
GEOG111: LEC 7 - NEW GLOBAL TECTONICS
OCEANIC AND CONTINENTAL CRUST
Continental crust (~2.7 g/cm³)
largely granite
Ocean Crust (~3.0g/cm³)
Largely basalt and gabbro
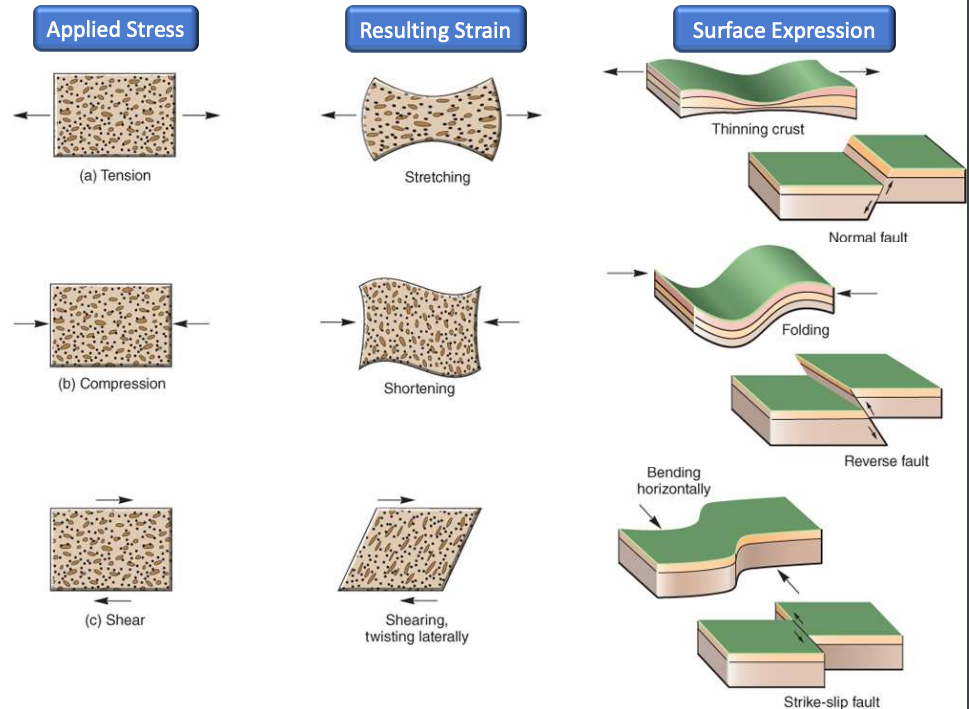
Tectonics: the folding and breaking of rocks due to pressure within the earths crust
Folding: the bending of crustal rocks, normally due to compression (soft deformation)
Faulting: the breaking and resultant displacement of a rock body (brittle deformation)
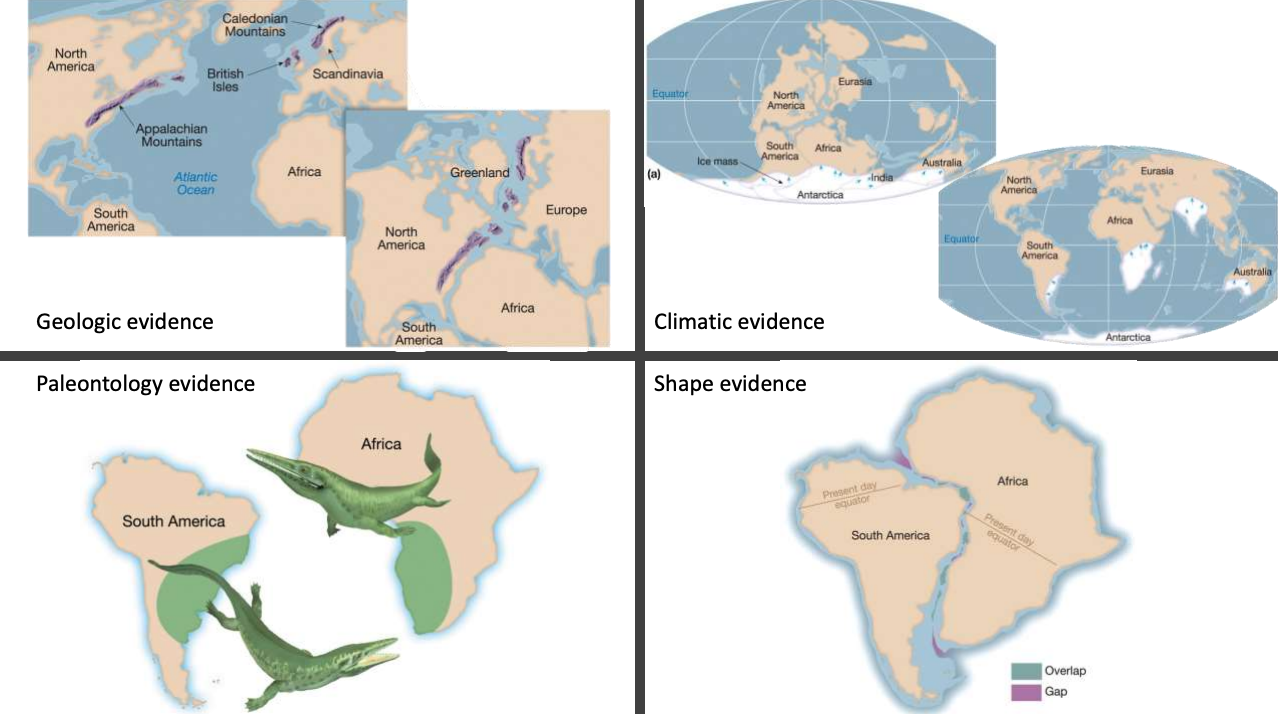
Continental Drift: Wegeners Pangea
Modern reconstruction of Pangea
Evidence: geologic, climatic, paleontology, shape
Critical point missing: doesn’t mention any processes
SEAFLOOR TOPOGRAPHY - MARIE THARP
Character of a Divergent margin
Plate types: O/O, C/C
Applied stress: Extension
Resulting strain: Stretching
Surface Expression: Low ridge with central trench
Seismicity: Low energy, shallow depth
Volcanism: Low explosivity, fluid lava
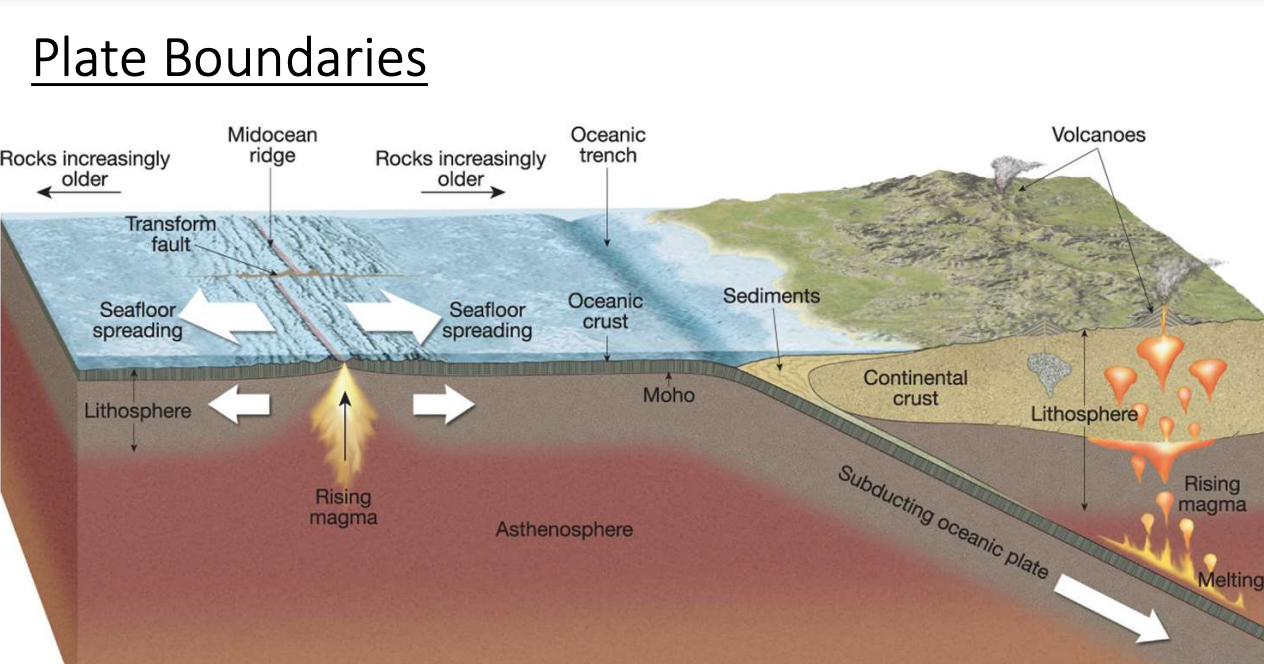
Divergent boundary - fast spreading ridge
Mid ocean ridge processes:
Hot mantle rock risees
Melt forms under the lithosphere
Magma rises into magma chamber in crust and is injected as dikes forming in new crust
law erupts onto ocean floor adding to crust
Plates move apart, cool, and thicken
Character of a transform margin
Plate types: O/O, O/C, C/C
Applied stress: shear
Resulting strain: shearing/twisting laterally
