Chapter 14 - Amniotic Fluid
Physiology
Function
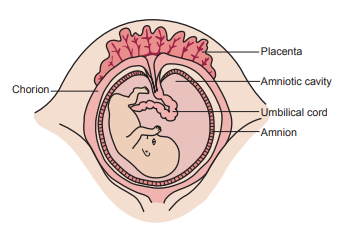
Amniotic fluid is present in the amnion, a membranous sac that surrounds the fetus.
It acts as a cushion for the fetus, allows fetal movement, stablizes the temperature, permits proper lung development and allows exchanges of water and chemicals to take place between the fluid, the fetus and the maternal circulation (intramembranous flow).
Volume
- Amniotic fluid volume is regulated by a balance between the production of fetal urine and lung fluid and the absorption from fetal swallowing and intramembranous flow.
- The amount of amniotic fluid increases throughout pregnancy.
- During the first trimester, approximately 35 mL of amniotic fluid is derived primarily from the maternal circulation.
- After the first trimester, fetal urine is the major contributor to the amniotic fluid volume and it is regulated by fetal swallowing.
- Failure to swallow results in accumulation (polyhydramnios) and is an indication of fetal distress.
- It is often associated with neural tube disorders, fetal structural anomalies, cardiac arrhythmias, congenital infections or chromosomal abnormalities.
- Increased fetal swallowing, urinary tract deformities and membrane leakage are possible causes of decreased amniotic fluid (oligohydramnios).
- Oligohydramnios may be associated with umbilical cord compression, resulting in decelerated heart rate and fetal death.
- During the latter third to half of pregnancy, the fetus secretes a volume of lung liquid necessary to expand the lungs with growth.
- During each episode of fetal breathing movement, secreted lung liquid enters the amniotic fluid, as evidenced by lung surfactants that serve as an index of fetal lung maturity.
- During the third trimester, amniotic fluid reaches a peak volume of 1 L.
\
Chemical Composition
- Amniotic fluid has a composition similar to that of the maternal plasma and contains a small amount of sloughed fetal cells from the skin, the digestive system and the urinary tract.
- The fluid also contains biochemical substances that are produced by the fetus, such as bilirubin, lipids, enzymes, electrolytes, nitrogenous compounds and proteins.
- The chemical composition of the amniotic fluid changes when fetal urine production begins.
- The concentrations of creatinine, urea and uric acid increase, whereas glucose and protein concentrations decrease.
- Concentrations of electrolytes, enzymes, hormones, and metabolic end products also vary but are of little clinical significance.
\
Maternal Urine vs Amniotic Fluid
| Maternal Urine | Amniotic Fluid | |
|---|---|---|
| Creatinine | >3.5 mg/dL, as high as 10 mg/dL | <3.5 mg/dL |
| Urea | >30 mg/dL, as high as 300 mg/dL | <30 mg/dL |
| Glucose | negative | positive |
| Protein | negative | positive |
| Fern Test | negative | positive |
- In the fern test, a vaginal fluid specimen is spread on a glass slide, air-dried at room temperature, and observed microscopically for the presence of “fern-like” crystals.
\
Specimen Collection
Collection
- Amniotic fluid is obtained by needle aspiration into the amniotic sac, a procedure called amniocentesis.
- The procedure most frequently performed is a transabdominal amniocentesis.
- Using continuous ultrasound for guidance, the physician locates the fetus and placenta to safely perform the procedure.
- A thin, hollow needle is inserted through the mother’s abdomen into the mother’s uterus and into the amniotic sac to aspirate the amniotic fluid.
- Vaginal amniocentesis may also be performed; however, this method carries a greater risk of infection.
- In general, amniocentesis is a safe procedure, particularly when performed after the 14th week of gestation.
- Fluid for chromosome analysis is usually collected at approximately 16 weeks’ gestation, whereas tests for fetal distress and maturity are performed later in the third trimester.
- A maximum of 30 mL of amniotic fluid is collected in sterile syringes.
- The first 2 or 3 mL collected can be contaminated by maternal blood, tissue fluid, and cells and are discarded.
