ch 10 glaciers and deserts
glacier: thick mass of ice that forms over land from the compaction and recrystallization of snow and shows evidence of past or present flow
glaciers
valley, or alpine glaciers
thousands of small glaciers
stream of ice that flows downvalley, slowly
form in mountainous areas
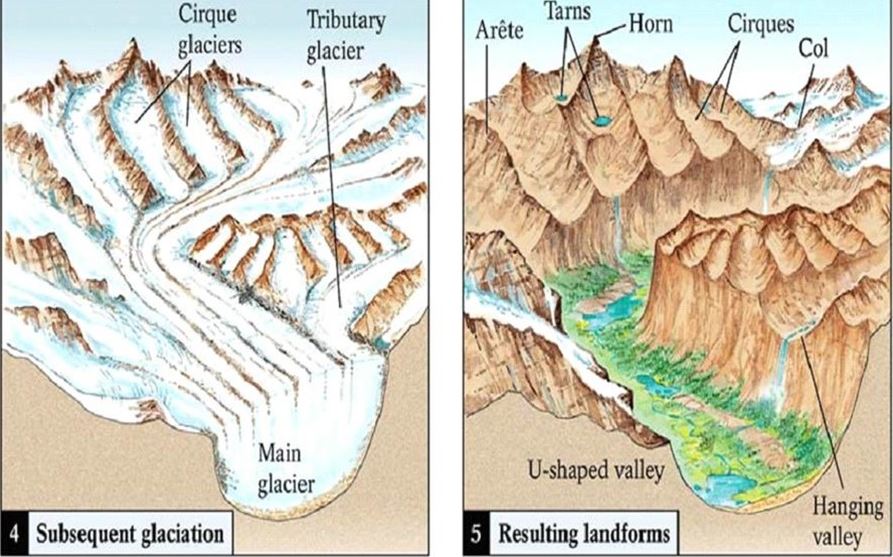
landforms created from alley, or alpine glaciers
glacial trough: narrow valleys are transformed as the glacier widens and deepens them, creating a U-shaped. normal valleys are v shaped
hanging valley: main glaciers, also called trunk glaciers, cut their valleys deeper than do their smaller tributary glaciers. Thus, after the ice has receded, the valleys of tributary glaciers are left standing above the main glacial trough
crique
arte: sinuous, knife-edged ridges
horn: pyramid-like peaks
fiord: A steep-sided inlet of the sea formed when a glacial trough was partially submerged.
ice sheets or continental glaciers
completely cover land with ice
alternating glacial and interglacial periods
ice caps and piedmont glaciers
completely cover land with ice
smaller than ice sheets
types of glacial movements
plastic flow - can be cracked
basal slip - along the ground lubricated from melt water
zone of fracture
uppermost 50 meters
crevasses form in brittle ice
crevasses - common in upper parts of glaciers bc ice is subjected to tension. open where brittle parts of glacier is stretched and cracks as it moves over a steeper slope in its valley
zone of accumulation - area where glacier forms
zone of wastage - area where there is net loss due to melting
glacial erosion
plucking: acquire sediment load by lifting rock blocks on sides and base
abrasion: ice and sediment load slide over bedrock. striation (grooves) in bedrock are evidence
glacial deposits
glacial drift
all sediments of glacial origin
types of glacial drift:
till: material deposited by ice with wide variation of glast sizes
stratified drift: sediment deposited by meltwater
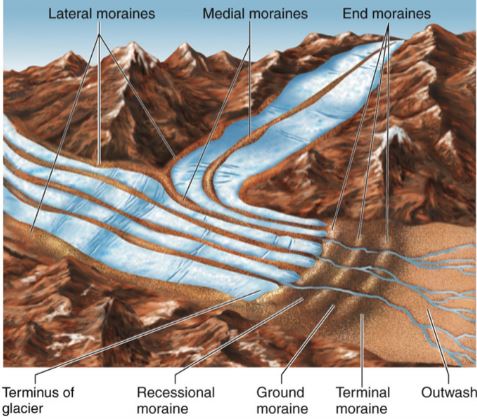
depositional features
moraines: layers or ridges of till.
lateral
medial
end
ground
outwash plain/valley train
kettles
drumlins
eskers
kames
ice age glaciers
many in earth’s history
most recent began 2-3 million years ago
called the plestocene epock
ice covered 30% of earth’s land area
effect of ice age glaciers
animals/plants migration
crust rebounding upwards
worldwide change in sea level
more ice - lower sea level
less ice - higher sea level
climate changes
glacial cycle knowledge is based on
ice cores
seafloor sediments
variations in earths orbit - milankovitch hypothesis
shape (eccentricity) of earth’s orbit varies
angle of earth’s axis (obliquity) changes
axis wobbles (precession)
deserts
place with a water deficiency
distribution and causes of dry lands
global distribution of air pressure and winds
deep interiors of landmasses
high mountains
many deserts created bc lack of rain, and regional topography, or if area is in a rain shadow
weathering
not as effected in bc shortage of water and organic acids
mechanical weathering forms unaltered rock and minerals
some chemical weathering that does occur
clay forms
thin soil forms
role of water
desert streams are ephemeral
flow only during perios of rainfall. dry most of the time
desert rainfall
rain occurs as heavy showers sporadically. causes flash floods
erosional work done by running water
names for desert streams
wash
arroyo
wadi
donga
nullah
basin and range: evolution of desert landscape
uplifted crustal blocks
interior drainage into basins produces
alluvial fans and bajadas
playas and playa lakes
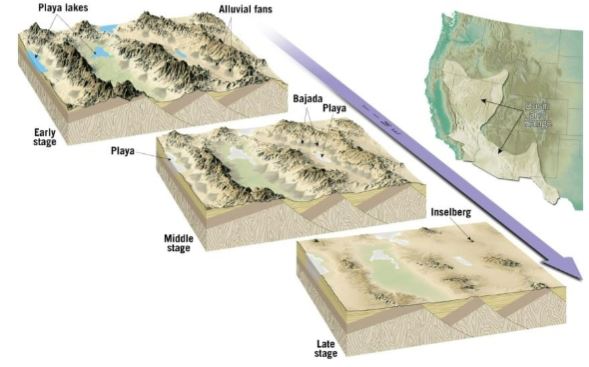
playa lakes - salty
salt concentration goes up in lake, eventually salt deposits are vissible
wind erosion
less effective than water bc less dense
only moves small particles, but it can travel long distances
deflation: lifting of loose material which produces
blowouts
desert pavement
abrasion: sand paper rubbing
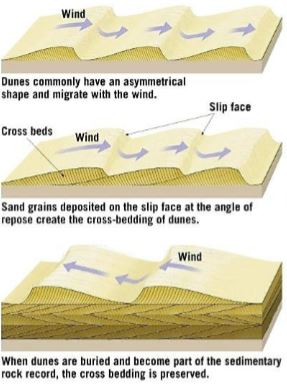
sand dunes
mounds and ridgest formed from wind’s bed load. characteristics include
slip face: leeward slope of due
cross beds: sloping layers of sand in due
loess
desert hazards
sand/dust storms