unit 2
Protected area - A place conserved by a set of rules
Gross domestic product(GDP)- The total value of all goods and services produced in a country in the year
Negative impacts- that affects the travel and tourism has on a place and/or local people
Biodiversity- The degree of Variation in living things
Ecosystem- The net worth of things between living things and the environment
2.1
Growth and travel and tourism has had economic, environmental, and social cultural impacts
Economic impacts- The effects travel and tourism has on money and jobs
Environmental impacts- The effects that travel and tourism has on the environment. impacts can be positive or negative
Sociocultural impacts- The effects that travel and tourism has on people and their way of life
Economic factors are affect tourism demands
economic factors-to do with moneyyy
Tourism demand- has much desire there is to travel to destinations
Ex: National governments of countries manage the factors that affect demand for tourism in their countries
Disposable income - The remaining parts of income after paying taxes and buying necessities
people having to spend on travel
Social
social factors affect tourism demand
Social factors- to do with people and communities
Demographic- facts about population including numbers, age ,and disposable income
demographics are affected by the outbound tourist from a country
Ex: some countries have increased retired people who have more leisure time to travel
Health awareness has increased demand for outdoor activities
Social consciousness- an awareness of other people and the difficulties they face in life
social media has increased consumer awareness
Socially sustainable tourism- minimizes the negative social impact and maximizes the positive social impacts of travel and tourism on a destination
Technological
Technological factors- to do with practical science applications and engineering
ex: more airports bigger and faster trains
develop information technology(IT) online booking and social media
Online booking - use of the Internet to reserve
ex: accommodation and transport
Social media - ways of sharing information using the Internet
Political
Political factors -to do with how the countries are governed and what can happen as a result
terrorism and war deter tourism
Political and instability reduce tourism
Safety concerns decreased travel demands
Travel restrictions to limit tourism
Factors- reasons that affect how things are and how things change
Environmental
Environmental factors-to do with nature and climate
Extreme weather(storms hurricanes and typhoons)
Natural disasters( earthquakes tsunami‘s volcanic eruption‘s)
Health
Health factors- to do with peoples health and with disease
Ex: cOVID-19 pandemic change the travel and tourism
Sustainable tourism is growing
helps the environment (protect nature)
Create jobs (local guides, eco lodges)
Protects culture( supporting local artisans )
Fits travel trends (people who want Authentic experience)
4 reasons why
Changing customers attitudes: tourism are increasingly concerned about the environmental and social impacts of tourism preferring sustainable options that protect local communities and the environment
