
In Class Notes 10/29: Understanding Puberty and Adolescent Development
Puberty 🌱
Puberty is a phase of rapid physical growth and sexual maturation that typically begins between the ages of 8 and 14. The norm is around 12 to 14 years old, but for girls, it starts about 2 years before boys.
Timing of Puberty
The timing of puberty is mainly determined by genetics. For girls, if their mother started puberty earlier, they probably will too. For boys, if their father started earlier or later, that's what will likely happen to them as well. Weight and stress can also influence the timing of puberty.
Physical Changes
During puberty, growth proceeds from the extremities to the core, which is the opposite of what happens in toddlers. The growth sequence is as follows:
Hands and feet grow first
Arms and legs grow next
Core grows last
This is why many kids in early puberty look like they're all arms and legs.
Sequence of Changes in Girls
Stage | Description |
1 | Nipple growth and pubic hair |
2 | Growth spurt in height |
3 | Accumulation of breast and hip fat |
4 | First menstrual period (menarche) |
5 | Second growth spurt in height |
Body growth is complete by about 4 years after it started.
Sequence of Changes in Boys
Stage | Description |
1 | Growth spurt |
2 | Growth of testes, penis, and pubic hair |
3 | First ejaculation of seminal fluid (spermarche) |
4 | Growth of facial hair |
5 | Peak growth spurt |
Final height is reached by age 20.
Hormonal Changes
Hormone production is regulated in the brain by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. These hormones stimulate the adrenal glands and gonads, causing physical and psychological changes.
Psychological Effects
"The storm and stress of adolescence" - a time of significant psychological change.
Moodiness
Attraction and influence of emotions
Social drama and relationship drama
Depression and anxiety disorders (more common in girls, but often underdiagnosed in boys)
Brain Changes
Brain growth and development accelerate during puberty, similar to the rapid growth seen in infancy and early childhood. This is a time of significant brain restructuring.
Psychopathology
Mid to late adolescence is the time when serious psychopathology can begin. Depression, anxiety disorders, and bipolar disorder may first appear during this stage.
"Depression in boys often looks different than depression in girls. In boys, it may manifest as acting out, rather than sadness and withdrawal."## 🧠 Brain Development in Adolescence
Limbic System and Prefrontal Cortex
The limbic system, located near the core of the brain, is responsible for fear and strong emotions like anger. In adolescents, the limbic system is on overdrive, while the prefrontal cortex, which controls impulses and logical thinking, is still developing.
"The prefrontal cortex is like the brakes on a car. It helps you stop and think before acting on impulse."
The prefrontal cortex is not fully developed until the age of 25, which is why adolescents often struggle with impulse control and emotional regulation.
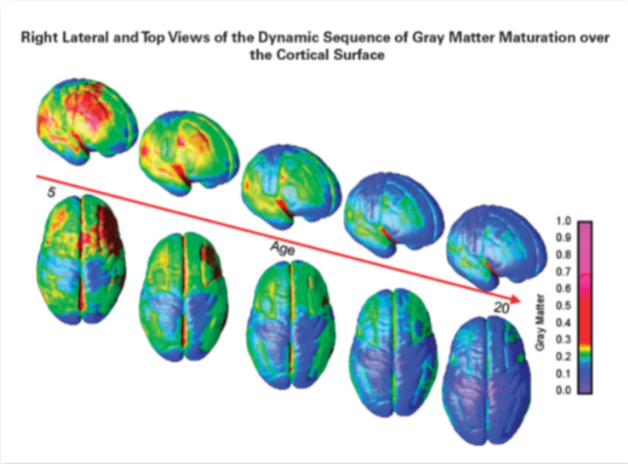
Brain Pruning and Maturation
During adolescence, the brain undergoes a process called pruning, where unnecessary connections are eliminated to make way for smoother cognition paths. This process starts at the back of the brain and moves forward, which is why the frontal lobes and prefrontal cortex are the last to finish developing.
Brain Region | Age of Maturity |
Occipital Lobe | 15-16 years old |
Frontal Lobes | 25 years old |
Prefrontal Cortex | 25 years old |
Circadian Rhythm and Sleep
The circadian rhythm, or biological clock, governs our day-night cycle of biological activity. In adolescents, the circadian rhythm shifts later due to puberty, making it harder to wake up in the morning.
"The circadian rhythm is like an internal clock that tells our body when to be awake and when to sleep."
Genetics and culture also influence our tendency to be morning people or night owls. The blue spectrum light from electronics can suppress melatonin production, making it harder to fall asleep.
