SCIQ4G9
Hydrocarbon Derivatives
Alcohol Hydroxyl Functional group
Oxygen atom bonded to a hydrogen atom
Formula: CnH2n+OH
Hydroxyls are often written as OH on structures and chemical formulas
Alcohols are polar.
In chemical reactions, alcohols often cannot leave the molecule on their own; to leave, they often become protonated to water, which is a better-leaving group. Alcohols also can become deprotonated in the presence of a strong base.
Protonation: the addition or transfer of protons to a Bronsted Lowry Base
Deprotonation: the removal or transfer of a Bronsted Lowry acid in an acid base reaction
Bronsted Lowry Theory of Acids and Bases
also called proton theory of acids and bases
introduced independently in 1923 by the Chemist Johannes Nicolaus Bronsted and Thomas Martin Lowry
states that any compound that can transfer a proton to any other compound is an acid, and the compound that accepts the proton is a base.
proton is a nuclear particle with a unit positive electrical charge; it is represented by the symbol H+ because it constitutes the nucleus of a hydrogen atom.
Uses of Alcohols:
found in beverages, anti septics, and fuels
can be used as preservatives for specimens in science
Methanol
“wood alcohol”
fuel at Indianapolis 500
common industrial solvent
toxic dose: 100ml
Ethanol
fermentation of sugar and starches in grains
produces “hard liquors”
denatured alc is used as solvent
Gasahol: 10% alcohol in gasoline
Toxic dose: 200ml
2-Propanol=”Rubbing alcohol”
Ether Functional Group
consists of an oxygen atom forming a bridge between two different parts of a molecule
Formula: ROR
non polar because of the presence of an alkyl group
more polar than alkenes. Have low chemical reactivity
Uses of Ether
Dimethyl Ether is used as a refrigerant and as a solvent
Diethyl ether is a common ingredient in anesthesia. Common solvent for oils , resins, etc.
Ether is used along with petrol as a motor fuel
Phenyl ether can be used as a heat transfer medium
Aldehyde Functional Group
made up of carbon and oxygen double bonded together
Formula: R-COH
Uses of Aldehyde
Formaldehyde is used for preservation of biological specimen, embalming, etc.
used for drug testing and photography
can be used in perfumes, dyes, cosmetic products, production of acetic acid
Ketone Functional Group
a carbon atom double bonded to an oxygen atom that appears as a bridge
carbonyl functional group
Formula R-COR
Uses of Ketone
acetone. used as a nail paint thinner
Carboxylic Acid Functional Group
carboxyl functional group
substituent R is a hydrogen atom
Formula: R-COOH
Used as precursors to form other compounds such as esters, aldehydes, and ketones.
used in the production of polymers, pharmaceutical, solvent, and food additives
Important Acids:
Acetic acid is in vinegar and other foods
used industrially as solvent, catalyst, and reagent for synthesis
fatty acids from fats and oils.
Ester Functional Group
consisting of a carbonyl group connected to an ether group.
Formula: RCOOR
more polar than ethers. more volatile than carboxylic acids
soluble in water
Uses of Ester:
Fragrance and Flavor
known for their pleasant fruity or floral odor
scents in essential oils
medicine: asthma and leprosy
antioxidants
natural flavorings
food and drug preservatives
Amine Functional Group
derivatives of ammonia. where one or more of the hydrogen atoms are replaced by an alkyl or aryl functional group.
amines are found everywhere
used for gas treatment such as removing co2 from combustion gases
NH3
Dopamine=neurotransmitters
epinephrine=adrenaline
histamin-dilates blood cells
Amide Functional Group
-combination of carbonyl and amine
Thiol Functional Group
similar to hydroxyl group except the oxygen atom in the hydroxyl group is a sulfur atom.
also known as sulfhydryl functional group.
Formula: -SH
Uses of Thiol Group:
Covid 19 treatment
catheters and vascular stents
skunk smell
many thiols resemble the scent of onions and garlic
Phenyl Functional Group
benzene ring where one hydrogen atom is replaced by the R substituent group.
often denoted by the abbreviation Ph in structures in formulas
have formula: C6H5
VOLCANOES
Volcano
A hill, mountain, or fissure from which molten rocks, hot gasses and ashes are ejected.
Crater formed by the removal of pre-existing materials, or a hill, or a mountain formed from the accumulation of ejected materials.
