Chapter 14 - Molecular Spectroscopy 2: Electronic Transitions
The characteristics of electronic transitions
14.1 The electronic spectra of diatomic molecules
Selection rules concerned with changes in angular momentum

Laporte selection rule for centrosymmetric molecules and atoms - The only allowed transitions are transitions that are accompanied by a change of parity.
Centrosymmetric - Those with a center of inversion.
Vibronic transition - A transition that derives its intensity from an asymmetrical vibration of a molecule.
Franck-Condon principle - Because the nuclei are so much more massive than the electrons, an electronic transition takes place very much faster than the nuclei can respond.
Vertical transition - Used to denote an electronic transition that occurs without a change of nuclear geometry.
Franck-Condon factor - Because the transition intensity is proportional to the square of the magnitude of the transition dipole moment, the intensity of absorption is proportional to
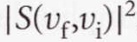
14.2 The electronic spectra of polyatomic molecules
- Chromophores - Groups with characteristic optical absorptions.
- Charge-transfer transitions - When the electron moves through a considerable distance, which means that the transition dipole moment may be large and the absorption is correspondingly intense.
- Polarized light - Electromagnetic radiation with electric and magnetic fields that oscillate only in certain directions.
- Plane polarized light - When the electric and magnetic fields each oscillate in a single plane.
- Circular polarization - The electric and magnetic fields rotate around the direction of propagation in either a clockwise or a counter-clockwise sense but remain perpendicular to it and each other.
- Circular dichroism - The differential absorption of left- and right-circularly polarized light.
The fates of electronically excited states
- Radiative decay process - A process in which a molecule discards its excitation energy as a photon.
- Nonradiative decay - The excess energy is transferred into the vibration, rotation, and translation of the surrounding molecules.
14.3 Fluorescence and phosphorescence
- Fluorescence - Spontaneous emission of radiation occurs within a few nanoseconds after the exciting radiation is extinguished.
- Phosphorescence - The spontaneous emission may persist for long periods.
- Intersystem crossing - A nonradiative transition between states of different multiplicity, and become a triplet state.
- Jablonski diagram - Where the various types of nonradiative and radiative transitions that can occur in molecules are often represented.
14.4 Dissociation and predissociation
- Dissociation - The breaking of bonds.
- Internal conversion - A radiationless conversion to another state of the same multiplicity.
Lasers
14.5 General principles of laser action
- Requirements for laser action
- Metastable excited state - An excited state with a long enough lifetime for it to participate in stimulated emission.
- The existence of a greater population in the metastable state than in the lower state where the transition terminates.
- Pumping - Stimulation with an intense flash of light.
- Spatial coherence - The waves are in step across the cross-section of the beam emerging from the cavity.
- Temporal coherence - The waves remain in step along the beam.
- Q-switching - The modification of the resonance characteristics of the laser cavity.
- Pockels cell - An electro-optical device based on the ability of some crystals.
- Saturable absorber - A solution of a dye that loses its ability to absorb when many of its molecules have been excited by intense radiation.
14.6 Applications of lasers in chemistry
- Multiphoton spectroscopy - States inaccessible by conventional one-photon spectroscopy become observable because the overall transition occurs with no change of parity.
- State-to-state reaction dynamics - Where a specific state of a reactant molecule is excited and we monitor not only the rate at which it forms products but also the states in which they are produced.
- Isotope separation
- Photoionization - The ejection of an electron by the absorption of electromagnetic radiation.
- Photodissociation - The fragmentation of a molecule following absorption of electromagnetic radiation.
- Photoisomerization - The conversion of a species to one of its isomers on absorption of electromagnetic radiation.
- Photodeflection - Based on the recoil that occurs when a photon is absorbed by an atom, and the linear momentum of the photon is transferred to the atom.
- Time-resolved spectroscopy - Here laser pulses are used to obtain the absorption, emission, or Raman spectrum of reactants, intermediates, products, and even transition states of reactions.
- Continuum generation - In which focusing an ultrafast laser pulse on a vessel containing liquid results in an outgoing beam with a wide distribution of frequencies.
- Spectroscopy of single molecules
- Nearfield optical microscopy (NSOM) - A very thin metal-coated optical fiber is used to deliver light to a small area.’
- Far-field confocal microscopy - A laser light focused by an objective lens is used to illuminate a very dilute sample placed beyond the near field.
- Wide-field epifluorescence method - Where a two-dimensional array detector detects fluorescence excited by a laser and scattered back from the sample.