- All fluid for chemical testing should be separated from cellular elements and debris using centrifugation or filtration as soon as possible to prevent distortion of chemical constituents by cellular metabolism or disintegration.
- Fluid for bilirubin analysis in cases of hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN) are placed in amber-colored tubes or covered with a black plastic cover to protect from light.
- Fluid for fetal lung maturity (FLM) tests should be placed in ice and can be refrigerated or frozen up to 72 hours prior to testing.
- Frozen specimens should be thoroughly mixed, by vortexing, after thawing.
- Repeated freeze-thawing is not recommended.
- Filtration is recommended for FLM methods to prevent loss of the phospholipids.
- Specimens for cytogenetic studies are maintained at room temperature or body temperature (37°C incubation) prior to analysis to prolong the life of the cells needed for analysis.
Indications for Amniocentesis
- Amniocentesis is recommended when blood screening tests and ultrasonography yield results that are abnormal.
- Biochemical substances produced by the fetus can be analyzed by fluorescence polarization and thin-layer chromatography to evaluate the health of the fetus.
- Fetal epithelial cells in amniotic fluid indicate the genetic material of the fetus and the biochemical substances that the fetus has produced.
\
Indications for Performing Amniocentesis
- Amniocentesis may be indicated at 15 to 18 weeks of gestation for the following conditions to determine early treatment or intervention:
- mother’s age of 35 or more at delivery
- family history of chromosome abnormalities, metabolic disorders and genetic diseases
- earlier pregnancy or child with birth defect or neural tube disorder
- elevated maternal serum alpha fetoprotein
- abnormal triple marker screening test
- three or more miscarriages
- Evaluation of amniocentesis is indicated later in the pregnancy (20 to 42 weeks) to evaluate:
- fetal lung maturity
- fetal distress
- hemolytic disease of the newborn caused by Rh blood type incompatibility
- infection
\
\
\
Appearance
| Color | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|
| colorless | normal |
| slight to moderate turbidity | normal (late stage of fetal development) |
| blood-streaked | traumatic tap, abdominal trauma, or intra-amniotic hemorrhage |
| yellow | presence of bilirubin, red blood cell destruction (HDN) |
| dark green | presence of meconium (newborn’s first bowel movement) |
| dark red-brown | fetal death |
\
Tests for Fetal Distress
Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn
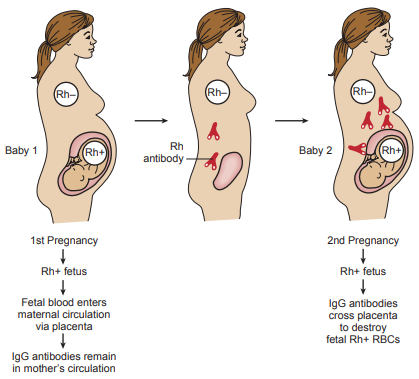
Initial exposure to foreign red cell antigens occurs during gestation and delivery of the placenta, when fetal red blood cells enter into the maternal circulation and stimulate the mother to produce antibodies to the antigen.
These bind to the antigen on the fetal cells and destroy them, forming unconjugated bilirubin in the amniotic fluid.
The measurement of amniotic fluid bilirubin is performed by spectrophotometric analysis.
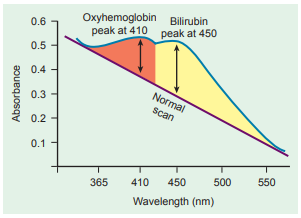
The optical density (OD) of the fluid is measured in intervals between 365 nm and 550 nm and the readings plotted on semilogarithmic graph paper.
In normal fluid, the OD is highest at 365 nm and decreases linearly to 550 nm, illustrated by a straight line.
When bilirubin is present, a rise in OD is seen at 450 nm because this is the wavelength of maximum bilirubin absorption.
The maximum absorbance of oxyhemoglobin occurs at 410 nm and can interfere with the bilirubin absorption peak, but it can be removed by extraction with chloroform if necessary.
A control may be prepared by diluting commercial chemistry control sera 1 to 10 with normal saline and treating it in the same manner as the patient specimen.
