Classification of Joints
A&P Lab: Classification of Joints
FALL SEMESTER 2024
Instructor: William (Bill) Scharf Made by: Ruby :x
wscharf@rutgers.edu

Fibrous Joints
There are three types of fibrous joints.
Gomphosis
Fibroblasts in periodontal ligaments play an essential role in responses to mechanical force by remodeling and replacing damaged matrix components.
Suture
Bones connected by dense irregular connective tissue with no joint cavity
Syndesmosis
Dense fibrous tissue with an oblique orientation
Cartilaginous Joints
Either hyaline cartilage or fibrocartilage between articulating surfaces and lack a joint cavity.
Synchondroses (contain hyaline cartilage) Symphyses (contain fibrocartilage) |
  |
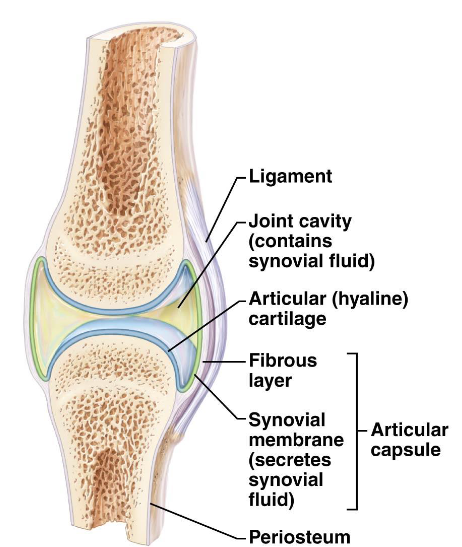
Synovial Joints
Bones are covered with articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage).
Outer fibrous capsule of dense irregular connective tissue + inner layer of loose connective tissue or synovial membrane.
Sensory nerve fibers detect paint and joint stretching.
The joint cavity contains synovial fluid that is viscous and reduces friction.
Fibroblastic cells called type B synoviocytes manufacture synovial fluid which contains hyaluronic acid and lubricin.
Type A synoviocytes are phagocytic white blood cells that capture and remove debris.
Some synovial joints have fat pads made of adipose tissue acting as a cushion.
Some have a sac as an extension of the synovial membrane called a bursa. Bursae contain synovial fluid and act as a cushion.
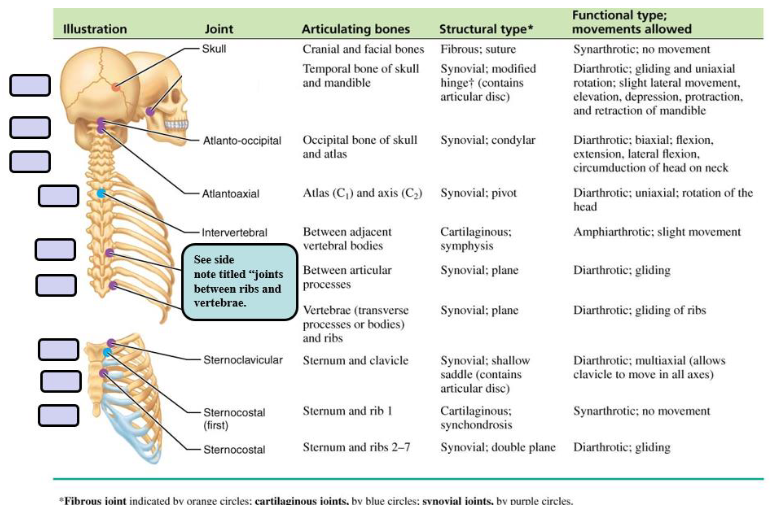
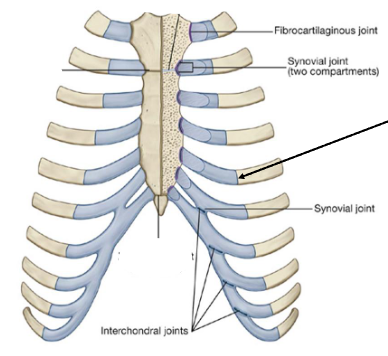
Joints of Rib Cage and Sternum
A&P Lab: Shoulder and Elbow
FALL SEMESTER 2024
Instructor: William (Bill) Scharf Made by: Ruby :x
wscharf@rutgers.edu

Joints of the Rib Cage and Sternum
Sternocostal joints are between the upper 7 costal cartilages and the sternum.
