Lab Safety and Equipment
Dress Code:
Safety goggles must be worn whenever working with chemicals, heat, sharp objects, or any substance that can get in your eyes.
Wear gloves when working with specimens or when handling strong chemicals.
Tie long hair. Don’t wear baggy clothes or hanging jewelry that can touch heat or chemical sources.
Open-toed shoes are not allowed for the lab. Wear sneakers.
General Safety:
Be serious, alert, and never horse around in the lab.
Read all instructions for an investigation and follow all instructions exactly as written.
Do not handle any lab equipment without permission. Some materials should be only handled by the teacher.
If any spills occur, notify the teacher immediately.
NO Food or Drinks in the lab, including gum. Wash your hands before and after handling lab material
Keep the lab area clean & free of books, papers, coats, backpacks, and equipment.
First Aid
Notify the teacher if you have any medical problems, such as asthma & allergies.
Report any accidents or injuries to the teacher immediately.
Know the location of all lab safety equipment, including the fire extinguisher, fire blanket, eyewash station, first aid kit, and safety shower.
Heat / Fire:
Goggles must be worn when heat is involved, such as the hot plate and Bunsen burner.
Point test tubes that are being heated away from yourself and others. Chemicals can splash, boil, or even explode out of a heated tube.
Never heat liquid in a closed container. Expanding gases may blow the container apart.
Never pick up a container that has been heated with your bare hands. Use tongs if instructed.
Chemicals:
Never mix materials for the “fun of it.” You may create a dangerous, possibly explosive substance.
Never use glassware that appears dirty. There may be left over chemicals, which could pose a threat.
Never inhale or smell fumes directly from the container. Use a wafting motion if instructed to smell.
Properly dispose of waste- never put materials down the sink or in the regular trash without told to by your teacher.
Glassware / Sharp Objects:
Handle glassware with care and always wear goggles.
Report broken glassware to the teacher and do not handle. Never put broken glass into the regular trash can.
Notify your teacher immediately of chipped or cracked glassware, and do not use.
Cleanup:
When an investigation is completed, clean up your work area and return all equipment to its proper place as instructed by your teacher. Follow ALL cleanup instructions.
Lab Equipment:
Test tube holder = Used to handle a single test tube, for transport, holding a test tube in a flame, or placing a test tube in a hot water bath,
Thermometer = For measuring temperature.
Beaker = Glass container to hold, mix and heat chemicals
Stirring rod = For stirring chemicals.
Bunsen burner = A heat source in the science lab that uses natural gas.
Retort stand = Clamps can be attached to this so that objects can be held up keeping your hands free.
Test tube rack = Used to hold groups of test tubes.
Electronic balance = Used to find the mass of various materials.
Flint striker = Used to ignite the Bunsen burner.
Mortar and pestle = Used to grind chemicals into powder.
Funnel = Used for filtering and for adding chemicals without spilling.
Scoopula (metal scoop) = Used to add (“scoop”) small amounts of solid from place to place.
Beaker tongs = Used to transport hot beakers.
Test tube brush = Used to clean glassware.
Graduated cylinder = Used for accurately measuring the volume of liquids.
Eye dropper = For adding small amounts of chemicals — usually by drops.
Rubber stopper = Used to plug up a test tube — can have holes for thermometers and for other probes that may be used.
Ring clamp (iron ring) = Attaches to a retort stand and used to hold an object above a Bunsen burner flame.
Test tube = Used for mixing and heating chemicals and running reactions — smaller than a beaker or flask.
Hot plate = Used as a heat source that can easily be adjusted to control the temperature.
Safety Symbols: HHPS
HHPS stands for Hazardous Household Products Symbol
It contains a set of symbols that warn buyers what dangers the product can cause
These symbols are mandatory for all chemical products, and they MUST be drawn on the labels of all chemical products.
a) Poison

A poisonous substance causes immediate damage to an organism.
b) Flammable

A flammable substance catches fire very easily.
c) Explosive
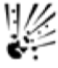
An explosive substance can explode easily if heated or dropped.
d) Corrosive

A corrosive substance can easily eat through other pieces of matter.
Borders
The HHPS also describes to us how severe the danger is with these borders that outline the different symbols.



[Physical Hazards]

Explosives: Chemicals that can detonate (blow up)
Explosive
Self reactive
Organic peroxide

Flammables: Chemicals that can ignite (catch fire) easily
Self- reactive
Pyrophoric self-heating
Emits flammable gas
Organic peroxides

Oxidizers: Chemicals that may cause or intensify combustion causing rapid fire upon contact

Gases: Chemicals that can escape at a velocity of a missile, becoming uncontrolled rockets or pinwheels, causing explosion, harming health
Self reactive
Pyrophoric self-heating
Emits flammable gas
Organic peroxides

Corrosives: Damages metals and living tissues on contact
Skin corrosion
Serious damage to eyes
Corrosive to metals
Health Hazards

Chemicals that are fatal or toxic
Acute Toxicity

Harmful/Irritant: Chemicals that are harmful on exposure, harmful if swallowed or inhaled; cause skin irritation, eye irritation, allergic skin reaction, respiratory irritation, drowsiness, dizziness
Irritant (skin and eye)
Skin Sensitizer
Acute Toxicity (harmful)
Narcotic Effects
Respiratory Tract Irritant

Health Hazard: Chemicals that may cause cancer, genetic defects, allergy or asthma symptoms or breathing difficulties; may damage fertility and adversely affect organs
Carcinogenity
Respiratory Sensitizer
Reproductive Toxicity
Target Organ
Toxicity Mutagencity
Environmental Hazards
Environmental Toxic: Chemicals that are extremely toxic to aquatic life, affect public health; harm the environment by damaging the ozone layer.
Aquatic Toxicity