Media influence: information about sustainable tourism widely discriminated throughout various media influence public opinions and promoting awareness. social media platforms facilitate the sharing of information and experience further amplifying the message
Availability and promotion of sustainable tourism product and service: The increased demand for sustainable tourism has led to a great supply of eco-friendly travel options. tourism providers actively promote these products and services to attract environmentally conscious tourist
Government policies: National government actively support sustainable tourism initiative because it’s generates economic benefits while protecting the environment in local cultures. they implement policies to encourage and regulate sustainable tourism practices
Directly employed- this means having a job in a travel and tourism organization
Green destinations- A status awarded by the green destinations foundation
Greening-making something environmentally sustainable
Value chain -The set of linked products and services on which tourists spend money to create income for a destination
2.2
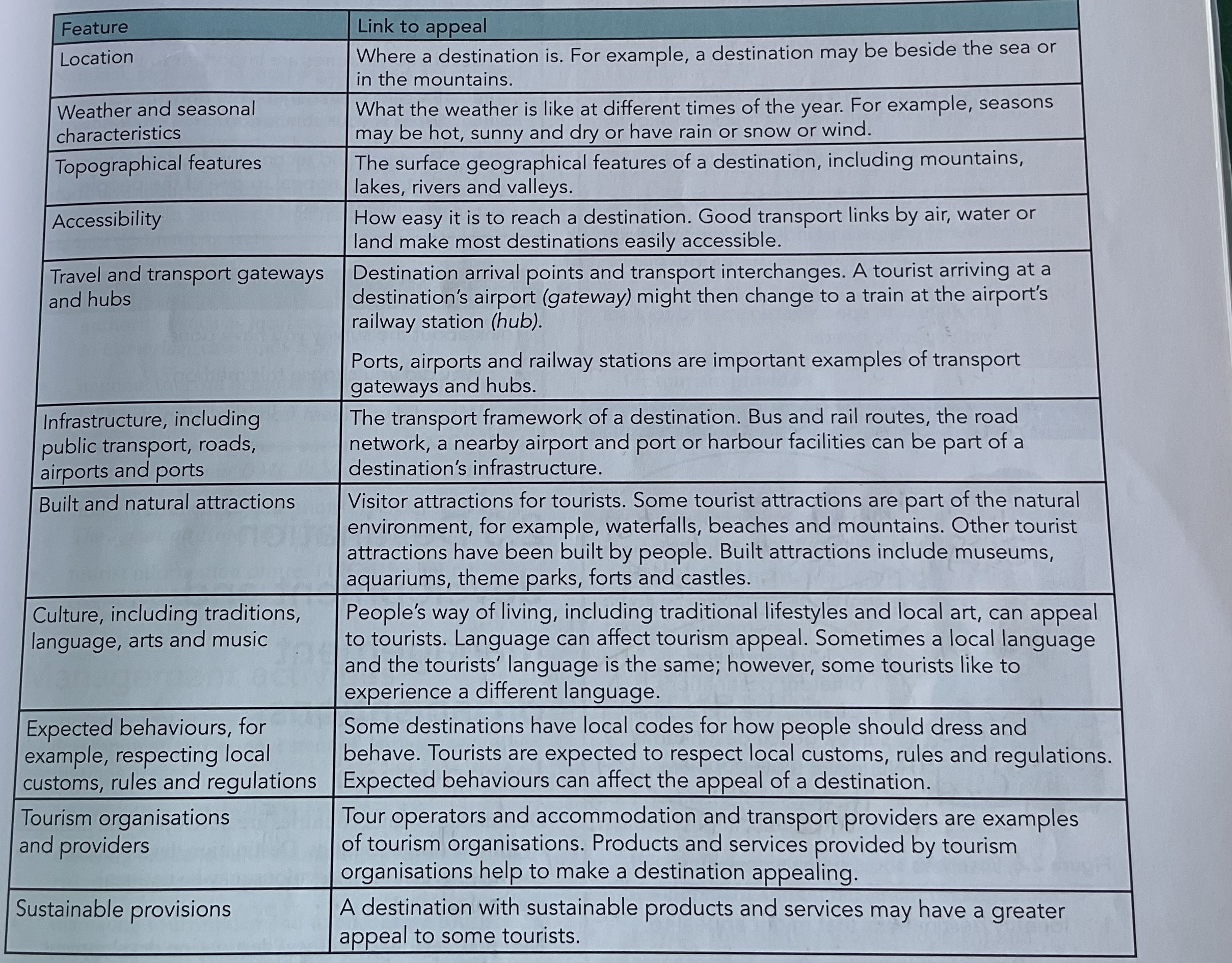
location- where a destination is
Accessibility (Paris with its airports and roads and rail lines)
Unique appeal( Maldives )
Weather and seasonal characteristics
predictable weather patterns
ex: Santa Barbara ( summer sunshine )
Ex: Brecldcenbrige (winter sports from November to April)
Topological features- surface features of the landscape such as mountains ,lakes, rivers ,and valleys
natural landscapes
ex: Breckenridge (mountains, biking ,hiking ,fishing ,white water rafting, golfing)
Accessibility- how is it a destination is to reach
good transport links and provision for tourist with special needs
Ex: Orlando Florida international airport and Copenhagen Airports services for persons with mobility issues
Gateways- An entry point to a destination
ex: airports railway stations in arrival towns
Hub- place where tourist change from one type of transport to another
gateways and hubs Airport improve accessibility
Ex: Orlando international airport gateways for international flights and hub for domestic connections
Infrastructure- The transport framework of a destination including public transport roads airport and ports
public transport, roads,airport’s , & ports for assess ability
Ex : Paris ( international airports, motorways , and high- speed rail networks)
Appeal comes from natural beauty and built environments)
Ex: Ha long bay (Vietnam) - limestone island rainforest, and the old part of Hoi An
cultural Attraction like markets , traditions, and performance draws tourist
ex : Marrakech ( Morocco) - Jemma el- Fna square with traders , food stalls , performance
respecting local customs influences tourist Appeal
ex : Modest dressing in Marrakech and cultural sensitivity in New Zealand’s Bay of Plenty
Toursim providers shape the tourist experience
Ex: Package tour in Australia
Sustainable Tourism - Promoting eco-friendly practices
Ex: Implementing recycling programs in hotels
Risk management- handling crises like disease outbreak
Ex: Covid-19 protocols in tourist areas
Demand Control: Managing over tourism
ex: limited daily visitors to popular sites
Policy Development: Attracting tourist through polices
ex: Visa-free entry for certain nationalities
Future plans: Developing long-term tourism plans
