
Islam
Abraham marries to Hagar, who was an Egyptian princess. Ishmael, meaning “God is heard” is born first before Isaac.
Allah commands them to be dropped off in the desert (modern day Saudi Arabia)
Crescent Moon & Star: adopted following the defeat of Constantinople (adopted their symbol). 5 points represents 5 pillars of the Muslim faith.
Muhammad: “the last prophet”, a descendant of Ishmael. Islam is based around the story of Muhammad, born 530 CE.
Muhammad is not depicted or drawn; is not considered divine but rather human.
Khadija: first wife and favourite wife. First believer in Islam. 6 children; 2 boys who died, 4 girls.
Abu Jahl: murderer and opponent of Islam.
Bilal: slave, converts to Islam and is the first man to do a call to prayer
Abu Talib: the uncle to the prophet, a mediator, peaceful.
Abdallah: uncle, does not convert to Islam.
Pre-Muhammad, Mecca was a tribal society; a trade and religious centre with polytheism and payment to enter.
Muhammad tries to rededicate the Ka’baa to one God, Allah; creating conflict.
At 40 years old, Muhammad travels to a cave to pray and contemplate injustice. The Angel Gabriel calls Muhammad to service and cannot escape as the Messenger of God. Night of Power and Excellence.
Al-Isra: Muhammad is taken to Jerusalem on a flying Buraq (horse)
Isra Mi’raj: Muhammad’s journey to Heaven to speak.
1st level: Adam
2nd level: John & Jesus (Isa)
3rd level: Joseph
4th level: Idris
5th level: Aaron
6th level: Moses
7th level: Abraham
God gives Muhammad the Quran, the central teachings. Likened to a magical power.
Revelations include monotheistic equality & righteous respect for women.
Quran: Reading or Recitation
expresses Allah’s attributes, man’s relationship with Allah and Day of Judgement (spiritual destiny)
5 main categories seen throughout in the 114 Suras (chapters)
Nature of Spiritual World: angels, judgement, heaven/hell
Law & Commandments: Moses, Abraham, social and moral laws: Sharia Law
Historical Accounts: the prophets before Muhammad.
The Wisdom: believers and non-believers separated; often figurative.
The Prophets: Muhammad, the day of judgement & paradise.
All of Muhammad’s followers individually memorized each section then recited to a written copy.
Demands of Muhammad was to be prophet and become literate.
Summayah: first martyr of Islam at the hands of Abdullah.
Muslims flee to Abyssinia as refugees; the king is Christian and is a good soul.
Jahal’s cousin joins Islam; plagues as outcasts.
Hamzah: great warrior, represented with a bow.
Muhammad is summoned to Yethrip (Medina) to bring peace to an Arab conflict.
Muhammad’s cousin sleeps in his bed to foil assassination plot.
In Medina (city of the prophet), worship is without fear. Bilal completes the first call to prayer.
War for Mecca: Humzah becomes a great warrior; Islamic call of prayer present.
2nd war commences at the Mountain of Umud.
Muhammad is believed to die by boulder — lives instead.
Tribe leaders agree to hunt Muhammad and force his death in Medina. Trench surrounding city foils plot; sandstorm sent by God defeats armies.
Keyholder of the Ka’baa: journeys to Mecca, develops a 10 years peace. Abu Jahl converts without resistance; Mecca heals.
Muhammad passes away at age 63.
Dome of the Rock: mosque located in Jerusalem.
Ka’baa: large building, believed to be built by Abraham in the desert. Black Stone is embedded, which is believed to have fallen from heaven either to point to or indicate the position of the Ka’baa.
Allah: one God, transcendent to Muslims: personal, omniscient and omnipotent. Given 99 names / attributes.
Tawhid: belief in one God, there are no equals to Allah. Avoid distractions from the Almighty. Everlasting, beget and begotten.
Shir: to equate oneself to God. (blasphemy)
Sunna: collection of Muhammad’s own words and actions (approved/disapproved) which were first recorded by his family and friends that contain customs and traditions. Means ‘beaten path’
Hadith: Oral record of Muhammad’s individual teachings and sayings that were compiled centuries after his death. Main source of the Sunna; religious law & moral guidance.
