Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks
Slide 3: The Rock Cycle
Rocks are classified based on the origin of their formation
The three types of rocks:
Igneous - when hot, molten rock crystallizes and solidifies.
Sedimentary - form from deposits of pre-existing rocks that eventually cement together.
Metamorphic - forms due to alterations to rocks, like being subjected to high heat, high pressure, hot mineral-rich fluids or, more commonly, some combination of these factors.
Slides 4 and 5: What Holds a Rock Together?
1.) Cement
Rock - a naturally occurring solid that consists of an aggregate of minerals, or detrital grains.
Cement - like glue, it is deposited between little tiny pore spaces between crystals.
Cement is provided by water running through the pore spaces.
Clastic sedimentary rocks are held together by cement.
Indicates that it was a sedimentary rock.
2.) Crystals
Crystalline rocks are held together by interlocking crystals.
Indicates it was a igneous or metamorphic rock.
Slide 6: Rock-Forming Environments
Igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks form in very different environments.
The Rocky Mountains are a grand mountain chain that runs north to south. It is a very old core of metamorphic rock.
Slide 7: Bedrock Is Attached to Earth’s Crust
An exposure of bedrock is called an outcrop.
Broken clasts of rock on Earth’s surface are not bedrock.
Exposures of bedrock can be either natural or human-made.
Example of human made: roads running along a mountain side. They were shape to make room for the roads.
Las Vegas is NOT built on bedrock.
Granite is a common type of bedrock, it is a crystalline type rock.
Class Question
Granite is a common bedrock of the continental crust, it is considered what type of rock?
Crystalline
Slide 12: Rock Groups
Igneous
From lava
From magma
Sedimentary
Cemented
Precipitated
Metamorphic
Chemically and physically altered
Slide 13: Devil’s Tower
Formed beneath Earth’s surface.
Was a volcano, eventually froze.
Outer part of volcano eroded and left a “neck”.
Slide 14: A Review
Oceanic crust is more dense.
Lithosphere
The oceanic and continental crust.
The outer part of the upper mantle.
Rigid.
Asthenosphere
Upper mantle.
Allows heat to release.
Where melting take place.
Slide 15: Intrusive vs. Extrusive
The extrusive realm is above ground.
Lava is found on Earth’s surface.
The intrusive realm is below ground.
Magma is found beneath Earth’s surface.
Slide 17: Extrusive: Lava Flows
Lava erupts as a fountain from a volcanic vent on Hawaii.
A fast-moving river of lava then flows downslope.
At a distance from the vent, the lava has completely crusted over with new rock, but the interior of the flow remains molten.
Eventually, the flow cools completely and becomes a layer of new rock.
Basalt = extrusive, igneous rock, crystal state stays small.
70% of Earth’s crust is made of basalt.
All of the oceanic crust is made of basalt.
Intrusive rocks form below ground (ex: granite cut by a mafic dike).
Extrusive includes lava flows and pyroclastic deposits (ex: ash alternating with andesite).
Each is characterized by unique textures for how magma crystallized or the lava exploded or solidified.
Extrusive example: Hawaii
Intrusive example: Sierra Nevada Range
Slides22-26: How Do Rocks Melt?
Decompression melting
Pressures decreases but temperature remains constant, creating a melt.
Changing pressure (relieving pressure), not temperature.
Where: Geologic environments where decompression melting occurs:
Decompression melting occurs at mantle plumes, continental rifts, and divergent-plate boundaries.
Rift zone - where Earth is being pulled a part.
Decompression melting happens at mid-ocean ridges.
Black rocks from decompression melting spill on surface (basalt).
Add volatiles (flux)
Volatiles help break chemical bonds, creating a melt (molten rock).
Volatiles are gaseous components of magma that can vaporize at surface pressures (can easily vaporize).
Takes place at subduction zone.
Volatiles such as H2O and CO2 are driven from the oceanic crust into the asthenosphere, creating a melt above the sub-ducting plate.