Volcanism
♡It happens when underground molten rocks called magma find a path through the lithosphere
♡Lithosphere is Earth's rigid outer part, made up of crust and upper mantle
Why does magma rise to the Earth's surface
・❥・Since molten rocks are less dense thwn the surrounding solid rocks they have a natural tendency to rise
・❥・ A magma chamber may be squeezed by tectonic forces, creating pressure that pushes the magma upwards
Magma
✎ It is an important material in volcanism
✎The type of magma ejected onto the Earth’s surface influences both the formation and eruption of volcanoes
Properties of magma
✿Viscosity
It is the resistance of a fluid to flow.
The more viscous a material is, the greater its resistance to flow.
High-viscosity magma flows more slowly than low-viscosity magma does.
✿Content
It is the small quantities of volatile elements or compounds where magma’s viscosity depends on.(Silica)
TYPES OF MAGMA
80% of these volcanoes are formed through Convergent Boundaries
15% are formed by Divergent Boundaries
5% are formed by hotspots
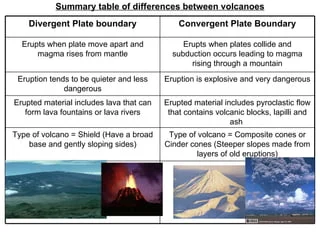
Convergent boundaries have plates that move toward each other
Divergent boundaries have plates that move away from each other
a hotspot is an area of the Earth's mantle from which hot plumes rise upward, forming volcanoes on the overlying crust.
Three different types of volcanoes:
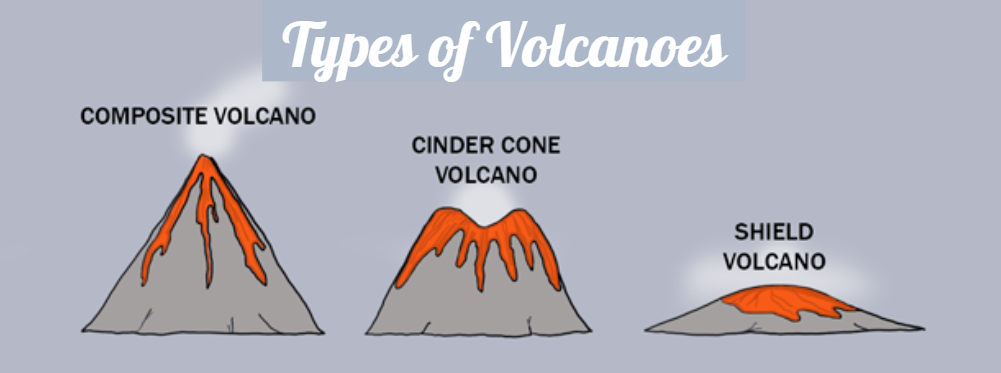
Stratovolcano or Composite Volcano:
Produced when lava of andesitic composition flows out over a long time.
Ejects pyroclastic materials that fall near the summit. This builds a steep-sided mound of cinders.
The mount is built of altering layers of lava and pyroclastic materials
example: Mt. Mayon, Mt. Pinatubo
Cindercone Volcanoes
Built from ejected lava fragments
Mainly composed of tephra and cinders.
They are small, 300 m high, and are formed near or inside large volcanoes.
The most abundant type of volcano.
ex: Smith Volcano
Tephra-airborne pyroclastic material ejected in an eruption
Fumarole-openings in the Earth’s surface that emits steam
Shield Volcano
Formed by basaltic lava flow.
Since basaltic lava is free to flow, the volcanoes formed have very wide base and are slightly domed.
