unit 2 - population & migration
vocabulary
midlatitudes - the regions on Earth lying between 30 and 60 degrees latitude from both the equator and poles
social stratification - a system by which a society ranks people in a hierarchy
arable land - fertile land that can be used for farming
redistricting - a procress where new district bounds are drawn
infrastructure - the basic physical and organization structures needed for a society to function
carrying capacity - the maximum number of individuals that an environment can support
cohorts - a group of individuals with a shared characteristic
dependent population - under 15, over 64; rely on others for financial support
dependency ratio - ratio between those not working, and those working
immigrants - those coming into another country
emigrants - those coming out of a country
demographic momentum - the tendency of a population to grow even after fertility rates decline
antinatalist policies - policies implemented to decrease the country’s birth rate
pronatalist policies - strategies implemented to encourage citizens to have more children
push factor - conditions that compel individuals to migrate
pull factor -a positive condition that attracts people to migrate
intervening obstacles - an environmental or cultural feature that hinders migration
asylum - protection granted to a refugee
transhumance - moving livestock seasonally between highland and lowland areas, nomadic
xenophobia - dislike of people from other countries
ecumene - inhabited land
agglomerations - lots of different things gathered together
arithmetic density - total population / total land area
physiological density - total population / area of arable land
agricultural density - # of farmers / area of arable land
natural hazards - a natural event that could threaten the population, does not kill anyone
greying population - country relies on elderly population; more old than young
cultural/ethnic enclave - an area where a particular ethnic group is clustered
remittances - funds sent from migrants → home country
refugees - legally recognized people who fled from country for different reasons
international - between different countries
interregional - between different regions, within a country
intraregional - within a region, within a country
guest workers - someone who is allowed to live in a country temporarily for work
rates
crude birth rate (CBR) - # of live births / 1000 people
crude death rate (CDR) - # of deaths / 1000 people
infant mortality rate (IMR) - # of deaths of babies <1 year / 1000 births
total fertility rate (TFR) - average # of children born to each woman
replacement fertility - amount of fertility needed to keep population stable/same
doubling time - amount of time it takes for population to double
natural increase rate / rate of natural increase (NIR/RNI) - % of growth/decline, excluding immigration and emigration
net migration - refers to if more people are migrating in or out
types of migration
step migration - when an individual migrates through stages
counter migration - migration in the opposite direction
return migration - migration back to the place of origin
forced migration - when people leave their homes due to factors outside their control
voluntary migration - when people can choose to migrate
step migration - gradual, takes steps to migrate
chain migration - moving because of family and nationality - “chain reaction”
net-in migration - more people coming in (immigrating) - per 1000 people
net-out migration - more people going out (emigrating) - per 1000 people
models
population pyramids