The joint between rib 1 and the manubrium consists of a fibrocartilaginous connection between the manubrium and the costal cartilage.
The 2nd to 7th joints are synovial and have thin capsules reinforced by surrounding sternocostal ligaments.
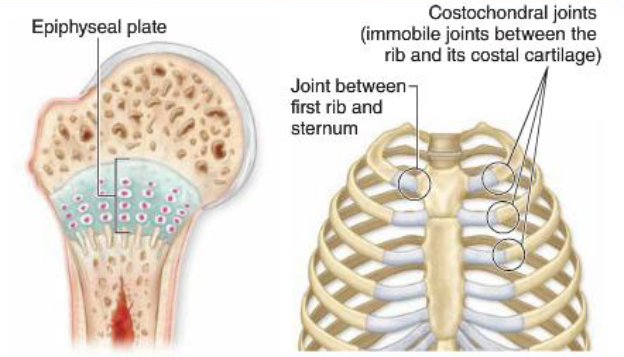
Costochondral joints are between ribs and cartilage.
All are cartilaginous and synarthrotic (no movement).
Interchondral joints occur between the costal cartilages of adjacent ribs.
Mainly between ribs 7-10 are synovial.
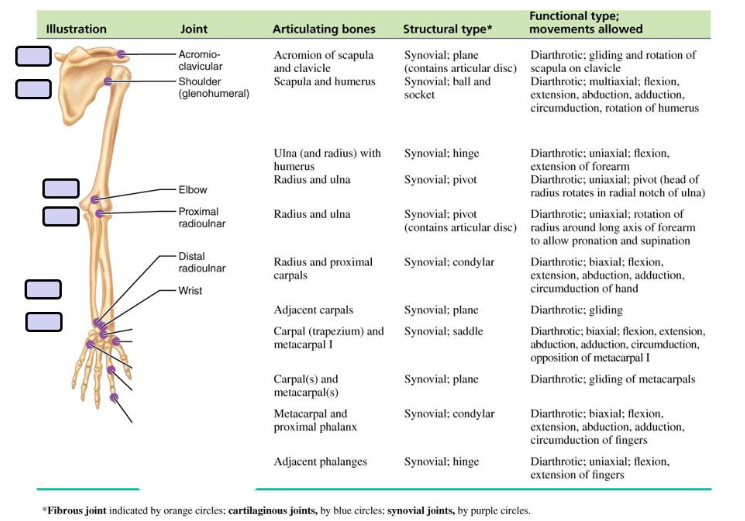
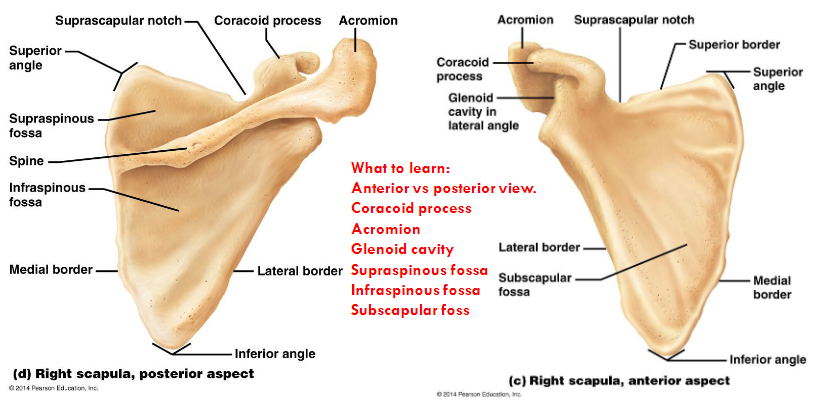
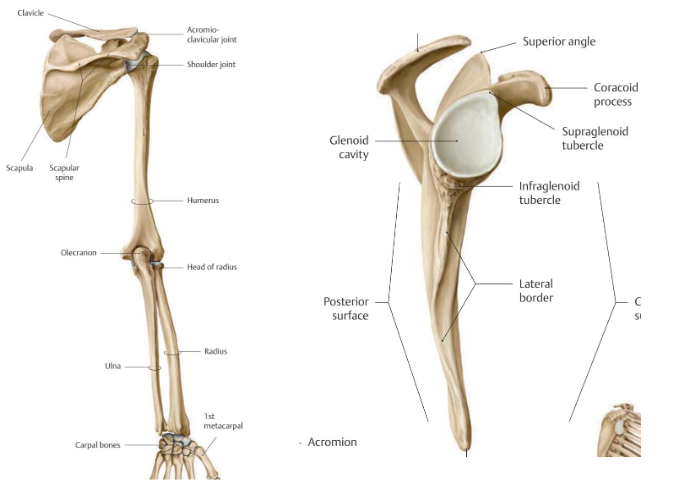
Scapula
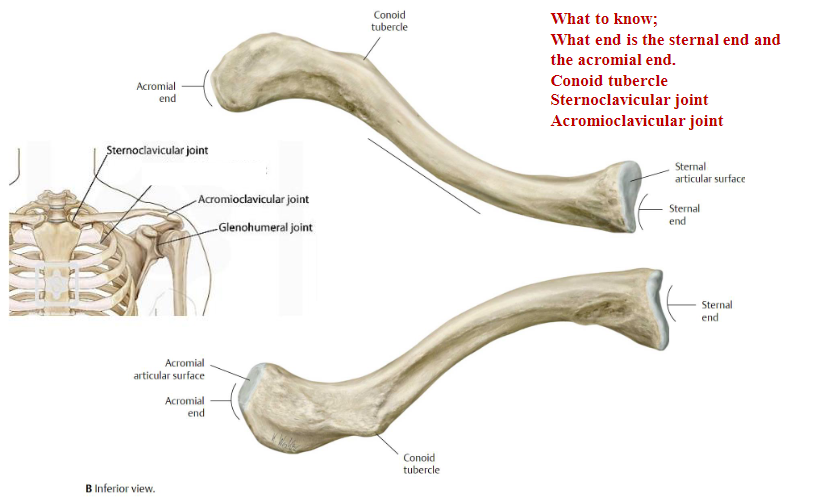
Clavicle
Glenohumeral Joint
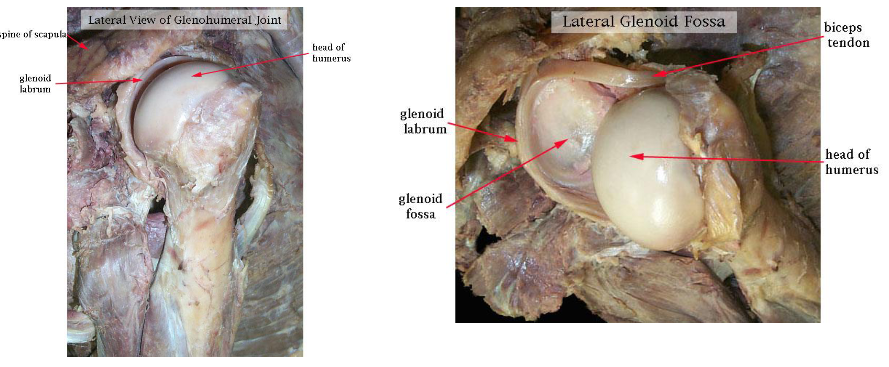
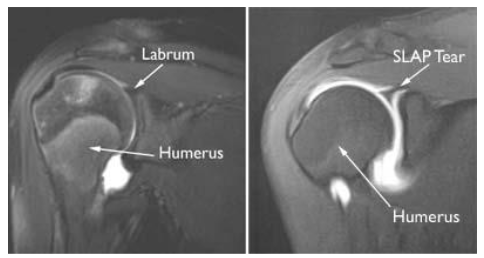
Glenoid Labrum Tear
The humeral head rests in a shallow socket in the shoulder blade called the glenoid cavity.