Factors Affecting Sleep | Description |
Circadian Rhythm | Biological clock that governs day-night cycle |
Genetics | Influence our tendency to be morning people or night owls |
Culture | Technology and social media can interfere with sleep |
Blue Spectrum Light | Suppresses melatonin production |
Sleep Deprivation in High School Seniors
Three out of four high school seniors are seriously sleep deprived. Factors contributing to sleep deprivation include:
Workload and academic pressure
Stress and expectations from teachers and parents
Extracurricular activities and part-time jobs
Social media and technology use before bed
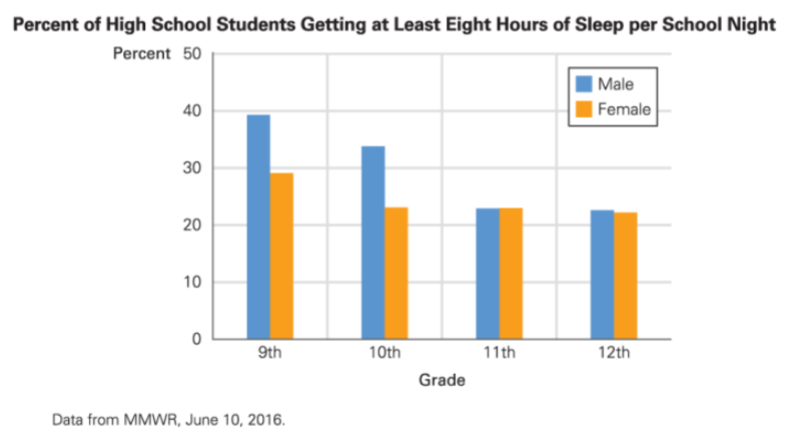
Grade Level | Percentage of Students Getting 8 Hours of Sleep |
9th Grade | 40% (male), 30% (female) |
10th Grade | 35% (male), 25% (female) |
11th Grade | 20% (male), 20% (female) |
12th Grade | 20% (male), 20% (female) |
Note: The data shows that boys tend to get more sleep than girls in 9th and 10th grade, but the difference disappears in 11th and 12th grade.## Adolescent Development 🤯
Sleep Patterns and Impulsivity
Adolescents tend to be sleep-deprived due to a combination of factors, including a natural shift in sleep patterns and cultural influences. Girls, in particular, tend to prioritize getting ready in the morning, while boys often rush to get out the door.
"Impulsivity is the tendency to act on impulse without fully thinking through the consequences of one's actions."
Hormones, such as testosterone, contribute to increased impulsivity in adolescents. This, combined with an immature prefrontal cortex, can lead to reckless decision-making.
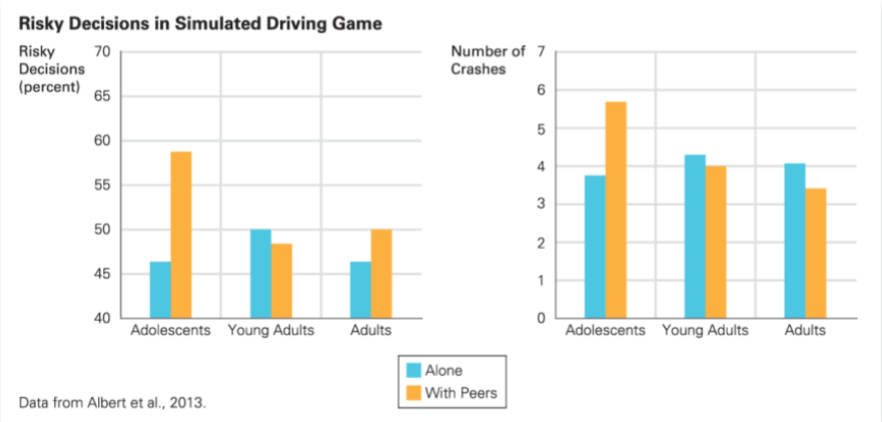
Risk-Taking and Social Approval
Adolescents are more likely to engage in risk-taking behavior, especially when with their peers. This is due to the brain's reward system and the desire for social approval.
Age Group | Risky Decisions Alone | Risky Decisions with Peers |
Adolescents | Some | Many |
Young Adults | Few | Fewer |
Adults | Few | Few |
Nutritional Issues
Adolescents often have unhealthy diets, leading to deficiencies in essential minerals like iron, calcium, and zinc. This can be attributed to peer influence and environmental factors.
Mineral | Importance | Deficiency Risks |
Iron | Essential for healthy red blood cells | Fatigue, weakness, poor cognitive function |
Calcium | Crucial for bone growth and development | Weakened bones, osteoporosis |
Zinc | Important for immune function and wound healing | Impaired immune function, slow wound healing |
Eating Disorders
Eating disorders, such as anorexia, bulimia, and binge eating disorder, can develop during adolescence. These disorders are often linked to body image issues, depression, and anxiety.
