Chapter 3

Prenatal Development
The course of prenatal development can be divided into three periods:
Germinal Embryonic
Fetal
Germinal Period
The germinal period takes place in the first 2 weeks after conception
Includes
The creation of the fertilized egg - zygote
Rapid cell division - mitosis
The attachment of the zygote to the uterine wall - implantation
Embryonic period
The embryonic period takes place 2 to 8 weeks after conception
Includes:
The specialization of cells to perform specific tasks - cell differentiation
The mass of cells is now considered an ambryo, and it is conformed of 3 layers of cells.
Endoderm 0 the inner layer which will develop into the digestive and respiratory systems
Mesoderm - the middle layer which will become the ciculatory system, bones muscles, excretory system, and reproductive system
Ectoderm - the outermost layer which will become the nervous system and brain, sensory receptors, and skin parts (e.g., hairs and nails).
Fetal Period
The fetal period lasts about seven months, it is the prenatal period between 2 months after conception and birth (in typical pregnancies).

Teratology and Hazards to Prenatal Development
A teratogen is any agent that can potentially cause a birth defect or negatively alter cognitive and behavioral outcomes.
Dose, genetic susceptibility, and the time of exposure to a teratogen influence both the severity of the damage to the embryo/fetus, and the type of defect
Teratogens
Prescription and nonprescription drugs; antibiotics, asma medications, some antidepressants, certain synthetic hormones, and Acutane
Psychoactive drugs: caffeine, alcohol, nicotine, cocaine, marijuana, and heroin.
Synthetic opioids and opiate-related pain killers: fentanyl, OxyCotin, and Vicodin
Environmental hazards: toxic waste, chemical pollutants, x-ray radiation, fertilizers, and pesticides.
Other Hazards to Prenatal Development
Maternal Diseases
Rubella
Syphilis
Genital herpes
AIDS
Other parental factors
Maternal diet and nutrition
Parental age
Maternal emotional states and stress
Parental genetic factors
The Birth Process
There are 3 main stages of birth:
1st stage - uterine contractions are 15-20 minutes apart and last up to 1 minute
2nd stage - begins when the baby’s head starts to move through the cervix and birth canal
Ends when the baby completely emerges from the mother’s body.
3rd stage - afterbirth; when the placenta, umbilical cord, and other membranes are detached and expelled.
Childbirth settings and attendants
In 2020 in the United States:
98% of births took place in hospitals
1.26% in homes
0.74% in free-standing birth centers
Midwifery is a profession that provides health care to women during pregnancy, birth, and the postpartum period
A doula is a caregiver who provides continuous physical, emotional, and educational support for the mother before, during, and after childbirth.
Unlike midwives, duolas do not have medical training and cannot be used as a substitute for a doctor in delivering a baby
Methods of childbirth
Natural childbirth is a method that aims to reduce mother’s pain by decreasing fear through
Education about childbirth
Relaxation techniques during delivery
Medicated and non-medicated
Prepared childbirth includes a special breathing technique to control pushing in the final stages of labor, as well as detailed education about anatomy and physiology
Cesarian delivery is a surgical procedure in which the baby is removed from the uterus through an incision made in the abdomen
Although some may choose a scheduled cesarian as their birth plan, other’s may require one if the baby is in breech position - baby’s buttocks are the first part to emerge from the vagina
Assessing the Newborn
Almost immediately after birth, a newborn is taken to be weighed, cleaned up, and tested for signs of developmental problems that may require urgent attention.
