Lab Safety & Introduction to Chemistry
- Safety rules for working in the lab.
- Common lab equipment pictures/names
- GHS pictograms
- Key terms:
- Matter
- Chemistry
- Worldview
- Hypothesis
Unit 2: Matter
- Know the following terms: (also list examples for the ones with an *)
- Physical property*
- Physical change*
- Chemical property*
- Chemical change*
- Atom
- Pure substance
- Element*
- Compound*
- Mixture
- Homogeneous Mixture*
- Heterogeneous Mixture*
- Know the difference between:
- Monatomic elements
- Diatomic elements
- Draw particle diagrams for each of the following Pure Substances:
- Elements (monoatomic & diatomic) Compounds
![]()
![]()
![]()
- Describe solids, liquids, and gases (be specific about how the particles are arranged.)
- Be able to recognize the difference in solids, liquids and gases in particle diagrams.
- Phase changes: (know definitions and particle diagrams)
- Melting
- Freezing
- Condensing
- Evaporation
- Sublimation
- Deposition
Practice Questions:
Use the particle diagrams at the right to answer the following questions:
- Which of the particle diagrams is a pure substance made up of a compound? ________
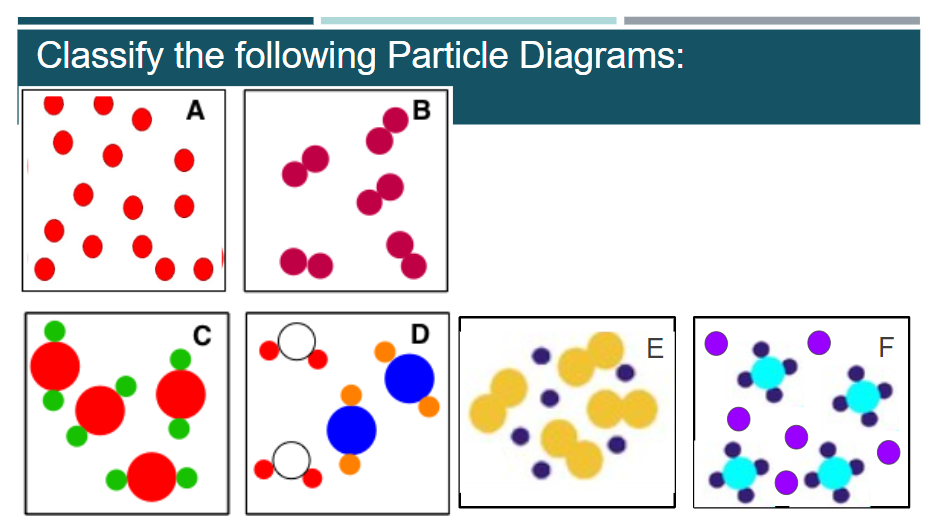
- Which of the particle diagrams is a mixture of a compound and a monatomic element? _______
- Which of the particle diagrams is a pure substance made up of a diatomic element? ______
- Which of the particle diagrams is a mixture made up of a monatomic element and a diatomic element? ______
- Which of the particle diagrams is a pure substance made up of a monatomic element? ______
- Which of the particle diagrams is a mixture of 2 different compounds? ______
- Put the correct term in the blank to describe the phase changes represented in this image at the right:
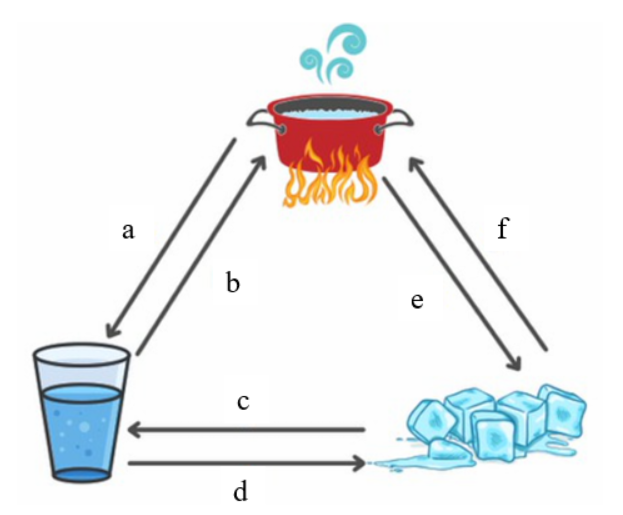
- ____________________________
- ____________________________
- ____________________________
- ____________________________
- ____________________________
- ____________________________
- List the name of the phase change represented by each of the following particle diagrams:
- Temperature Conversions: (you will be given these equations on the test)
TF = TC + 32 TC = (TF – 32) TC = TK - 273.15 TK = TC + 273.15
- Carbon dioxide freezes at -78°C. What is this temperature in Kelvin?
- A temperature of 74 degrees Celsius is what temperature in degrees Fahrenheit?
- Convert 175°F into °C.