ex: Creating new attractions for future visitors
Services:
marketing strategies: Building a destination brand
ex: “Visit Dubai” campaign
Destination Promotion: Advertising the destination
ex: Tourism ads on TV and online
Product Development: Creating new tourist experiences
ex: Adventure tour of cultural festivals
infrastructure funding : Improving facilities
ex: Building new roads or airports
information Provision : Supply info to tourist
Ex: Offering training to hotel staff
Quality Control: Maintaining high standards
Ex:Hotel star rating
Marketing strategies - Plans that aims to market destinations. Marketing destinations involves making destination attractive to tourism customers
Consultation Support- Advice provided to help tourism organizations
National tourism organizations (NTO) - a government agency that promotes and market the tourism Product of a country
Destination management company (DMC)- A tourism business with local knowledge of a destination. A DMC provides customers with event, activities, tours , transport, and other services in the destination
Non -Government Organization(NGO)- a not-for profit organization of people who want to promote a product, services or causes, such as sustainable tourism. NGO’S are independent of government
2.4
Sustainability
Key idea- balance tourism with nature and local culture
ex: Eco-lodges that use solar power and hire local guides.
Risk& resilience
Key idea- Prepare for disaster and bounce back quickly
Ex: Building hotels on higher ground to avoid floods
Carrying capacity-the maximum numbers of visitors a destination or attraction can welcome without causing environmental damage or spoiling the tourism experience
Over tourism- where are too many tourist in a destination. This harms the destination environment and causes difficulties for local people.Tourism do not enjoy the destination as much
Carrying capacity
Key idea - Don’t let too many tourist ruin the place
ex: Limited the numbers of daily visitors to a national park
Seasonality
Key idea- Make money year- round, not just peak- season
Ex: Ski resorts offering hiking and mountains
Government objectives
key idea- Government wants tourism to help the economy, protect, resources, and keep tourist safe
Ex: Creating laws to protect coral reef from damage.

Host community- a destination local people
World Heritage sites(WHS)- Destination and attraction that have been identified as especially important part of natural or build environment by UNESCO
Homestay holiday- holidays involving tourist staying in local people houses
2.5
Combat climate change- to take action against changes in the earths climate .Action such as producing less pollution are aimed at reducing climate change
Indigenous Communities
Communities of the original inhabitants of a place.
Social Enterprises
Organizations that try to be profitable while also supporting local and indigenous communities.
Protect Nature and Historical Sites
Key Idea: Minimize harm to nature and historical sites.
Examples:
Enforcing strict waste disposal policies and recycling programs in tourist areas.
Restoring historic buildings using sustainable materials.
Community Tourism
Involves local communities inviting tourists to visit and stay in their homes.
Often involves indigenous communities.
