Recent Quiz
Coniferous Trees: needles stay green all year; needles stay on trees
Decidous Trees: Trees: has leaves; turns colors in the fall; loses leaves in the fall
O Tundra: Cold, dry, poor soil — Plants: Shrubs, mosses, small flowers
O Boreal & Taiga: Cold, wet, poor soil, mostly coniferous trees
O Deciduous Forest: Long hot summers, mild winters, lots of precipitation, fertile soil, mostly deciduous trees
O Grasslands: Cold winters, hot summers, dry precipitation, fertile soil, long grass, some areas of trees. Coniferous in the North, Deciduous in the South
O West Coast Forest: Mild temperature, lots of rain, mixed soil, lots of trees; rainforest
O Cordilleran Vegetation: Warm in the valleys, colder in the mountains. Dry in valleys, but rain on West side of mountains. All types of soil depending on elevation. Grasses and cactuses in dry valleys; coniferous trees on mountains
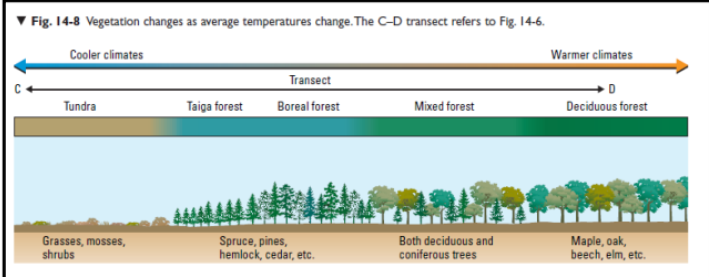
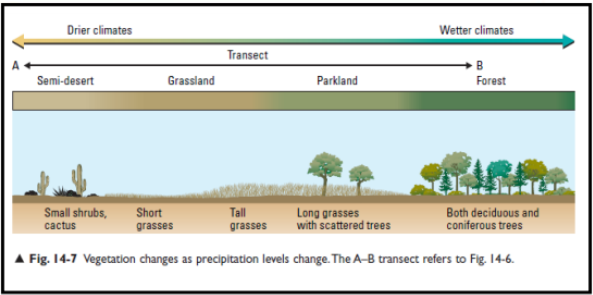
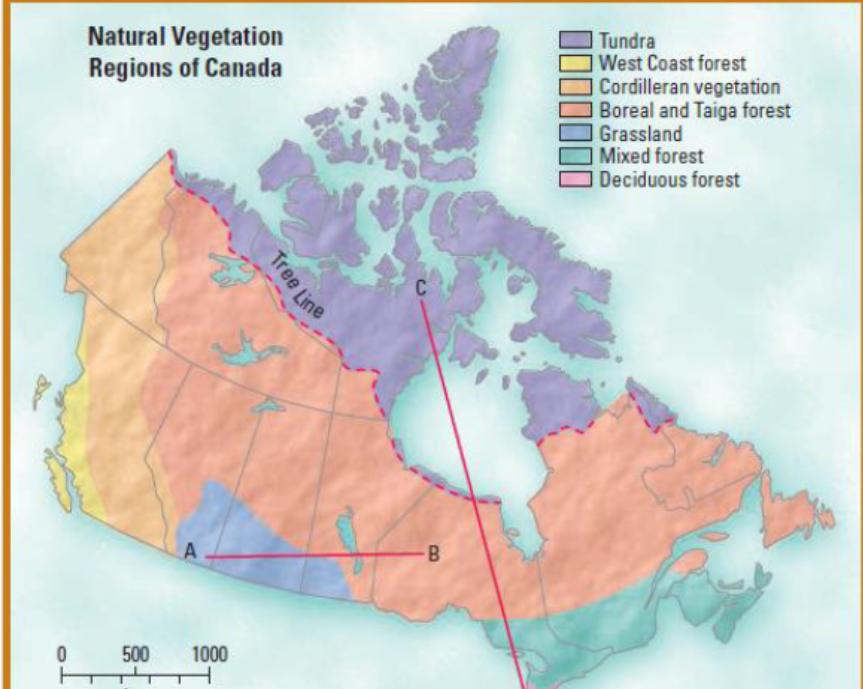
Vegetation Regions
Canada has seven (7) different vegetation regions.
Vegetation regions are determined by climate and soil.
Transition regions: gradual changes between regions.