Surface expression: offset surface
Seismicity: low to moderate energy, shallow
Volcanism: not generally present
How do tectonics play a significant role in recycling rocks
Divergent/transform boundaries
Driven by convection currents within the earth
Different boundaries have different surface expression and geophysical indicators
Earthquakes, volcanic activity, trenches, ridges
Character of a convergent margin
Plates locked = stress and deformation
Plates release = earthquake and tsunami
Platetypes: O/O, O/C (Subduction)
Applied stress: Compression
Resulting strain: shortening
Resulting expression: trench, uplifted mountains
Seismicity: high energy, shallow to very deep
Volcanism: high explosivity, thick lava
TERRANE ACCRETION
GEOG111: LEC 7 - NEW GLOBAL TECTONICS
OCEANIC AND CONTINENTAL CRUST
Continental crust (~2.7 g/cm³)
largely granite
Ocean Crust (~3.0g/cm³)
Largely basalt and gabbro
Tectonics: the folding and breaking of rocks due to pressure within the earths crust
Folding: the bending of crustal rocks, normally due to compression (soft deformation)
Faulting: the breaking and resultant displacement of a rock body (brittle deformation)

Continental Drift: Wegeners Pangea
Modern reconstruction of Pangea
Evidence: geologic, climatic, paleontology, shape
Critical point missing: doesn’t mention any processes

SEAFLOOR TOPOGRAPHY - MARIE THARP