Flux happens along subduction zones
Heat transfer (conduction)
Heat from magma melts adjacent rocks, more melting.
Rocks surrounding magma chambers can be melted through heat-transfer.
Sharing heat.
Slides 28-30: Not All Melts Are the Same
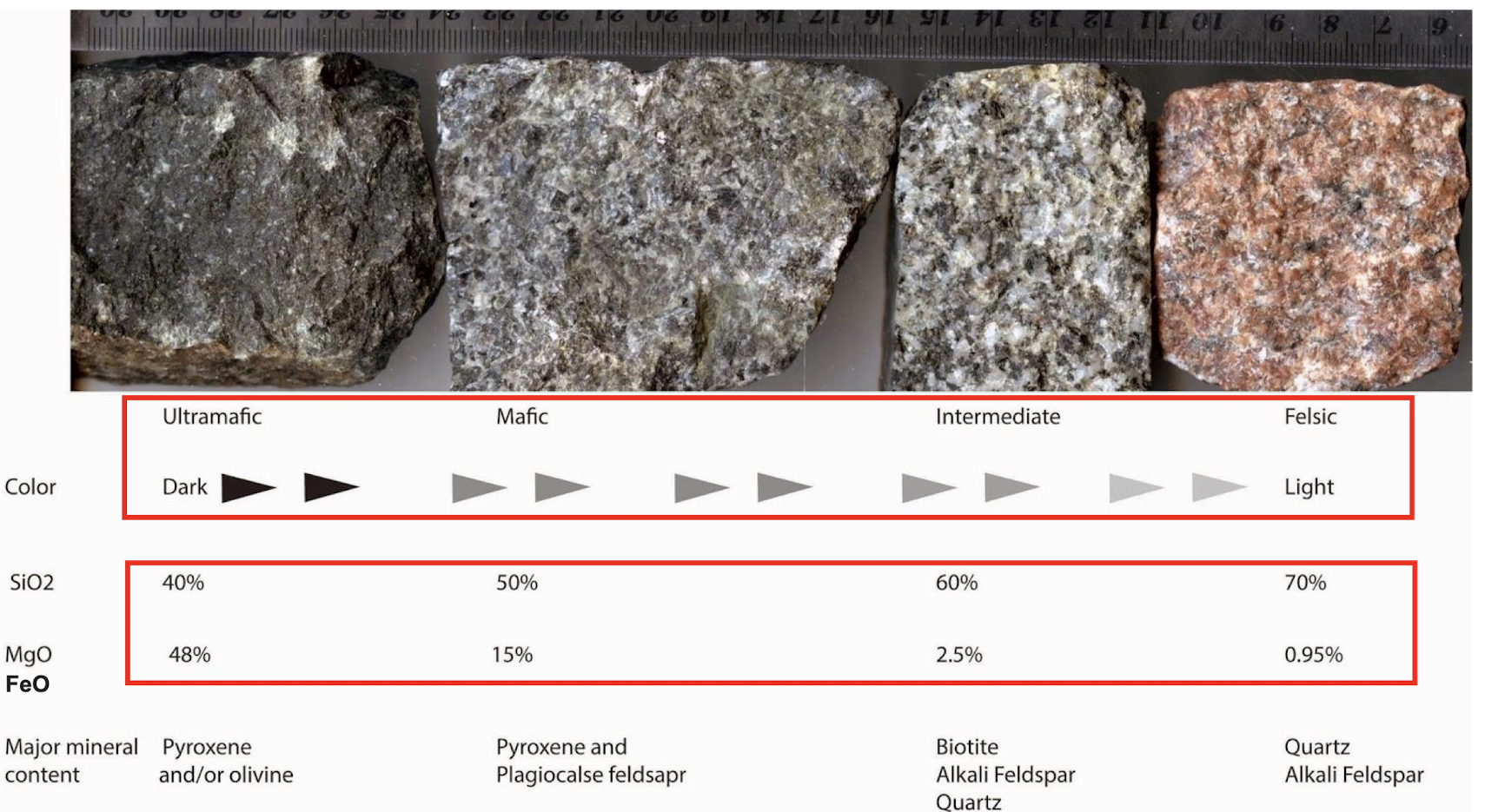
Difference = silica content
Different Types of Melts Based on Silica Content
 Class Question
Class Question
The _____ content of a melt determines a melt’s viscosity and, ultimately, the name given to a particular unit.