Nature Reserves
Areas where the natural environment and biodiversity are protected.
Regional Tourism Organisation (RTO)
An organization that promotes and markets the tourism product of a country.
Combat Climate Change
Key Idea: Reduce the carbon footprint of tourism.
Examples:
Reducing over-consumption, food waste, energy use, and water usage.
Empower Local Communities
Key Idea: Give communities control and benefits from tourism.
Examples:
Establishing community-owned and operated tourism businesses such as guided tours and craft shops.
Creating cultural centers where locals can showcase their traditions.
Supporting Social Sustainability
Key Idea: Promote businesses that benefit both the community and the environment.
Examples:
Supporting local farmers who supply restaurants with organic produce.
Creating jobs for local people to increase economic and social sustainability of the destination.
Customs
Local-established ways of behaving or traditional customs of local and indigenous destinations.
Communities may have their own ways of living.
Sustainable Infrastructural Development
Improving destinations' transport and tourism facilities sustainably.
Involving Visitors
Clean-ups: Tourist activities helping locals to tidy the environment by removing rubbish.
Cultural Homestay
A type of community tourism where tourist customers stay in the homes of local people and experience indigenous culture.
2.6
Economic Impacts
Affecting money and jobs.
Environmental Impacts
Affecting the environment.
Sociocultural Impacts
Affecting people in their ways of life.
Positive Economic Impacts
Benefit local people.
Examples:
Tourism bringing jobs and money.
Travel & tourism organizations employ people, creating large numbers of jobs in destinations.
Carbon Footprint
The amount of carbon dioxide pollution produced by a person or organization.
Quota
A limit allowed to the number of visitors to a destination or attraction.
Over-Dependence
When a destination depends too much on travel and tourism.
Example: Dubai relying heavily on tourism.
All-Inclusive Resorts
Hotels that provide a wide range of products and services on one site.
Positive Environmental Impacts
Destination management.
Carrying capacity.
Tourism education.
Awareness programs.
Tourism organizations manage visitor numbers to ensure they are within the destination's limits.
Responsible tourism.
Increased environmental awareness for tourists and tourism staff.
Positive influence in environmental conservation and regeneration through investment projects.
Negative Environmental Impacts
Include air, water, and noise pollution.
Air pollution from transport (aircraft, motor vehicles, ships) pollutes the atmosphere, rivers, seas, and lakes.
Tourism traffic creates congestion, spoiling the environmental appeal of destinations.
Litter spoils the appeal of destinations and harms wildlife.
High visitor numbers can damage natural habitats.
Waste disposal.
Tourism facilities, including hotels produce waste which causes pollution.
Over-tourism causes depletion of resources like food, energy, and water.
Assets of a Destination
Valued things that add appeal to a destination.
Natural assets include wildlife, landscape features.
Built assets include historic monuments and architecture.
Game Drives
A drive in a 4x4 vehicle through a natural habitat to view wildlife.
Safari Walks
An overland journey in a natural habitat to view wildlife.
Tourist Organizations
Spending helps travel and tourism organizations to make money and generate profit.
Tourist spending enables organizations to invest and grow, and also to employ staff (creating more jobs).
Multiplier Effect
How wealth created from tourist spending circulates in destinations.
Tourist spending benefits travel and tourism organizations, local businesses, and the government through taxes and other revenues.
Negative Economic Impacts
Inflation
When prices increase.
Example: Rent for an apartment used to be 2,000 per month, but increases to 3,500.
Import Leakage
Happens when travel and tourism providers spend money abroad instead of buying locally.
Example: Hotels importing food & drinks from abroad.
Export Leakage
Can happen when hotels are foreign-owned and profits leave the country.
Economic Leakage
When money from travel and tourism leaves (or leaks from) a country.
Job Losses
People lose their jobs due to low season, where there is less demand compared to in-season.
Opportunity Cost
When choices are made, the chance to do something else has been lost because something else has been chosen.
Example: The opportunity to build a new school for local people can be lost due to tourism-related import/export leakage.