Soil Health Threats
Erosion (water or wind removes topsoil)
Prevention: contour plowing, windbreaks, cover crops
Nutrient Depletion (over-farming drains N, P, K)
Prevention: crop rotation, green manure, organic fertilizers
Salinization (irrigation leaves salts behind)
Prevention: proper drainage, salt-tolerant crops
L = Latitude
O = Ocean Currents
W = Wind
E = Elevation
R = Relief
N = Nearness to Water
Maritime Continent = Region close to a body of water
Continental = Not close to a body of water
How does climate affect us?
1. A Drought (no rain, very dry period) can destroy
crops and soil.
2. Major snow/rain storms can cause major
transportation problems
3. Climate affects the vegetation, soil and
wildlife (animals).
4. Climate also affects certain industries in
Canada like farming and mining.
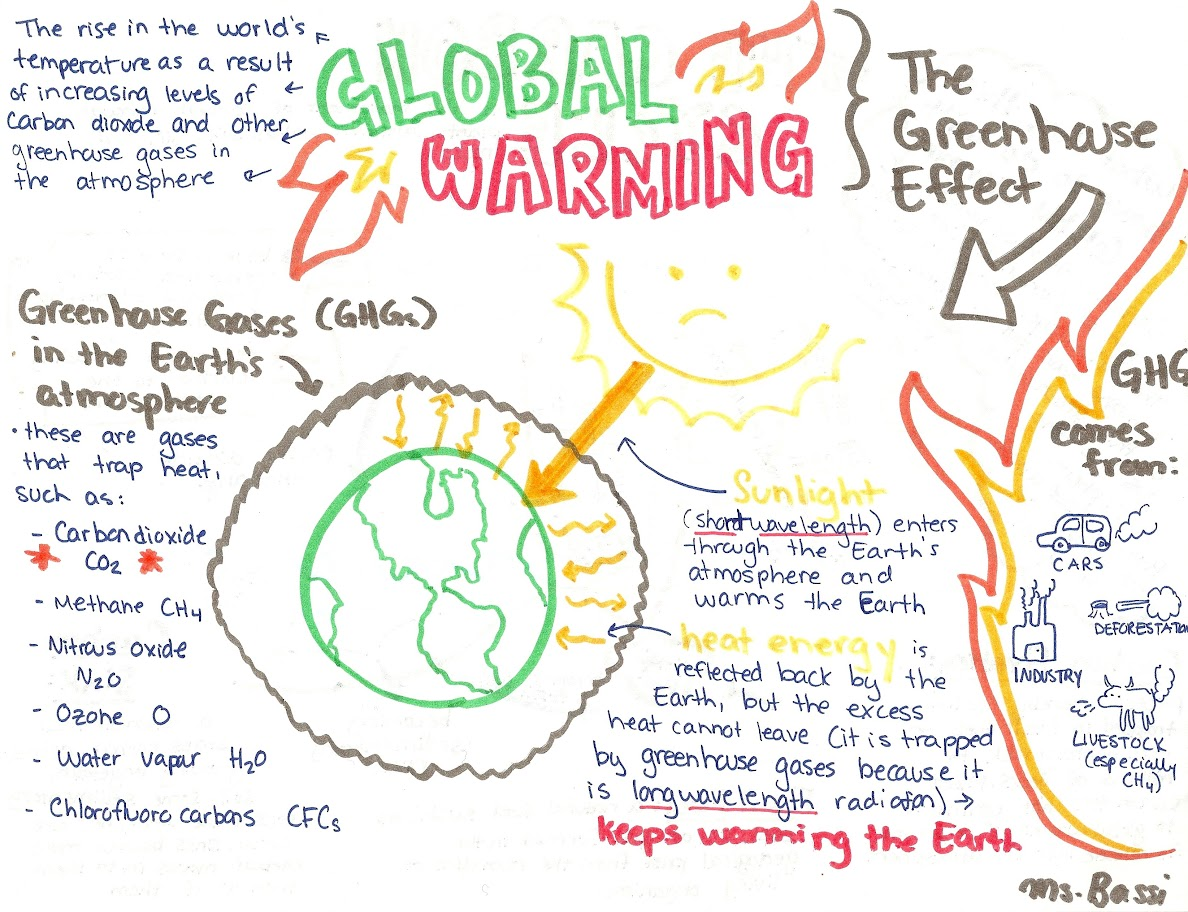

Climate Change:
Global Warming: The Earth’s atmosphere is
getting warmer due to human
activities
The Greenhouse Effect: Greenhouse gases trap heat
from the sun and raise the
temperature of the Earth’s
atmosphere
Fossil Fuels: Energy sources that are
formed in the geologic past
from the remains of living
things, such as coal, oil, or
natural gas