Character of a Divergent margin
Plate types: O/O, C/C
Applied stress: Extension
Resulting strain: Stretching
Surface Expression: Low ridge with central trench
Seismicity: Low energy, shallow depth
Volcanism: Low explosivity, fluid lava
Divergent boundary - fast spreading ridge
Mid ocean ridge processes:
Hot mantle rock risees
Melt forms under the lithosphere
Magma rises into magma chamber in crust and is injected as dikes forming in new crust
law erupts onto ocean floor adding to crust
Plates move apart, cool, and thicken
Character of a transform margin
Plate types: O/O, O/C, C/C
Applied stress: shear
Resulting strain: shearing/twisting laterally
Surface expression: offset surface
Seismicity: low to moderate energy, shallow
Volcanism: not generally present
How do tectonics play a significant role in recycling rocks
Divergent/transform boundaries
Driven by convection currents within the earth
Different boundaries have different surface expression and geophysical indicators
Earthquakes, volcanic activity, trenches, ridges
Character of a convergent margin
Plates locked = stress and deformation
Plates release = earthquake and tsunami
Platetypes: O/O, O/C (Subduction)
Applied stress: Compression
Resulting strain: shortening
Resulting expression: trench, uplifted mountains
Seismicity: high energy, shallow to very deep
Volcanism: high explosivity, thick lava

TERRANE ACCRETION