- Convert 202.5°C into Kelvin.
- Convert 348.5 K to °C.
- 88.4 K is what temperature in °F?
Unit 3: Measurements in Chemistry
- Key Terms:
- Significant Figures
- Accuracy

- Precision
- Density
- Measurements Practice:
- Use the graduated cylinder at the right to answer the following:
- What is the change in the large scale? ________ mL
- What is the change in the small scale? ________ mL
- To what precision can you report your measurement? +/-_______ mL
- What is the measurement? ______ +/- ______ mL
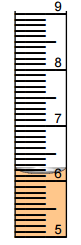
- Use the graduated cylinder at the right to answer the following:
- What is the change in the large scale? ________ mL
- What is the change in the small scale? ________ mL
- To what precision can you report your measurement? +/-_______ mL
- What is the measurement? ______ +/- ______ mL
- Use the ruler at the right to answer the following:
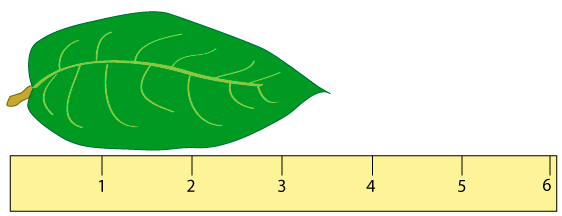
- What is the change in the large scale? ________ cm
- What is the change in the small scale? ________ cm
- To what precision can you report your measurement? +/-______ cm
- What is the measurement? ______ +/- ______ cm
- How many Significant Figures are in each of the following? (Assume they are all measurements. Units have been left off for simplicity.)
_______ 18) 49.568 _______ 23) 10,050 ______ 28) 1.80 x 10–5
_______ 19) 104.07 _______ 24) 11.0 ______ 29) 100.050
_______ 20) 450. _______ 25) 0.0010 ______ 30) 4.72 x 10-4
_______ 21) 0.000563 _______ 26) 0.05060 ______ 31) 607
_______ 22) 25,000 _______ 27) 5.630 x 108 ______ 32) 42.50
- Rounding with Significant Figures
_________________ 33) Round 68.45 to 3 significant figures
_________________ 34) Round 0.005043 to 1 significant figure
_________________ 35) Round 103.6780 to 5 significant figures
_________________ 36) Round 3550 to 2 significant figures
_________________ 37) Round 0.60081 to 3 significant figures
- Operations with Significant Figures
- Remember the Significant figure rules are different for addition/subtraction and multiplication/division.
- Addition/Subtraction - Answer is reported to the same number of decimal places as the measurement with the least number of decimal places.
- Multiplication/Division - Answer is reported to the same number of significant figures as the measurement with the least number of sig. figs.
- Remember the Significant figure rules are different for addition/subtraction and multiplication/division.
Consider all of the following values to represent measurements. Typically, these types of values will be accompanied by the unit of measure. We will ignore units for now to avoid confusion.
Calculator Answer Final Answer with correct
number of Sig Figs
38) 3.08 + 5.2 _______________ _______________
39) 6.54 - 0.37 _______________ _______________
40) 724 + 22.2 _______________ _______________
41) 0.085 x 0.050 x 0.655 _______________ _______________
42) 2.6 / 3.78 _______________ _______________
43) 39 / 24.2 _______________ _______________
44) 3.15 x 2.5 x 4.00 _______________ _______________
45) 752.97 / 0.0062 _______________ _______________
- Calculating percent error:

- Use significant figures rules for all parts of the equation and
express your answer with the correct number of significant figures.
- A student measured the volume of a liquid to be 255.89 mL. The actual volume was 275.0 mL. What was the student’s percent error?
- A standard mass of 250.0 g was placed on a balance. The balance said it had a mass of 243.9 g. What is the balance’s percent error?
- Joe extracted 2.75 g of iron filings from his mixture sample in the chemistry lab. The teacher told him that he should have been able to extract 2.895 grams. What is Joe’s percent error?
Unit 4: Atomic Structure
- Know how the model of the atom changed throughout history and the scientists (and their experiments) that are responsible for the development for these different models.
- List the 3 subatomic particles and the charge of each.
- Which 2 subatomic particles are located in the nucleus?
- Where are the electrons located?
- What are isotopes?
- Distinguish between atomic mass and mass number.
- What are ions?
- What is a cation? How does an element become a cation?
- What is an anion? How does an element become an anion?
- Using the periodic table, fill in the chart below:
Element | Symbol | Atomic # | Atomic Mass | Mass # (of most common isotope) | # p+ | # n | # e- |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Sodium | |||||||
Titanium | |||||||
Chlorine | |||||||
Phosphorus | |||||||
Copper | |||||||
Gold |
- Identify the number of subatomic particles and the isotope name for each isotope:
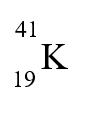
![]()
![]()
# p = _________ # p = _________
# n = _________ # n = _________
# e = _________ # e = _________
Isotope Name: ___________________ Isotope Name: _____________________