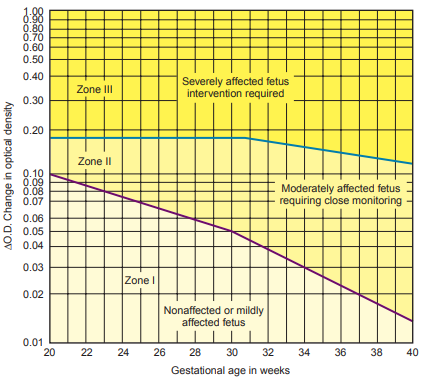
The difference between the OD of the theoretic baseline and the OD at 450 nm (absorbance difference ∆A450) represents the amniotic fluid bilirubin concentration, which is then plotted on a Liley graph to determine the severity of the hemolytic disease.
Values falling in zone I indicate no more than a mildly affected fetus
Values falling in zone II require careful monitoring.
Values falling in zone III suggests a severely affected fetus.
- Intervention through induction of labor or intrauterine exchange transfusion must be considered when a ∆A450 is plotted in zone III.
Neural Tube Defects
- Increased levels of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in both the maternal circulation and the amniotic fluid can be indicative of the skin failing to close over neural tissue, causing fetal neural tube defects.
- AFP is the major protein produced by the fetal liver during early gestation (prior to 18 weeks).
- Measurement of amniotic fluid AFP levels is indicated when maternal serum levels are elevated, a family history of previous neural tube defects exists, or there is a multiple pregnancy.
- Normal values are based on the week of gestational age, as the fetus produces maximal AFP between 12 and 15 weeks’ gestation, after which levels in amniotic fluid begin to decline.
- Both serum and amniotic fluid AFP levels are reported in terms of multiples of the median (MoM).
- A value two times the median value is considered abnormal (greater than two MoM) for both maternal serum and amniotic fluid.
- Elevated amniotic fluid AFP levels are followed by measurement of amniotic acetylcholinesterase (AChE).
- The test is more specific for neural tube disorders than AFP.
- It should not be performed on a bloody specimen, because blood contains AChE.
\
Tests for Fetal Maturity
Fetal Lung Maturity
- Respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) is the most frequent complication of early delivery and is a cause of morbidity and mortality in the premature infant.
- This disease is caused by a lack of lung surfactant, a substance that normally appears in mature lungs and allows the alveoli (air sacs of the lung) to remain open throughout respiration, prevent them from collapsing by decreasing surface tension and allow them to inflate with air more easily.
Lecithin-Sphingomyelin Ratio
- Lecithin is the primary component of the surfactants (phospholipids, neutral lipids and proteins) that make up the alveolar lining and account for alveolar stability.
- Lecithin is produced at a relatively low and constant rate until the 35th week of gestation, at which time a noticeable increase in its production occurs, resulting in the stabilization of the fetal lung alveoli.
- Sphingomyelin is also produced at a constant rate after about 26 weeks’ gestation and can serve as a control on which to base the rise in lecithin.
- Prior to 35 weeks’ gestation, the L/S ratio is usually less than 1.6 because large amounts of lecithin are not being produced at this time, but It will rise to 2.0 or higher when lecithin production increases to prevent alveolar collapse.
- A preterm delivery is usually considered to be a relatively safe procedure.
- Falsely elevated results are encountered in fluid contaminated with blood or meconium as both these substances contain lecithin and sphingomyelin.
- Quantitative measurement of lecithin and sphingomyelin is performed using thin-layer chromatography, but the procedure is labor intensive and subject to high coefficients of variation.
- Many have replaced it with more cost-effective procedures like phosphatidyl glycerol immunoassays, fluorescence polarization, and lamellar body density.
\
Amniostat-FLM
- The presence of another lung surface lipid, phosphatidyl glycerol, is also essential for adequate lung maturity.
- The production of phosphatidyl glycerol normally parallels that of lecithin, but its production is delayed in cases of maternal diabetes.
- Respiratory distress occurs in the presence of an L/S ratio of 2.0.
- The immunologic agglutination test for phosphatidyl glycerol is more rapid and does not require a laboratory to be equipped to perform thin-layer chromatography.
