pltw mi : unit 4 study guide
Author Notes
hello and thank you for visiting! i hope this helps you with the EOC and unit 4 test!! i tried my best to grab the information that might be on the EOC since my class didn’t get to finish the unit :,)
use the mighty “test me” feature of knowt to test yourself on this knowledge!!!
like this study guide? I made all the other units too, so feel free to check it out via my profile <33
﹙✦﹚﹒﹒this guide uses abbreviations! 4.2 is not included..
﹙Overview﹚
revisit the science of diabetes as you learn to purify a protein and understand the production of insulin. follow through the world of organ-related interventions
╭ Other Resources :
:: no links atm ﹒﹒ i’ll probably make a term deck if i’m motivated enough
﹙4.1 - Manufacturing Human Proteins﹚
✦﹒recall the function of insulin
insulin is a peptide hormone produced by groups of cells within the pancreas called beta islet cells
cells are released when blood glucose levels exceed healthy range
lowers blood glucose levels
✦﹒insulin can be produced thru genetic engineering— recall the function of recombinant DNA technology as it can produce insulin with the help of bacteria
recombinant DNA technology uses enzymes + lab techniques to manipulate and isolate DNA segments of interest
the gene of interest is separated frm DNA by restriction enzymes tht cut the DNA and leave sticky ends
restriction enzymes r the “molecular scissors”
MUST have sticky ends in order to combine with plasmid
restriction enzyme cuts a part of the plasmid so the gene of interest can be inserted into the plasmid
DNA ligase works to glue or ligate the gene of interest and plasmid together
plasmid is now recombinant plasmid ; acts as a vector to carry the DNA to the cell
protein of interest is made in cell and multiples as cell undergoes division; used to make vaccines
plasmid may experience self-ligation or inversion, causing the protein of interest to not be produced
self-ligation - plasmid ligates w/o the gene of interest
inversion - gene of interest goes into plasmid backwards
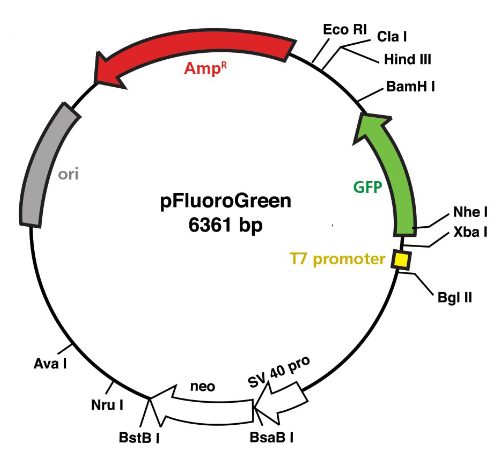
the plasmid in this experiment is a pfluoroGreen
pfluorogreen has a T7 promoter that acts as an on/off switch for hte expression of GFP; typically off, it will be turned on in presence of IPTG
the GFP gene (green) allows the cell to produce green fluorescent protein; this fluorescence is derived from jellyfish
in addition to the gfp gene being translated, the ampᴿ will too— it provides ampicilin resistance
“ori” is the DNA sequence from which bacteria can initiate the copying of the plasmid
heat shock facilitates the entry of the plasmid DNA into the cells by changing the cell wall’s permeability
transformation efficiency is a quantitative measurement tht tells scientists how accurate + successful they were of getting the desired DNA into cells
^ specific formula for transformation efficiency
✦﹒chromatography is a technique used to separate and purify components in a mixture of gases, liquids, or dissolved liquids
in this technique, mixture is dissolved in gas/liquid, sample is passed over a filter, trapping and releasing chemicals frm the mixture based on chemical + physical properties
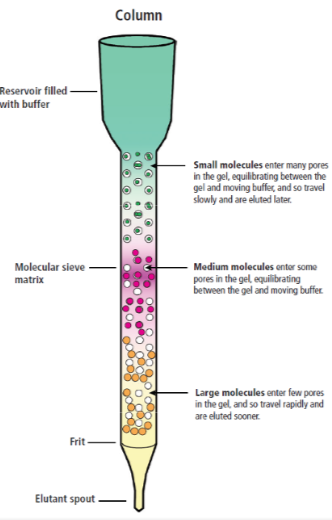
column chromatography can purify GFP as the larger the molecule, the more difficult it is for them to pass thru the pores, making them flow arnd btwn beads
column has microscopic pores and internal channels
larger + higher molecular weighted proteins will movve more rapidky thru the matrix and will be first to drip out aka elute
a protein’s structure consists of the following—
hydrophobic amino acids - water hating, tucked inwards of the protein
hydrophilic amino acids - water loving, pointed outwards of the protein’s surface
acidic amino acids - has a negative charge, is attracted to basic amino acids (opposites attract) forming a neutralized bond and salt bridge
basic amino acids - has a positive charge, is attracted to acidic amino acids forming a neutralized bond and salt bridge
cysteine - amino acids form disulfide bridges with another cysteine
✦﹒protein electrophoresis uses sodium dodoecyl polyacrylamide sulfate to disrupt the 3D bending + folding of a protein and coat them w/a negative charge to ensure separation is accurate
﹙✦﹚﹒have a understanding of insulin, column chromatography, protein structure electrophoresis
→not included ; 4.1.5 as it was just abt careers
﹙4.3 - Transplant﹚
✦﹒The National Organ Transplant Act (NOTA) established the framework for a national system of organ transportation
outlaws sale of human organs