The head is much larger than the socket
Fibrocartilage called the labrum surrounds the socket to help stabilize the joint
An arthrogram (MRI with contrast) is used to confirm diagnosis of a Slap tear (shoulder labrum anterior to posterior tear).
Shoulder
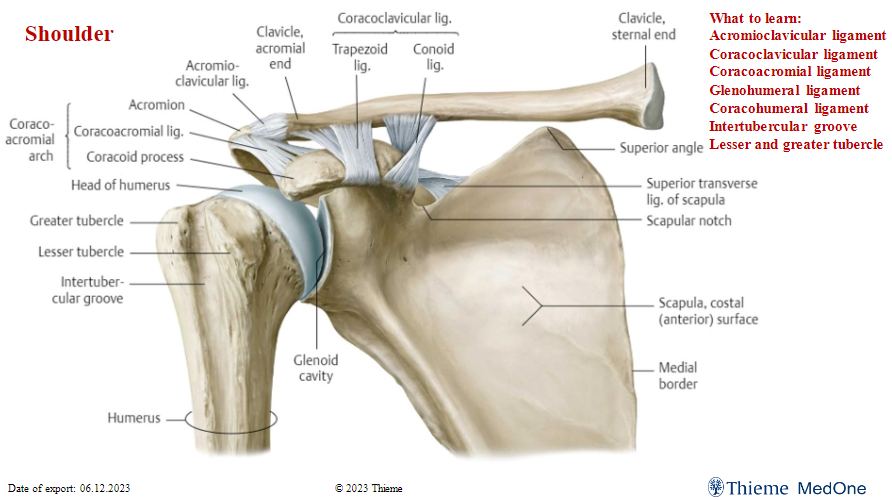
Glenohumeral ligament and Coracohumeral ligament cross off!!! Don’t need to know.
Know the intertubercular groove
Humerus, Ulnar and Radius
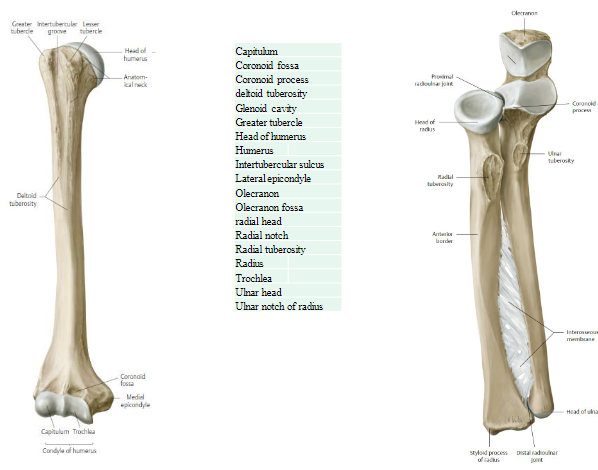
The head of the radius articulates with the radial notch of the ulnar to form the proximal radioulnar joint.
Intersseous membrane is a fibrous joint.
The head of the ulna articulates with the ulnar notch of the radius to form the distal radioulnar joint.