ex: Mauna Loa(Hawaii)
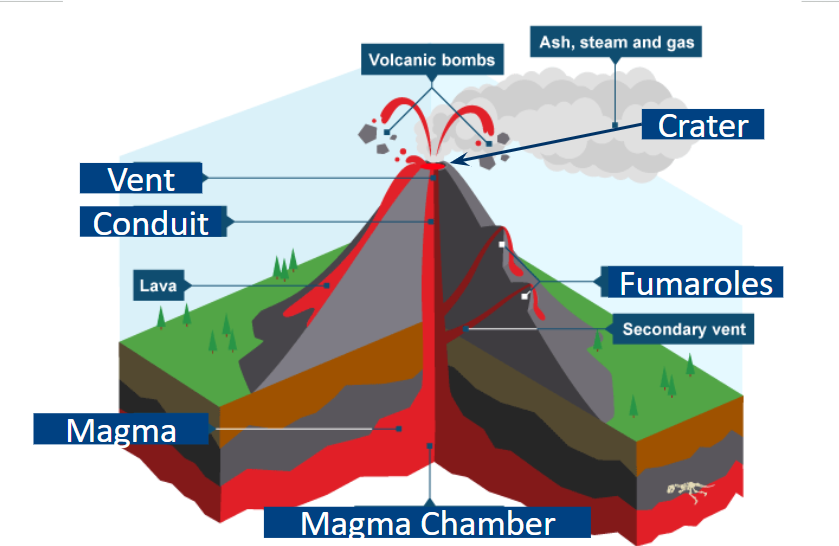
Parts of a Volcano:
Vent-central opening.
craters-circular depression connected to the vent
conduit-passage in the volcano where magma passes through
fumaroles-secondary vents emits steam and gases
caldera- larger depressions. believed to happen when the summit(peak) of a volcano collapses
Magma Chamber-large pool of magma beneath the Earth’s surface
PHIVOLCS: Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology
Active Volcanoes:
has erupted within 600-10k years ago
ex: Mt. Mayon, Mt. Bulusan
Inactive Volcanoes:
no record of eruption
some may erupt with little to no warning
ex: Mt. Batulao, Alligator Lake
Volcanic Materials
Pyroclastic flow
Fast movement of a turbulent mass of fragmental volcanic materials(ash, volcanic materials). Can reach more than 60 mph
Lava flow
Stream-like flow of incandescent, molten rock materials erupted
from a volcano.
Ash fall
Shower of grained volcanic materials and other airborne volcanic materials from an eruption
can cause respiratory problems if inhaled for long durations of time
Lahar
Rapid-flow of a mixture of volcanic materials and water, usually generated
along river channels by extreme rainfall.
Volcanic gases are harmful to the health because of the different chemicals that come out of it in an eruption
Benefits:
sources of minerals and building materials
beneficial to agriculture
geothermal energy
Climate Change
Weather
changes in the condition of the atmosphere at a particular place over a short period of time.
Climate
average weather of a region over a several years
PAGASA-Philippine Atmospheric Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration
Climatology
the study of atmosphere and weather
Factors affecting weather
Atmospheric temperature
describes how cold or hot the surrounding air in a place is
Atmospheric pressure
the force per unit area exerted by air due to its weight
Wind
the natural movement of air in the atmosphere caused by variations in air pressure
wind speed is the measure of how fast air is moving
wind direction describes where wind originated and the direction it is blowing
Precipitation
condensed water vapor that falls to Earth’s surface
Relative Humidity
indicates the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere
Factors affecting climate
Latitude
distance from the equator. It is horizontal
Altitude
vertical elevation or distance above sea level. As Altitude increases, temperature decreases
Distance from the sea
distance affects climate. Coastal areas are colder
Ocean Current Circulation
redistributes large amounts of heat all over the earth through ocean currents and deep ocean tunnels
Prevailing winds
it is affected by the dominant wind system or prevailing winds. Moves in 1 direction
Topography
arrangement of the surface features of a place.
mountains and volcanoes act as natural barriers to prevent air from passing through
Global Climate Phenomena
Global Warming
both a natural and human-induced increase in the average global climates
linked to an increase in carbon dioxide
Types of climates:
Tropical - Hot and humid. 2 seasons. near the equator(Philippines)
arid/desert - dry areas. rarely experiences rainfall(ex: Sahara Desert)
temperate - normal temperature. 4 seasons(America, Germany, Japan)
continental - Cold winters hot summers. Inland(Sweden, Russia)
polar/alpine - freezing areas of the Earth(ex: North, South Pole)
Stars and Constellations
Universe
made up of anything in space
was created over 13 billion years ago
made up of thousands of different galaxies
Stars
a large sphere of glowing dust and gases such as helium and hydrogen. The sun is a medium sized star.
they are formed when spinning balls of gas form inside large clouds of dust and gas
twinkle because light has to travel through Earth’s atmosphere. The light bends as it travels from star to Earth
Blue stars are the hottest, red stars are the coolest
The milky way
composed of billions of stars bound by gravity
large spiral galaxy that holds over 100 billions stars. has spiral arms and bright central bulge called nucleus(flat disk)
its disk is about 100k light years wide and 10k light years thick at the nucleus
a member of a cluster of about 25 galaxies known as the Local group
Astronomy
scientific study of everything in outer space
studies stars and galaxies
Astrology
based on the belief that the location of certain stars can predict the future.