Eating Disorder | Characteristics |
Anorexia | Restrictive eating, significant weight loss |
Bulimia | Bingeing and purging, weight fluctuations |
Binge Eating Disorder | Recurring episodes of excessive eating |
Sexual Maturation
Sexuality is a complex and multidimensional aspect of adolescent development. Primary and secondary sexual characteristics develop during this stage.
Primary Sexual Characteristics | Secondary Sexual Characteristics |
Development of reproductive organs (e.g., uterus, testicles) | Development of observable physical traits (e.g., facial hair, breast development) |
Adolescent Sexual Behavior
Sexual activity among friends is a strong predictor of an adolescent's sexual activity. Trends show a decrease in teen pregnancy rates and an increase in the use of protection.
Trend | Description |
Decreased teen pregnancy rate | 50-year low in the US |
Decreased teen abortion rate | Correlated with increased use of protection |
Increased use of protection | More adolescents using condoms and other forms of birth control |
States with High Teen Birth Rates
The following states have the highest teen birth rates in the US:
Arkansas
Mississippi
Louisiana
Oklahoma
Alabama
West Virginia
Kentucky
Texas
Tennessee
These states often have poor education systems, highlighting a correlation between education and teen birth rates.## 🧠 Formal Operational Thought
Formal operational thought is a stage of cognitive development characterized by the ability to use systematic logic and think about abstract ideas. This stage is typically reached during puberty.
"Formal operational thought is the ability to think logically and abstractly, using hypothetical thought and considering possibilities that may not be reflective of reality."
Characteristics of Formal Operational Thought
Ability to use systematic logic
Ability to think about abstract ideas
Use of hypothetical thought
Consideration of possibilities that may not be reflective of reality
Ability to use both deductive and inductive reasoning
Deductive and Inductive Reasoning
Type of Reasoning | Definition |
Deductive Reasoning | Reasoning from a general statement to a specific conclusion |
Inductive Reasoning | Reasoning from specific observations to a general conclusion |
🤯 Adolescent Thinking
Adolescent thinking is characterized by four distinct features:
1. Adolescent Egocentrism
"Adolescent egocentrism is the tendency to focus on oneself to the exclusion of others, and to be unable to take someone else's perspective."
Characteristics:
Self-centeredness
Inability to consider others' perspectives
Everything is about oneself
2. Rumination
"Rumination is the tendency to get stuck on things and to be unable to let go of negative thoughts or emotions."
Characteristics:
Inability to let go of negative thoughts or emotions
Tendency to dwell on past experiences or relationships
3. Imaginary Audience
"The imaginary audience is the belief that everyone else is watching and criticizing one's appearance, ideas, and behaviors."
Characteristics:
Belief that others are constantly watching and judging
Self-consciousness and anxiety about what others think
4. Personal Fable
"The personal fable is the belief that one's own thoughts, feelings, and experiences are more intense and important than others."
Characteristics:
Belief that one's own experiences are unique and more significant than others
Tendency to dramatize one's own emotions and experiences
5. Invincibility Fable
"The invincibility fable is the conviction that nothing bad can ever happen to oneself."
Characteristics:
Belief that one is invincible and immune to harm
Tendency to engage in risky behavior and poor decision-making
🧠 Dual Processing
Dual processing refers to the idea that the human brain has two separate processing networks:
Analytical logical reasoning
Intuitive emotional responses
Processing Network | Characteristics |
Analytical Logical Reasoning | Logical, analytical, and systematic thinking |
Intuitive Emotional Responses | Emotional, instinctual, and automatic responses |
Implications for Adolescent Thinking
Adolescents tend to rely more on intuitive emotional responses due to the underdevelopment of the prefrontal cortex
This can lead to impulsive and emotional decision-making
With age, adolescents become more logical and less idealistic as the prefrontal cortex develops
In Class Notes 10/29: Understanding Puberty and Adolescent Development
Puberty 🌱
Puberty is a phase of rapid physical growth and sexual maturation that typically begins between the ages of 8 and 14. The norm is around 12 to 14 years old, but for girls, it starts about 2 years before boys.
Timing of Puberty
The timing of puberty is mainly determined by genetics. For girls, if their mother started puberty earlier, they probably will too. For boys, if their father started earlier or later, that's what will likely happen to them as well. Weight and stress can also influence the timing of puberty.
