Chapter 13 - Properties of Solutions
- Solutions - Homogeneous mixtures of two or more pure substances.
- Solute - Part being dissolved. Usually smaller in quantity.
- Solvent - Thing that dissolves.
- Solvation - Dissolving process.
- Hydration - The dissolving process with water as the solvent.
- Substances depend on these to form solutions.
- Intermolecular forces
- Natural tendency to mix.
Natural Tendency to Mix
- Mixing of gases is spontaneous.
- Mixing causes more randomness in the position of molecules increasing the entropy.
Attractions involved when forming a solution
- Solute-solute interactions - Must be overcome to disperse these particles when making a solution.
- Solvent-solvent interactions - Must be overcome to make room for the solute.
- Solvent-solute interactions - Occur as the particles mix.
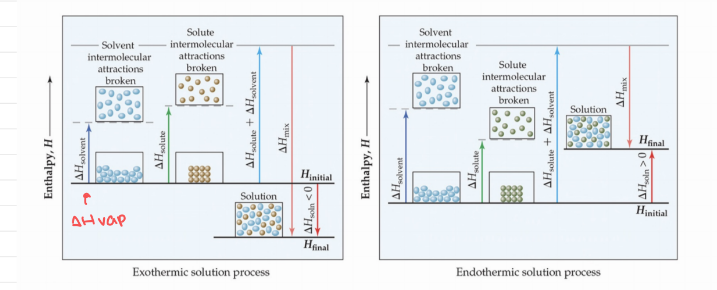
Energetics of Solution Formation
- ΔH solvent - Energy required to vaporize.
- Solubility - How much solute can be dissolved in a given amount of solvent at a given temperature.

- Saturated solutions - Can’t add more solute. More than enough.
- Unsaturated solutions - Can add more. Not enough.
- Supersaturated solutions - Temporary situation where the solution is cooled slowly and for it to react, a crystal from the solute is added.
Factors that affect solubility
- Solute-solvent interactions
- Temperature
- As it goes up, more solute is dissolved
- Pressure (for gas solutes)
- As it goes up, more solute can be added.
Pressure Effects
Solubility of solids and liquids isn’t affected by pressure.
Gas solubility is affected by pressure
Henry’s Law - The solubility of a gas is proportional to the partial pressure of the gas above the solution. It’s only true at a constant temperature.

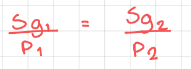
Temperature Effects on Solubility
- For most solids, as temperature increases, solubility increases.
- For all gases, as temperature increases, solubility decreases.
Solution Concentration Conversion Between Units
- Mass percentage (% m/m)
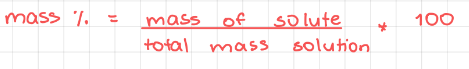
- Parts per million (ppm)
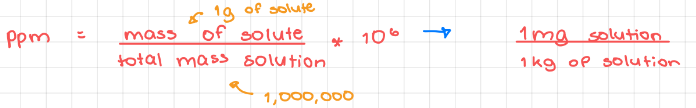
- Parts per billion (ppb)

- Mole fraction (X)

- Molarity (M)

- Molality (m)

Colligative Properties
- They depend only on the quantity, not on the identity of the solute.
- Vapor pressure reduction
- Boiling point elevation
- Freezing point depression
- Osmotic pressure
Vapor pressure reduction
- Raoult’s Law

Boiling point elevation
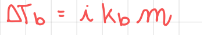
- i - Van-Hoff factor, the number of ions you get when dissolving the compound.
- Kb is a constant different for all compounds.
Freezing point depression

- Kf is a constant different for all compounds.
Osmotic Pressure
- Osmosis - The net movement of solvent molecules from a solution of low to a high concentration of solute across a semipermeable membrane.
- Semipermeable membrane - Smaller particles pass through it, but it blocks larger particles.
- Osmotic pressure - The applied pressure to stop bigger particles.

- If two solutions separated by a semipermeable membrane have the same osmotic pressure, no osmosis occurs.
Colloids
- Colloids - Suspension of particles larger than individual ions or molecules, but too small to be settled out by gravity.
- Ex. → Blood
- They have a hydrophobic end (tail) and a hydrophilic end (head).