establishes that social criteria (wealth, celebrity + prison status) is not considered for organ allocation
a potential candidate for organ transplant who tests for HIV positive but is in a asymptomatic state should not be excluded from candidacy, but shoud be advised about being in increased risks of morbidity and mortality
under NOTA is the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN), which formulates the organ allocation policies, and is based on the following criteria:
compatibility of donor and recipient
geographical proximity between donor and recipient
time on waiting list
age of recipient (preference given to children)
✦﹒donors for organ transplant need to have compatible blood and tissue types
human leukocyte antigens (HLA) are responsible for stimulating the immune resp. to recognize the tissue as self versus non-self
tissue/HLA typing is a test tht determines which HLA antigens r present by identifying similarities present in both donor + recipient
HLA is passed on frm parents; a set frm a parent is called a halotype
a kidney transplant looks for HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-DR antigens during testing
in HLA typing, patient’s DNA is isolated, PCR is used to amplify specific HLA genes, and then genes r sequenced to determine present alleles
after testing, Antibody Screening (also Panel Reactive Antibody) is done to determine different HLA antibodies a patient has in the blood
if patient reacts w/ 30/60 cells, they hv 50 Percent Reactive Antibody (PRA)
lower PRA = less likelihood of rejecting a transplant
final test is called the crossmatch test
where a small amt of potential donor’s white cells r mixed w/recipient’s serum
positive crossmatch - a reaction btwn donor + recipient’s sample occurred
can’t do transplant
negative crossmatch - no reaction btwn samples
transplant can be performed!
✦﹒there are a variety of ways to donate an organ (kidney for instance)
conduct two separate surgeries; first a nephrectomy which involves removal of a donor’s kidney, and then the actual transplant
laparoscopy, a minimally invasive surgical technique tht uses small cylindrical tubes called trocars to enter the abdominal cavity to all entry of a fiber-optic video camera (laparoscope)
trocars r a sharp-pointed surgical instrument fitted w/a small tube for insertion into a body’s cavity
gives less pain meds, shorter hospital stays + time b4 patient can go back to work compared to open surgeries
✦﹒different medical professions have a role in transplant surgery—
anesthesiologists specialize in anesthetic administration, pain relief, and care of patients before, during, and after surgery
sevoflurane is a nonflammable volatile liquid tht causes general anesthesia b4 + during surgey
administered by inhalation of vaporized liquid
mech of action - binds to ligand-gated in channels + blocking CNS neurotransmission
side effects r shivering, blurred vision, fast/irregular heartbeat, confusion, low body temp
nitrous oxide is a weak gen anesthetic tht usually isnt used alone; used in 70% concentration in gen anesthesia, or as a carrier gas w/ more potent gen anesthetic agents
administered by inhalation, absorbed by diffusion thru lungs + eliminated via respiration
mech of action - noncompetitive inhibition of the NMDA subtype of glutamate receptors
side effects r postoperative nausea + vomiting
thiopental helps patient relax b4 receiving gen anesthesia w/an inhaled med
administered intravenously
mech of action - binds @ distinct binding site associated w/Cl- inopore at the GABAa receptor, increasing duration of time for which the Cl- ionopore is open
side effects r drowsiness, weak breathing, slow heartbeat, chills, sneezing, bronchospasm
propofol is an intravenous anesthetic for procedural sedation during monitored care, or as an induction agent for gen anesthesia
administered as a bolus/infusion, or a combo of the two
mech of action - involves a positive modulation of the inhibitory function of the neurotransmitter gama-aminobutyric acid (GABA) thru GABA-A receptors
side effects r coughing, itching, cloudy urine, difficulty breathing, hallucinations
transplant surgeons are highly skilled in moving organs and tissue from one body to another
perioperative nurses work closely with surgeons and provide care and support to patients before, during, and after surgery
pharmacists supply patients with immunosuppressive drugs to prevent the chances of organ rejection; drugs include—
antiproliferative agents
corticoseroids
calcineurin phosphatase inhibitors
﹙4.4 - Building a Better Body﹚
✦﹒placeholder!!!
i literally don’t know what to write for 4.4
﹙✦﹚﹒looks like you reached the end! thank you for reading!!