Elbow Joint
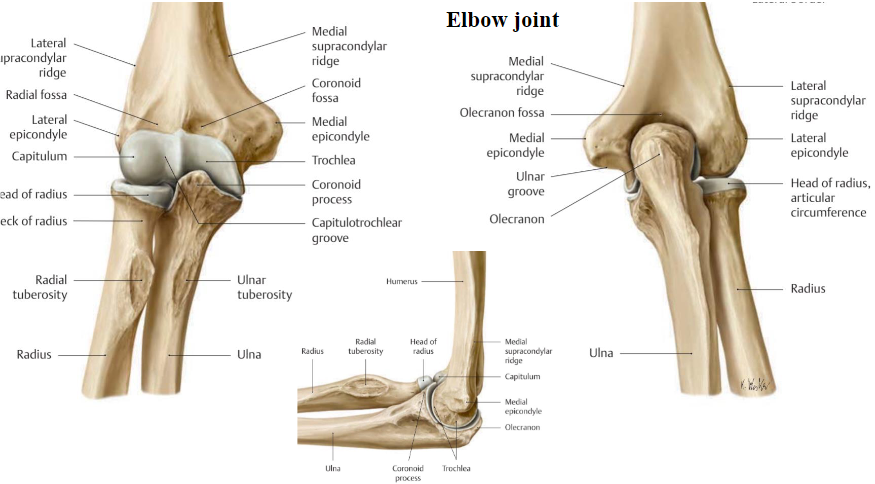
Tab 3
A&P Lab: Knee and Pelvis
FALL SEMESTER 2024
Instructor: William (Bill) Scharf Made by: Ruby :x
wscharf@rutgers.edu

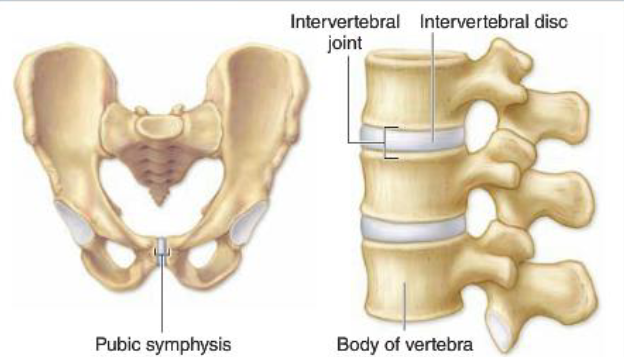
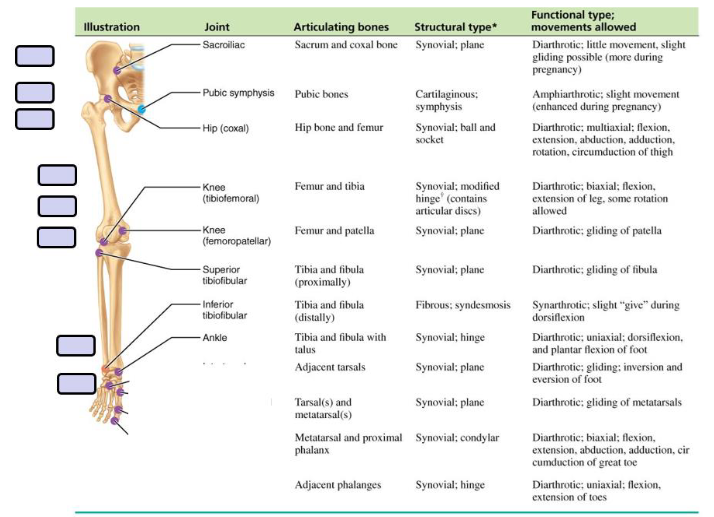
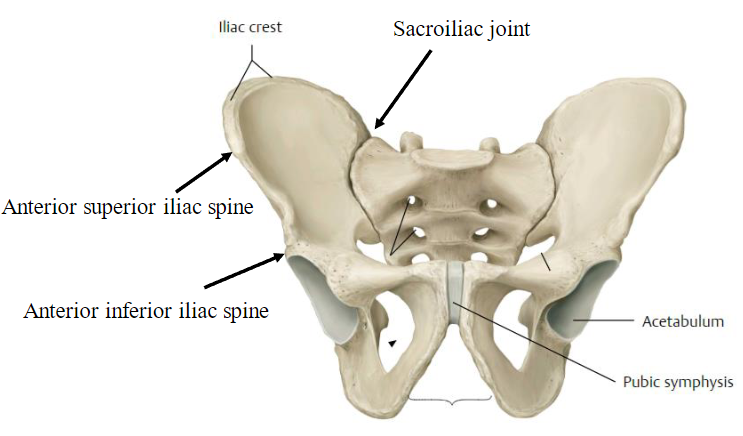