Physical Changes
During puberty, growth proceeds from the extremities to the core, which is the opposite of what happens in toddlers. The growth sequence is as follows:
Hands and feet grow first
Arms and legs grow next
Core grows last
This is why many kids in early puberty look like they're all arms and legs.
Sequence of Changes in Girls
Stage | Description |
1 | Nipple growth and pubic hair |
2 | Growth spurt in height |
3 | Accumulation of breast and hip fat |
4 | First menstrual period (menarche) |
5 | Second growth spurt in height |
Body growth is complete by about 4 years after it started.
Sequence of Changes in Boys
Stage | Description |
1 | Growth spurt |
2 | Growth of testes, penis, and pubic hair |
3 | First ejaculation of seminal fluid (spermarche) |
4 | Growth of facial hair |
5 | Peak growth spurt |
Final height is reached by age 20.
Hormonal Changes
Hormone production is regulated in the brain by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. These hormones stimulate the adrenal glands and gonads, causing physical and psychological changes.
Psychological Effects
"The storm and stress of adolescence" - a time of significant psychological change.
Moodiness
Attraction and influence of emotions
Social drama and relationship drama
Depression and anxiety disorders (more common in girls, but often underdiagnosed in boys)
Brain Changes
Brain growth and development accelerate during puberty, similar to the rapid growth seen in infancy and early childhood. This is a time of significant brain restructuring.
Psychopathology
Mid to late adolescence is the time when serious psychopathology can begin. Depression, anxiety disorders, and bipolar disorder may first appear during this stage.
"Depression in boys often looks different than depression in girls. In boys, it may manifest as acting out, rather than sadness and withdrawal."## 🧠 Brain Development in Adolescence
Limbic System and Prefrontal Cortex
The limbic system, located near the core of the brain, is responsible for fear and strong emotions like anger. In adolescents, the limbic system is on overdrive, while the prefrontal cortex, which controls impulses and logical thinking, is still developing.
"The prefrontal cortex is like the brakes on a car. It helps you stop and think before acting on impulse."
The prefrontal cortex is not fully developed until the age of 25, which is why adolescents often struggle with impulse control and emotional regulation.
Brain Pruning and Maturation
During adolescence, the brain undergoes a process called pruning, where unnecessary connections are eliminated to make way for smoother cognition paths. This process starts at the back of the brain and moves forward, which is why the frontal lobes and prefrontal cortex are the last to finish developing.
Brain Region | Age of Maturity |
Occipital Lobe | 15-16 years old |
Frontal Lobes | 25 years old |
Prefrontal Cortex | 25 years old |

Circadian Rhythm and Sleep
The circadian rhythm, or biological clock, governs our day-night cycle of biological activity. In adolescents, the circadian rhythm shifts later due to puberty, making it harder to wake up in the morning.
"The circadian rhythm is like an internal clock that tells our body when to be awake and when to sleep."
Genetics and culture also influence our tendency to be morning people or night owls. The blue spectrum light from electronics can suppress melatonin production, making it harder to fall asleep.
Factors Affecting Sleep | Description |
Circadian Rhythm | Biological clock that governs day-night cycle |
Genetics | Influence our tendency to be morning people or night owls |
Culture | Technology and social media can interfere with sleep |
Blue Spectrum Light | Suppresses melatonin production |
Sleep Deprivation in High School Seniors
Three out of four high school seniors are seriously sleep deprived. Factors contributing to sleep deprivation include:
Workload and academic pressure
Stress and expectations from teachers and parents
Extracurricular activities and part-time jobs
Social media and technology use before bed
Grade Level | Percentage of Students Getting 8 Hours of Sleep |
9th Grade | 40% (male), 30% (female) |
10th Grade | 35% (male), 25% (female) |
11th Grade | 20% (male), 20% (female) |
12th Grade | 20% (male), 20% (female) |
Note: The data shows that boys tend to get more sleep than girls in 9th and 10th grade, but the difference disappears in 11th and 12th grade.## Adolescent Development 🤯

Sleep Patterns and Impulsivity
Adolescents tend to be sleep-deprived due to a combination of factors, including a natural shift in sleep patterns and cultural influences. Girls, in particular, tend to prioritize getting ready in the morning, while boys often rush to get out the door.
"Impulsivity is the tendency to act on impulse without fully thinking through the consequences of one's actions."
Hormones, such as testosterone, contribute to increased impulsivity in adolescents. This, combined with an immature prefrontal cortex, can lead to reckless decision-making.
Risk-Taking and Social Approval
Adolescents are more likely to engage in risk-taking behavior, especially when with their peers. This is due to the brain's reward system and the desire for social approval.
