Interest and Policy Groups
Political issue - some problem society has, and people can not agree on how to solve it
Public policy - Laws made by the government that attempt to fix an issue
Government - An institution that attempts to solve political issues
Policy Agenda - Political problems that have gained serious attention and that the government is actively working on
Linkage Institutions - Ways that the people are connected to the government, how voices are expressed
Media is a linkage institution that informs the public about political issues and events while acting as a watchdog on government actions.
Political parties aggregate diverse interests, mobilizing voters and facilitating the electoral process.
Interest groups represent specific interests or causes, lobby legislators, and engage in grassroots efforts to influence public policy.
Interest Groups
Interest groups work to influence bureaucrats, the president, congress, and the court
Interest groups may work to influence local, state, and federal government
Different from political parties
Do not run candidates for office
Policy Experts
Pluralism - When different groups compete to win over the government
Collective goods lead to the free rider problem
Free Rider Problem
Collective goods lead to the free rider problem
Offer selective benefits if they are part of the interest group
Theories on Democracy
Elite: While people seem to have a voice, it is really the elite who control the government
Hyperpluralism: Too many groups, too many competitions, multiple groups achieve their goals
Pluralism
Participatory: People’s voice is represented through government action
Iron Triangles
An interest group, related congressional committee, and members of the related federal department/agency
Work together to pass and enforce legislation when their goals are common
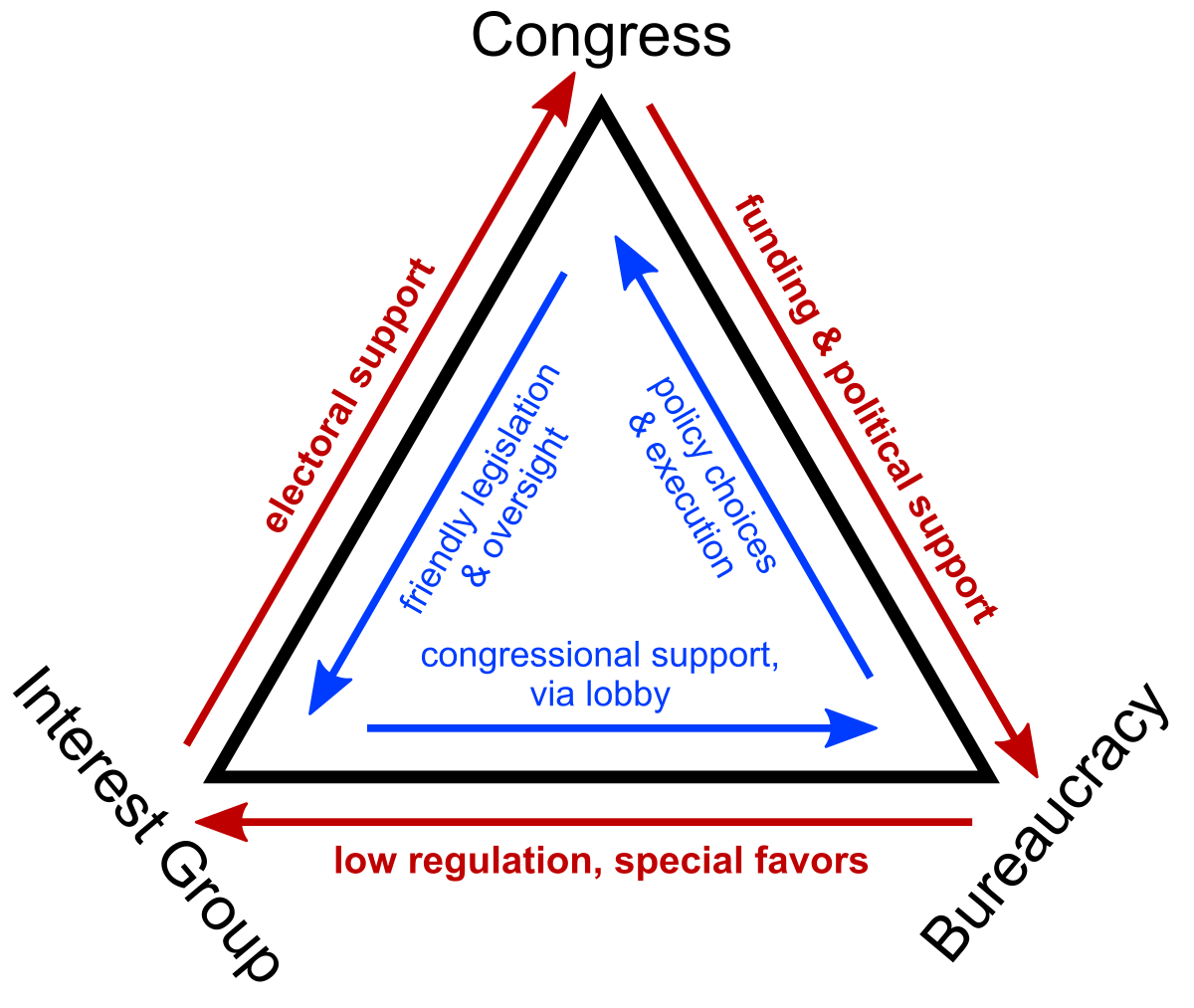
Agencies are bueracrats
Example:
AARP: Interest group
House Subcommittee on Aging: Congressional group
Social Security Administration: Buereaucracy
Attempts to prevent cuts to social security