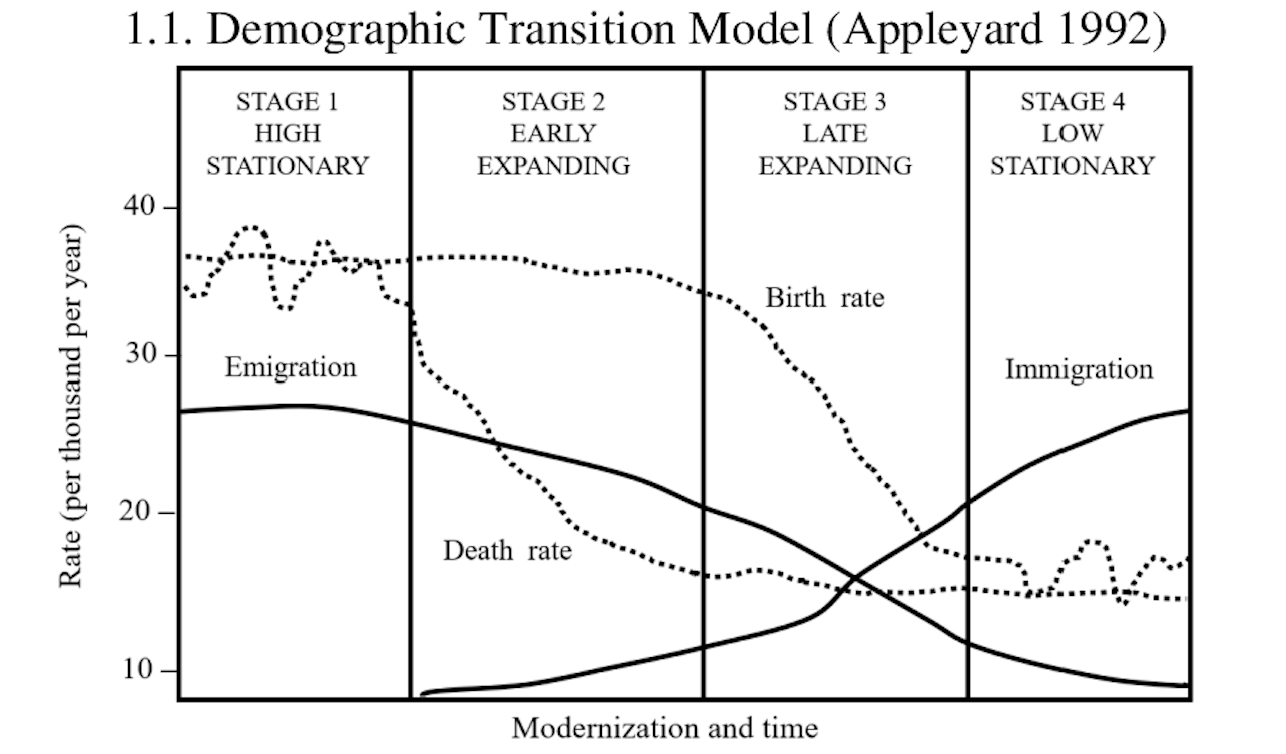
demographic transition model (DTM)
shows population change as a country develops
limitations:
no migration
does predict time in each stage
CBR is used, but it is not as accurate as TFR

stage 1 - births and deaths are high; small population
stage 2 - births are high, death rate drops; rapid population growth
stage 3 - births drop, death rate stays low; population growth slows
stage 4 - births and deaths are low; population growth plateaus
stage 5 - births and deaths are very low, aging population; population decreases
epidemiological transition model (ETM)
shows health and disease patterns as country develops
limitations:
does not take into account that health care depends on scale
no migration
does not predict time in each stage
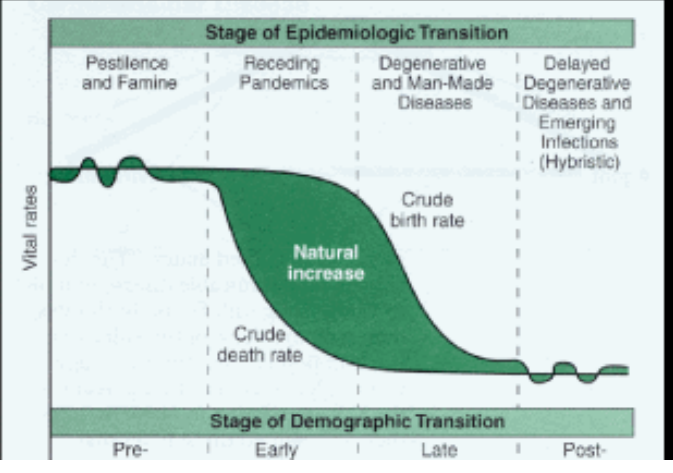
stage 1 - famine
stage 2 - receding pandemic
stage 3 - degenerative and human created diseases
stage 4 - delay degenerative diseases
stage 5 - reemergence of infectious diseases
malthusian model
too many people on Earth, not enough resources → war starts
Ester Boserup - against Malthusian theory
limitations:
new technology and innovation can avoid crisis and no resources

lee’s migration model
explains migration patterns based on push/pull factors
there are things that get into the way of migration and different factors that push/pull you away/towards from a place
limitations:
doesn’t apply to industrial areas, mostly individuals’ decisions
assumes all migration is voluntary and available
ravenstein’s laws of migration
migration flows produces counter-flows (chain migration)
females migrate more within their country, males more international
limitations:
no cultural/political factors
zelinsky’s migration
shows changes in migration patterns as countries develop
limitations:
ignores urbanization, focuses on industrialization instead
generalizations made - linear projection made isn’t always accurate
ignores migration within a country