Constellations
a group of stars that form a pattern or figure
the north star or “Polaris” is located directly above the North Pole. It appears in the same place every night all year long.
The Southern Hemisphere has 4 stars called the “Southern Cross”
ex: Orion, Ursa Minor, Ursa Major
Most stars rise in the east and set in the west during the night.
Celestial Sphere
an imaginary sphere of infinite radius with Earth at its center
Zenith
the point directly above you
Meridian
imaginary semi circle stretching from your horizon due south, through zenith, and due north
Asterism
a part of constellations but they aren’t constellations themselves
ex: Big Dipper
Orion the Hunter
named after a greek hunter.
it is one of the largest groups of stars in the sky
Taurus in the Northern Hemisphere. directly above Orion. Saw as a bull
Star Chart
a map of stars in the night sky
Projectile Motion
Law of Acceleration(2nd law)
force = mass x acceleration
Vector
-magnitude and direction
Scalar
-magnitude
Acceleration
the rate of change in velocity with time. It is a vector quantity
Circular motion
moves in a circle
If in circular motion, your direction of motion is constantly changing
Trajectory - it is the curved path followed by the projectile
Uniform Acceleration Motion(UAM)
a type of motion in which the velocity of an object changes
the value of the acceleration is constant. It does not change. The velocity changes at a constant rate.
An object with 0 acceleration is said to be in uniform motion
the vertical acceleration due to gravity is -9.8m2
objects at freefall also exhibit UAM.
Projectile Motion
combination of vertical motion(freefall) and horizontal motion(Uniform motion)
Horizontal Motion
x component
neglects air resistance
constant horizontal velocity
horizontal distance is defined as range(R or dx)
Vertical Motion
force of gravity
g=ay=ag or g =-9.8m/s²
vertical velocity is represented by vy is not constant
we call the vertical distance as height(h or dy)
Vx-horizontal velocity
Vix-initial horizontal velocity
Ax-horizontal acceleration
dx-range or horizontal distance
Vy-vertical velocity
Viy-initial vertical velocity
Ay-vertical acceleration
dy-vertical distance or height
Key components
θ-Initial Launch angle(theta)
T-time of flight
d- displacement
g- gravity
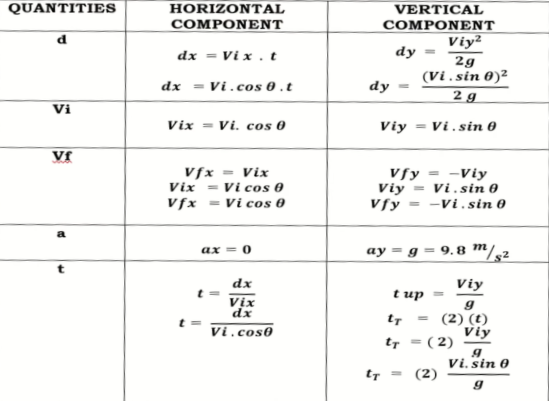
Projectile calculations
For projectiles launched horizontally:
Horizontal Distance
d=v(t)
Horizontal velocity
Vf= Vi+At
For projectiles launched vertically:
Vertical Distance
d=Vit+1/2 gt²
Vertical velocity
Vf=Vi+gt
Three common kinematic equations(horizontal motion)
x=Vix x t + 0.5 x Ax x t²
Vfx=Vix + Ax x t
Vfx²=Vix² + 2 x Ax x X
Three common kinematic equations(Vertical Motion)
y= Viy x t +0.5 x Ay x t²
Vfy= Viy + Ay x t
Vfy²= Viy² +2 x Ay x y
Angle Launched Projectile
objects projected at an angle to the horizontal
an object is projected from rest at an upward angle θ
Its initial velocity can be resolved with 2 components
the maximum range can be achieved when launched at 45 degrees
Formulas:
-