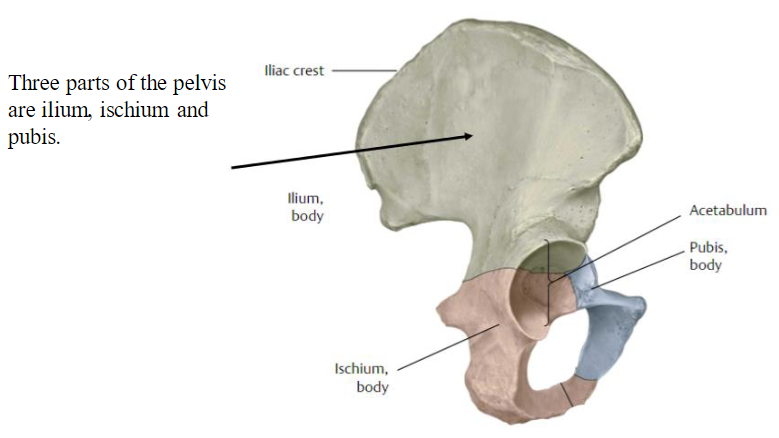
Pelvis
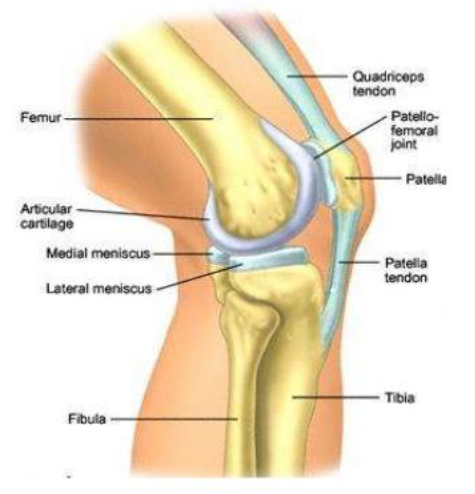
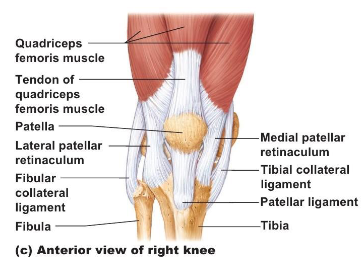
Knee
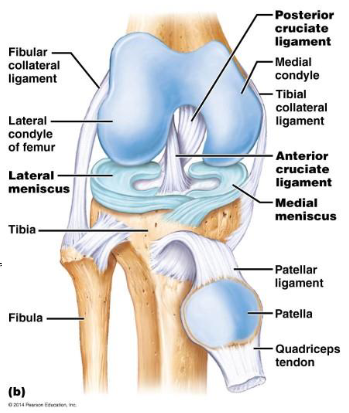

Posterior view of knee
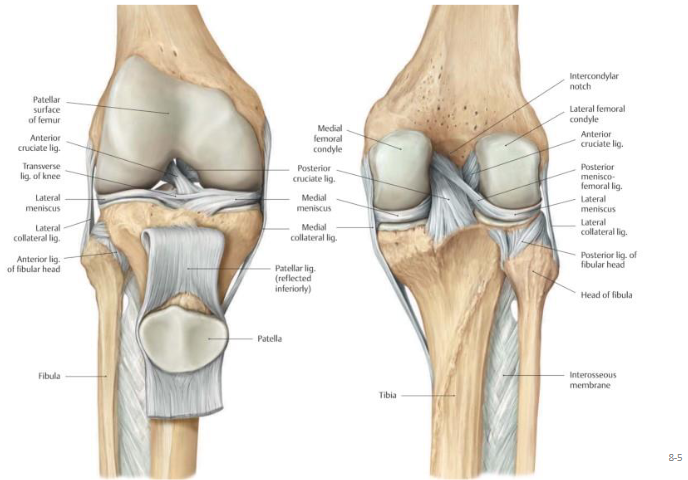
Patellofermoral joint