Sharia Law: set of moral and ethical rules that Muslims follow. Means “A path to life-giving water”
Obligation: 5x a day prayer; Hajj pilgrimage.
Recommended: memorize Quran, arranged marriages, extra prayers, volunteering
Neutral actions: eating chicken, occupation
Discouraged actions: foods: shrimp & garlic; smoking; divorce
Forbidden actions (haram): tattoos, alcohol, pork, adultery, murder, theft.
Umma: the community of Muslims.
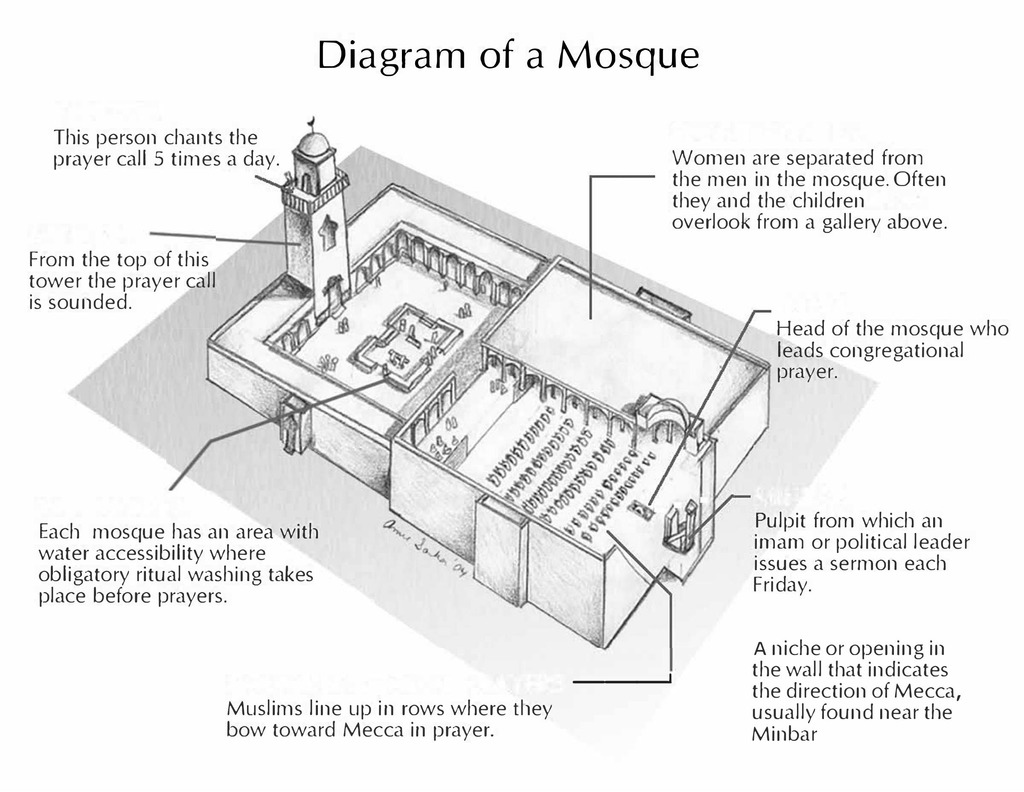
Imam: worship leader in a Mosque; provides religious guidance.
No central authority or hierarchy.
A community where salvation can be achieved. Community transcends all national, ethnic, racial and sexual differences.
Shahadah: confession of faith.
bear witness to God, Muhammad as messenger.
should be the beginning and end of one’s life.
Salat: prayer.
5 times a day facing Mecca.
Wudu ritual washing
Prayer mats
Prostration (movement)
Prayers in the Mosque on Friday (sacred day/sabbath)
Canada: face east.
Zakah: almsgiving/wealth sharing
2.5% of wealth shared to charity.
Receivers are those in need.
Sawm: fasting.
related to Ramadan, food as interaction with the Sacred.