Silica content
Slides 36-39: Why Do Melts Vary?
Based on base rock/source rock.
The source rock dictates the initial melt composition.
Partial melting of rocks makes the melt silica-enriched because felsic minerals melt first.
Low temperature rocks.
Partial melting - when heat is introduced to a solid rock (source rock).
Assimilation - as a melt rises, it assimilates the wall rock, changing the composition of the melt.
A good analogy is ice cubes melting into a glass of cola, it is “watering down” the cola.
Magma mixing - blending of crustal melt altering the composition.
Slides 41-43: How Does Magma Move?
Buoyancy - force to rise
Magma pressure
What Controls the Speed of Flow?
The resistance to flow, or viscosity of a liquid affects the speed at which the liquid moves.
Viscous - having a thick, sticky consistency between solid and liquid; having a high viscosity.
Not all molten rock has the same viscosity. The viscosity of molten rock depends primarily on its:
Temperature - a lower temp melt is more viscous than a higher temp melt.
Volatile content - a wet melt containing more volatiles is more viscous than a dry (volatile free) melt.
Silica content - a felsic melt is more viscous than a mafic melt, because relatively more silicon-oxygen tetrahedra occur in a felsic melt.
Viscosity Affects Melt Movement
Viscosity depends on temperature, volatile content, and percent of silica content.
Low viscosity:
Hotter
Less volatiles
Less SiO2
Mafic lava
High viscosity:
Cooler
More volatiles
More SiO2
Felsic lava
Slides 45-56: How Does Magma Crystallize?
Cooling Rates of Melts
Volcanic precipitation occurs when melts solidify, or freeze.
Depth matters because of temperature.
Size and shape of magma body matters.
Size determines how fast or slow the magma will cool.
This will have an impact on the texture of the crystallization.
Three things to consider:
1.) Shallow flows cool quickly. Deep plutons take a long time to cool.
2.) Spherical bodies cool slowly; tabular bodies cool faster.
3.) Circulating groundwater removes heat.
Fractional Crystallization Happens During Cooling
Mafic minerals crystallize first; felsic minerals crystallize last.
Bowen’s Reaction Series
Rocks formed from the top of the series are felsic.
Rocks formed from minerals at the bottom of the series are mafic.
From top to bottom (low to high temperature):
Felsic
Intermediate
Mafic
Ultramafic
Class Question
According to the Bowen’s reaction series, which statement is most correct?
With decreasing temperature, melts become more felsic.
Class Question
Which minerals would you expect to crystallize from a mafic magma?
Mafic magmas are characterized by their relatively high iron (Fe) and magnesium (Mg) content, as well as lower silica (SiO2) content compared to felsic magmas. As such, the minerals that commonly crystallize from mafic magmas tend to be rich in iron, magnesium, and calcium.
Olivine
Pyroxene
Plagioclase Feldspar
Which minerals would you expect to crystallize from a felsic magma?
Felsic magmas are characterized by their higher silica (SiO2) content and lower iron (Fe) and magnesium (Mg) content compared to mafic magmas. As a result, the minerals that commonly crystallize from felsic magmas tend to be rich in silica and aluminum.
Quartz
Orthoclase Feldspar
Muscovite
Biotite
Slides 58-65: Types of Magma Bodies
Magma Cooling Intrusively: Sills and Dikes
Dikes run vertically and cut across rock layers.
Sills run horizontally and are parallel to rock layers.