Age Group | Risky Decisions Alone | Risky Decisions with Peers |
Adolescents | Some | Many |
Young Adults | Few | Fewer |
Adults | Few | Few |

Nutritional Issues
Adolescents often have unhealthy diets, leading to deficiencies in essential minerals like iron, calcium, and zinc. This can be attributed to peer influence and environmental factors.
Mineral | Importance | Deficiency Risks |
Iron | Essential for healthy red blood cells | Fatigue, weakness, poor cognitive function |
Calcium | Crucial for bone growth and development | Weakened bones, osteoporosis |
Zinc | Important for immune function and wound healing | Impaired immune function, slow wound healing |
Eating Disorders
Eating disorders, such as anorexia, bulimia, and binge eating disorder, can develop during adolescence. These disorders are often linked to body image issues, depression, and anxiety.
Eating Disorder | Characteristics |
Anorexia | Restrictive eating, significant weight loss |
Bulimia | Bingeing and purging, weight fluctuations |
Binge Eating Disorder | Recurring episodes of excessive eating |
Sexual Maturation
Sexuality is a complex and multidimensional aspect of adolescent development. Primary and secondary sexual characteristics develop during this stage.
Primary Sexual Characteristics | Secondary Sexual Characteristics |
Development of reproductive organs (e.g., uterus, testicles) | Development of observable physical traits (e.g., facial hair, breast development) |
Adolescent Sexual Behavior
Sexual activity among friends is a strong predictor of an adolescent's sexual activity. Trends show a decrease in teen pregnancy rates and an increase in the use of protection.
Trend | Description |
Decreased teen pregnancy rate | 50-year low in the US |
Decreased teen abortion rate | Correlated with increased use of protection |
Increased use of protection | More adolescents using condoms and other forms of birth control |
States with High Teen Birth Rates
The following states have the highest teen birth rates in the US:
Arkansas
Mississippi
Louisiana
Oklahoma
Alabama
West Virginia
Kentucky
Texas
Tennessee
These states often have poor education systems, highlighting a correlation between education and teen birth rates.## 🧠 Formal Operational Thought
Formal operational thought is a stage of cognitive development characterized by the ability to use systematic logic and think about abstract ideas. This stage is typically reached during puberty.
"Formal operational thought is the ability to think logically and abstractly, using hypothetical thought and considering possibilities that may not be reflective of reality."
Characteristics of Formal Operational Thought
Ability to use systematic logic
Ability to think about abstract ideas
Use of hypothetical thought
Consideration of possibilities that may not be reflective of reality
Ability to use both deductive and inductive reasoning
Deductive and Inductive Reasoning
Type of Reasoning | Definition |
Deductive Reasoning | Reasoning from a general statement to a specific conclusion |
Inductive Reasoning | Reasoning from specific observations to a general conclusion |
🤯 Adolescent Thinking
Adolescent thinking is characterized by four distinct features:
1. Adolescent Egocentrism
"Adolescent egocentrism is the tendency to focus on oneself to the exclusion of others, and to be unable to take someone else's perspective."
Characteristics:
Self-centeredness
Inability to consider others' perspectives
Everything is about oneself
2. Rumination
"Rumination is the tendency to get stuck on things and to be unable to let go of negative thoughts or emotions."
Characteristics:
Inability to let go of negative thoughts or emotions
Tendency to dwell on past experiences or relationships
3. Imaginary Audience
"The imaginary audience is the belief that everyone else is watching and criticizing one's appearance, ideas, and behaviors."
Characteristics:
Belief that others are constantly watching and judging
Self-consciousness and anxiety about what others think
4. Personal Fable
"The personal fable is the belief that one's own thoughts, feelings, and experiences are more intense and important than others."
Characteristics:
Belief that one's own experiences are unique and more significant than others
Tendency to dramatize one's own emotions and experiences
5. Invincibility Fable
"The invincibility fable is the conviction that nothing bad can ever happen to oneself."
Characteristics:
Belief that one is invincible and immune to harm
Tendency to engage in risky behavior and poor decision-making
🧠 Dual Processing
Dual processing refers to the idea that the human brain has two separate processing networks:
Analytical logical reasoning
Intuitive emotional responses
Processing Network | Characteristics |
Analytical Logical Reasoning | Logical, analytical, and systematic thinking |
Intuitive Emotional Responses | Emotional, instinctual, and automatic responses |
Implications for Adolescent Thinking
Adolescents tend to rely more on intuitive emotional responses due to the underdevelopment of the prefrontal cortex
This can lead to impulsive and emotional decision-making
With age, adolescents become more logical and less idealistic as the prefrontal cortex develops