Sun up/sundown fasting; able-bodied only. Mecca time can be observed.
Promotes awareness of mortality and a dedication to spirituality.
Haram: prohibited foods.
Halal: approved foods.
Deliberately cultivates a peaceful and prayerful attitude of mind and physical discipline of giving up food and liquids for a period of time.
Hajj: a pilgrimage to the Ka’baa in Mecca at least once in one’s life.
Kiswa: a cloth that covers the Kaaba; every year a 670kg gold embroidered cloth is draped over.
Ihram: mental state: men with 2 white garments, state of peace and modesty.
Tawaf: circling the Ka’baa 7 times, the initiating event.
Sa’ey: conducted in memory of Hagar, who ran to find water between Marwa and Safa 7 times.
Well of Zamzam: where Hagar found water via the Angel Gabriel.
Mina: a tent city, depicting equality of community; is a holding ground.
Plains of Arafat: where the Mount of Mercy is → the most solemn point in their faith. Must stay until sun goes down.
Mount of Mercy: where Muhammad gave his final sermon; where people ask for forgiveness
Three pillars: throw rocks at the Three Pillars, emblematic of how Abraham threw stones at the devil as he tried to entice him into not killing Ishmael.
Feast of sacrifice: pay to sacrifice an animal, sent to the needy. Marks the end of the Hajj.
Cut hair, complete Tawaf one last time.
Mosque: place of prostration; the place of worship. First mosque in Medina.
 Holidays
HolidaysRamadan: fasting as a part of the 5 pillars of faith.
Eid al-Adha: festival of the Sacrifice, celebrating Abraham’s willingness to sacrifice Ishmael (final day of the Hajj)
Eid al-Fitr: festival of the Breaking of the Fast, celebrating the end of Ramadan with a feast.
Ali of Muhammad selected as the imam leader.
Husayn took over after Ali’s death.
Ashira: celebration to remember the deaths of Husayn (Muhammad’s grandson)
Ayaytolas: “sign of God”, clergymen who are experts in the Quran.
Imam - a descendent of Muhammad who leads Muslims and clarifies laws.
90% of the world Muslim population.
Elected Abu Bakr (Muhammad’s father in law) as the leader of Islam after Muhammad’s death.
Caliph - first four leaders seen as “rightfully guided”
Imam - leader of prayers in mosque.
following a mystical path that uses prayer and meditation to draw closer to God. Uses self-discipline such as fasting to clear the mind. Constant remembrance of God.
Whirling Dervishes: mystical path performed in Sufism.
Physical mediation: form of worship in Sufism.
Moses & the 10 commandments
Abraham
Ishmael and Isaac
Jesus is considered a prophet, son of the Virgin Mary; not the son of God.
Somebody else was crucified in Jesus’ place; Jesus ascended into Heaven directly.
Jesus will return with Muhammad on the Day of Judgement.
Jesus will die after establishing the Kingdom of God on Earth and be burried in Medina beside Muhammad.
Heaven and hell exists.
End of the world is judgement day.
Belief is that everyone will stand before Allah.
The righteous will receive paradise.
Evildoers (opponents of Islam) will go to hell.
The Quran provides the path to righteousness.
Jihad: exertion of an internal struggle against anything that distracts from Allah. Not violent.
Hijab: head covering, allows face and slight hair to be visible.
Chador: face only head covering
Niqab: eyes only head covering
Burka: complete coverage headcovering.
Abraham marries to Hagar, who was an Egyptian princess. Ishmael, meaning “God is heard” is born first before Isaac.
Allah commands them to be dropped off in the desert (modern day Saudi Arabia)
Crescent Moon & Star: adopted following the defeat of Constantinople (adopted their symbol). 5 points represents 5 pillars of the Muslim faith.
Muhammad: “the last prophet”, a descendant of Ishmael. Islam is based around the story of Muhammad, born 530 CE.
Muhammad is not depicted or drawn; is not considered divine but rather human.
Khadija: first wife and favourite wife. First believer in Islam. 6 children; 2 boys who died, 4 girls.