Dikes can spread rocks apart sideways, sills push rocks up and can change the relief.
Magma Cooling Intrusively: Plutons
Plutons are blob-shaped intrusions that solidify from magma chambers.
Magma Cooling Intrusively: Xenoliths
Magma moves upward by percolating between grains, wedging open cracks, melting, and breaking off blocks of the wall rock. Xenoliths are chunks of wall rock incorporated into the magma, but don’t melt.
Lava Cooling Extrusively: Debris and Pyroclastic Flow
Pyroclastic flows are deadly, fast-moving avalanches of superheated volcanic ash and debris.
Explosive volcanoes erupt various sizes of debris, ranging from microscopic ash to large pumice.
Lava Cooling Extrusively: Large Igneous Provinces (LIPs)
Large areas of mafic melt that appear periodically over geologic time.
LIPs result from mantle plumes at the base of the lithosphere that create huge volumes of low- viscosity mafic magmas. Lava flows cover large areas and can accumulate in thick piles.
Basalt sill.
Studied by James Hutton (Father of Geology), first to identify that these formed from the cooling of an igneous intrusion.
Slides 67-69: Identifying Igneous Rocks
Texture
Igneous rocks are described by the texture and mineral composition. Texture reveals info about the history of how the melt cooled.
Crystalline texture: crystals fit together like jigsaw puzzle pieces.
Phaneritic, Pegmatitic, Porphyritic, Aphanitic
Fragmental texture: Igneous chunks and shards welded together.
Pyroclastic, Vesicular/Frothy
Glassy texture: solid glass or glass shards.
Glassy
Vesicular - airy pockets
Pyroclastic - debris that was shot out of a volcano
Mineral Composition
Aphanitic - extrusive, formed outside
Phaneritic - intrusive, formed inside
Take Home Message
Magma is molten rock that is beneath the Earth’s surface (INSTRUSIVE) and crystallizes with a phaneritic or porphyritic texture (due to slower cooling rates).
Lava is molten rock at or above the Earth’s surface (EXTRUSIVE) and crystallizes with an aphanitic, frothy, vesicular, or glassy texture (due to quicker cooling rates).
Melts can be produced through decompression, addition of volatiles, or heat transfer.
The silica content of a melt determines a melt’s viscosity and, ultimately, the name given to a particular igneous rock.
Mafic minerals will crystallize out of a melt at higher temperatures (first) while felsic minerals crystallize at lower temperatures (last).
Extra Notes
Oxygen and silicon are the most abundant elements in rocks found in the Earth’s crust and mantle.
When magma or melt solidifies it forms igneous rocks.
If pre-existing rock is exposed to extreme heat or pressure its physical properties change and forms metamorphic rocks.
Rocks from weathered grains of other pre-existing rocks through lithification are sedimentary rocks.
The genetic scheme for classifying rocks is based on the origin of formation.
Igneous rocks cool from magma or lava either above or below ground.
Clastic sedimentary rocks are formed when clasts are cemented together.
Metamorphic rocks are formed due to a dramatic change in heat and/or pressure which can align minerals and cause rocks to fold.
Molten rock (melt) that is explosively ejected in a volcanic eruption is called pyroclastic.
Decompression (a decrease in pressure), the addition of volatiles such as water and carbon dioxide, and the transfer of heat from a nearby source such as another body of magma may all result in the melting of rock to form magma.
Lava is molten rock that has been erupted onto the surface of the Earth. The composition of lava can vary greatly among different volcanoes; this composition is dependent on the original composition of the parent magma and the processes of change it underwent prior to eruption.
During fractional crystallization, a mafic magma enters a magma chamber from below. As the magma reaches the upper part of the magma chamber where temperatures are lower, magnesium- and iron-rich minerals begin to crystallize. The mineral crystals, having a higher density than the surrounding magma, sink to the bottom of the chamber. This causes the overall composition of the remaining magma to have an increasingly intermediate to felsic composition.