\
Foam Stability
It is a mechanical screening test used to determine the presence of individual lung-surface lipid concentrations.
To perform this procedure:
- 0.5 mL of amniotic fluid is added to tubes containing increasing amounts of 95% ethanol ranging from 0.42 to 0.55 mL in 0.01-mL increments.
- These are vigorously shaked for 15 seconds and then left to sit undisturbed for 15 minutes.
- If a continuous line of bubbles forms around the outside edge, it indicates a sufficient amount of phospholipid is available to reduce the surface tension of the fluid even in the presence of alcohol, an antifoaming agent.
- A value of 47 or higher indicates FLM.
Blood and meconium cause false-negative results as they can reduce surface tension.
\
Microviscosity: Fluorescence Polarization Assay
- The presence of phospholipids decreases the microviscosity of the amniotic fluid, and this decrease can be measured using fluorescence polarization.
- The TDx/TDxFLx Fetal Lung Maturity II (FLMII) assay is a reagent system for the quantitative measurement of the ratio of surfactant to albumin in amniotic fluid for assessment of lung maturity of the fetus.
- This assay measures the polarization of a fluorescent dye that combines with both surfactants and albumin.
- Dye bound to surfactant has a longer fluorescence lifetime and exhibits low polarization, whereas dye bound to albumin has a decreased fluorescence lifetime and has high polarization.
- Albumin is used as an internal standard in the same manner as sphingomyelin because it remains at a constant level throughout gestation.
- The recorded changes in polarization produce a surfactant/albumin ratio expressed in milligrams surfactant to grams albumin that is compared with a calibration standard curve that includes phosphatidyl glycerol and ranges from 0 to 160 mg/g.
- Sample results are calculated from the stored standard curve using polarization values generated for each sample.
- A value of 55 mg surfactant per gram albumin or greater provides a conservative indicator of FLM and lower values may be considered.
- Immature results with the FLM II assay are less than or equal to 39 mg/g.
- Sequential L/S testing is recommended in such cases.
- Results between 40 mg/g and 54 mg/g cannot be declared “mature” or “immature” and must be evaluated with caution.
- An accurate gestational age is an important consideration in interpreting the results.
- The test requires at least 1.0 mL of amniotic fluid that has been filtered rather than centrifuged to prevent sedimentation of the lipids and reporting a falsely decreased result.
- Specimens contaminated with blood, meconium, suspected maternal urine and visibly icteric samples should not be used.
\
Lamellar Bodies and Optical Density
- The surfactants responsible for FLM are produced and secreted by the type II pneumocytes of the fetal lung and stored in the form of structures termed lamellar bodies at about 20 weeks of gestation.
- The lamellar bodies enter the alveolar spaces to provide surfactant and also enter the amniotic fluid at about 26 weeks of gestation.
- As the fetal lung matures, increased lamellar body production is proportional to the increase in amniotic fluid phospholipids and the L/S ratio.
- The presence of lamellar bodies increases the OD of the amniotic fluid.
- Specimens are centrifuged at 2000 g for 10 minutes and examined at a wavelength of 650 nm.
- An OD of 0.150 has been shown to correlate well with an L/S ratio of greater than or equal to 2.0 and the presence of phosphatidyl glycerol.
- Lamellar body diameter is similar to that of small platelets; therefore, lamellar body counts (LBCs) can be obtained rapidly with use of the platelet channel of hematology analyzers.
- The various instruments use different principles to identify platelets and are usually not invalidated by the presence of lysed blood, bilirubin or meconium.
- LBCs performed on amniotic fluid stored at 4°C are stable for up to 10 days.
- A count of 32,000-35,400 (depending on instrument used) or more particles per microliter represents adequate FLM.
\
\
Summary of Normal Values
| Test | Normal Values |
|---|---|
| AFP | <2.0 MoM |
| L/S Ratio | ≥2.0 |
| Amniostat-FLM | positive |
| Foam Stability Index | ≥47 |
| FLMII | ≥55 mg/g |
| OD 650 | ≥0.150 |
| LBC | ≥32,000/mL |
\