Abu Jahl: murderer and opponent of Islam.
Bilal: slave, converts to Islam and is the first man to do a call to prayer
Abu Talib: the uncle to the prophet, a mediator, peaceful.
Abdallah: uncle, does not convert to Islam.
Pre-Muhammad, Mecca was a tribal society; a trade and religious centre with polytheism and payment to enter.
Muhammad tries to rededicate the Ka’baa to one God, Allah; creating conflict.
At 40 years old, Muhammad travels to a cave to pray and contemplate injustice. The Angel Gabriel calls Muhammad to service and cannot escape as the Messenger of God. Night of Power and Excellence.
Al-Isra: Muhammad is taken to Jerusalem on a flying Buraq (horse)
Isra Mi’raj: Muhammad’s journey to Heaven to speak.
1st level: Adam
2nd level: John & Jesus (Isa)
3rd level: Joseph
4th level: Idris
5th level: Aaron
6th level: Moses
7th level: Abraham
God gives Muhammad the Quran, the central teachings. Likened to a magical power.
Revelations include monotheistic equality & righteous respect for women.
Quran: Reading or Recitation
expresses Allah’s attributes, man’s relationship with Allah and Day of Judgement (spiritual destiny)
5 main categories seen throughout in the 114 Suras (chapters)
Nature of Spiritual World: angels, judgement, heaven/hell
Law & Commandments: Moses, Abraham, social and moral laws: Sharia Law
Historical Accounts: the prophets before Muhammad.
The Wisdom: believers and non-believers separated; often figurative.
The Prophets: Muhammad, the day of judgement & paradise.
All of Muhammad’s followers individually memorized each section then recited to a written copy.
Demands of Muhammad was to be prophet and become literate.
Summayah: first martyr of Islam at the hands of Abdullah.
Muslims flee to Abyssinia as refugees; the king is Christian and is a good soul.
Jahal’s cousin joins Islam; plagues as outcasts.
Hamzah: great warrior, represented with a bow.
Muhammad is summoned to Yethrip (Medina) to bring peace to an Arab conflict.
Muhammad’s cousin sleeps in his bed to foil assassination plot.
In Medina (city of the prophet), worship is without fear. Bilal completes the first call to prayer.
War for Mecca: Humzah becomes a great warrior; Islamic call of prayer present.
2nd war commences at the Mountain of Umud.
Muhammad is believed to die by boulder — lives instead.
Tribe leaders agree to hunt Muhammad and force his death in Medina. Trench surrounding city foils plot; sandstorm sent by God defeats armies.
Keyholder of the Ka’baa: journeys to Mecca, develops a 10 years peace. Abu Jahl converts without resistance; Mecca heals.
Muhammad passes away at age 63.
Dome of the Rock: mosque located in Jerusalem.
Ka’baa: large building, believed to be built by Abraham in the desert. Black Stone is embedded, which is believed to have fallen from heaven either to point to or indicate the position of the Ka’baa.
Allah: one God, transcendent to Muslims: personal, omniscient and omnipotent. Given 99 names / attributes.
Tawhid: belief in one God, there are no equals to Allah. Avoid distractions from the Almighty. Everlasting, beget and begotten.
Shir: to equate oneself to God. (blasphemy)
Sunna: collection of Muhammad’s own words and actions (approved/disapproved) which were first recorded by his family and friends that contain customs and traditions. Means ‘beaten path’
Hadith: Oral record of Muhammad’s individual teachings and sayings that were compiled centuries after his death. Main source of the Sunna; religious law & moral guidance.
Sharia Law: set of moral and ethical rules that Muslims follow. Means “A path to life-giving water”
Obligation: 5x a day prayer; Hajj pilgrimage.
Recommended: memorize Quran, arranged marriages, extra prayers, volunteering
Neutral actions: eating chicken, occupation
Discouraged actions: foods: shrimp & garlic; smoking; divorce
Forbidden actions (haram): tattoos, alcohol, pork, adultery, murder, theft.
Umma: the community of Muslims.
Imam: worship leader in a Mosque; provides religious guidance.