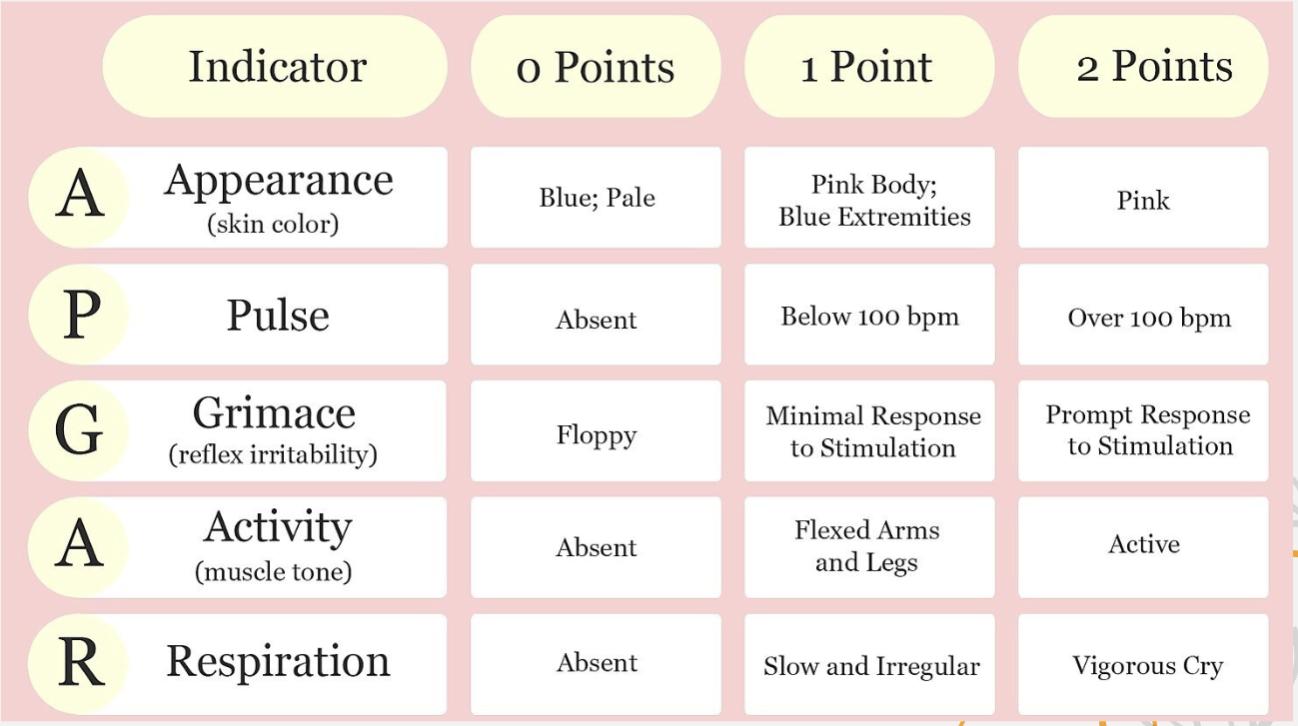
The Apgar Scale evaluates an infant’s heart rate, respiratory effort, muscle tone, body color; and flex irritability of a newborn at 1 and 5 minutes after birth
The obstetrician or nurse evaluates and gives newborn a score of 0, 1, or 2 in each of the 5 health signs
Total score of 7-10 indicates condition is good, score of 5 indicates there may be developmental difficulties, score of 3 or below signals emergency and indicates baby may not survive
Preterm and Low Birth Weight Infants
Low birth weight infants - those that weigh less than 5 ½ lbs at birth
Preterm infants - those born before the completion of 37 weeks of gestations
Small for date infants - those whose birth weight is below normal when the length of pregnancy is considered.
May be preterm or full-term
The Postpartum Period
Physical adjustments
Emotional and psychological adjustment
Bonding
Physical Adjustments
Period after childbirth lasts until the mother’s body has completed its adjustment and has returned to a nearly prepregnant state.
Body makes numerous physical adjustments in the first days and weeks after childbirth.
After delivery, the body undergoes sudden and dramatic changes in hormone production.
May have a great deal of energy or feel exhausted and let down
Fatigue can undermine their sense of well-being and confidence in their ability to cope with a new baby
Loss of sleep is a big concern as it can contribute to stress and impaired decision making
sleep affects everything else
Like your cognitive processes becoming fuzzy because of lack of sleep
Emotional and Psychological adjustments
Emotional fluctuations are common in the postpartum period.
For some, these fluctuations decrease within several weeks after delivery, but others may experience more long-lasting mood swings
About 70% of new mothers experience the postpartum blues
2-3 days after birth, they feel slightly depressed, anxious, and upset
May come and go for several months and tend to peak at 3-5 days after birth
mild version of postpartum depression
Other may develop postpartum depression, which involves a major depressive episode that typically occurs about 4 weeks after delivery
Strong feelings of sadness, anxiety, or despair that last for at least 2 weeks.
Full on clinically diagnosed depression
Bonding
Bonding is the formation of a connection, especially a physical bond between parents and the newborn in the period shortly after birth
Some hospital practices deter bonding:
Drugs given to the mother at a high dose can make them drowsy and unable to respond to or stimulate newborn
Parents and newborns are open separated shortly after delivery
Preterm infants are isolated from their parents even more than full-term infants
Many hospitals offer a rooming-in arrangement, in which baby remains in the room most of the time during the hospital stay. Testing procedures can also occur in the room.