No central authority or hierarchy.
A community where salvation can be achieved. Community transcends all national, ethnic, racial and sexual differences.
Shahadah: confession of faith.
bear witness to God, Muhammad as messenger.
should be the beginning and end of one’s life.
Salat: prayer.
5 times a day facing Mecca.
Wudu ritual washing
Prayer mats
Prostration (movement)
Prayers in the Mosque on Friday (sacred day/sabbath)
Canada: face east.
Zakah: almsgiving/wealth sharing
2.5% of wealth shared to charity.
Receivers are those in need.
Sawm: fasting.
related to Ramadan, food as interaction with the Sacred.
Sun up/sundown fasting; able-bodied only. Mecca time can be observed.
Promotes awareness of mortality and a dedication to spirituality.
Haram: prohibited foods.
Halal: approved foods.
Deliberately cultivates a peaceful and prayerful attitude of mind and physical discipline of giving up food and liquids for a period of time.
Hajj: a pilgrimage to the Ka’baa in Mecca at least once in one’s life.
Kiswa: a cloth that covers the Kaaba; every year a 670kg gold embroidered cloth is draped over.
Ihram: mental state: men with 2 white garments, state of peace and modesty.
Tawaf: circling the Ka’baa 7 times, the initiating event.
Sa’ey: conducted in memory of Hagar, who ran to find water between Marwa and Safa 7 times.
Well of Zamzam: where Hagar found water via the Angel Gabriel.
Mina: a tent city, depicting equality of community; is a holding ground.
Plains of Arafat: where the Mount of Mercy is → the most solemn point in their faith. Must stay until sun goes down.
Mount of Mercy: where Muhammad gave his final sermon; where people ask for forgiveness
Three pillars: throw rocks at the Three Pillars, emblematic of how Abraham threw stones at the devil as he tried to entice him into not killing Ishmael.
Feast of sacrifice: pay to sacrifice an animal, sent to the needy. Marks the end of the Hajj.
Cut hair, complete Tawaf one last time.
Mosque: place of prostration; the place of worship. First mosque in Medina.
 Holidays
HolidaysRamadan: fasting as a part of the 5 pillars of faith.
Eid al-Adha: festival of the Sacrifice, celebrating Abraham’s willingness to sacrifice Ishmael (final day of the Hajj)
Eid al-Fitr: festival of the Breaking of the Fast, celebrating the end of Ramadan with a feast.
Ali of Muhammad selected as the imam leader.
Husayn took over after Ali’s death.
Ashira: celebration to remember the deaths of Husayn (Muhammad’s grandson)
Ayaytolas: “sign of God”, clergymen who are experts in the Quran.
Imam - a descendent of Muhammad who leads Muslims and clarifies laws.
90% of the world Muslim population.
Elected Abu Bakr (Muhammad’s father in law) as the leader of Islam after Muhammad’s death.
Caliph - first four leaders seen as “rightfully guided”
Imam - leader of prayers in mosque.
following a mystical path that uses prayer and meditation to draw closer to God. Uses self-discipline such as fasting to clear the mind. Constant remembrance of God.
Whirling Dervishes: mystical path performed in Sufism.
Physical mediation: form of worship in Sufism.
Moses & the 10 commandments
Abraham
Ishmael and Isaac
Jesus is considered a prophet, son of the Virgin Mary; not the son of God.
Somebody else was crucified in Jesus’ place; Jesus ascended into Heaven directly.
Jesus will return with Muhammad on the Day of Judgement.
Jesus will die after establishing the Kingdom of God on Earth and be burried in Medina beside Muhammad.
Heaven and hell exists.
End of the world is judgement day.
Belief is that everyone will stand before Allah.
The righteous will receive paradise.
Evildoers (opponents of Islam) will go to hell.
The Quran provides the path to righteousness.
Jihad: exertion of an internal struggle against anything that distracts from Allah. Not violent.
Hijab: head covering, allows face and slight hair to be visible.
Chador: face only head covering
Niqab: eyes only head covering
Burka: complete coverage headcovering.