Intro and Organization of the Human Body
Anatomy:
Science of the structure of an organism and relationship of its parts
Structures often are designed to perform specific functions
Physiology:
Science of the Function of an organism and the relationship of its parts
Damage/change to the structure can impact the function
Levels of Organization
Cells come together to form a tissue
organs are made up of different tissues
Homeostasis:
The ability to maintain or restore an environment at a certain level, the general area where we want to be in for our health, homeostasis keeps this.
Feedback control loops maintain homeostasis
Components:
Eg. Temperature feedback loop
Stimuli: any factor which causes change from normal, eg. temp decreases
Sensor mechanism: specific sensors detect and react to any changes from normal, eg. temp receptors in the skin to nerve fibers
Integrating or control center: information analyzed and integrated, if needed specific action is initiated, eg. brain
Effector Mechanism: effectors influence controlled physiological variables, what ultimately causes a change, eg. motor neurons to start shivering
Feedback: process of information constantly flowing from sensor to the integrator
Flow: variable→ sensor→ integrator→ effector→ homeostasis
Feedback Loops
Negative:
Overall effect→ inhibitory to stabilize physiological variables(inhibiting the cold temp by shivering)
Action→ Produces effect opposite to change
Purpose→ maintain homeostasis
Frequency→ more common than positive
Positive:
Overall effect→ stimulatory, amplify the change that is occurring(increasing hormone levels during pregnancy and contractions, forming blood clots after getting a cut to not lose blood)
Action→ tend to produce destabilizing effects, disrupts homeostasis
Purpose→ bring specific body functions to swift completion
Frequency→ only these two
Levels of homeostasis in the body
Intracellular control
Within cells, genes and enzymes regulate cell processes
Intrinsic Control
Regulation within tissues or organs
Can involve chemical signals or built in mechanisms
Extrinsic Control
Regulation from organ to organ
May involve nerve signals, endocrine signals(hormones)
Anatomical Position
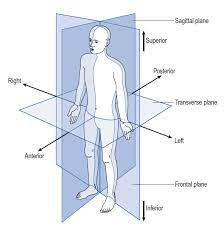
Body→ erect
Arms→ at sides
Palms→ facing forward
Head and feet→ pointing forward
Bilateral symmetry→ mirror images
Ipsilateral structures→ same side
Contralateral structures→ opposite side
Body Cavity
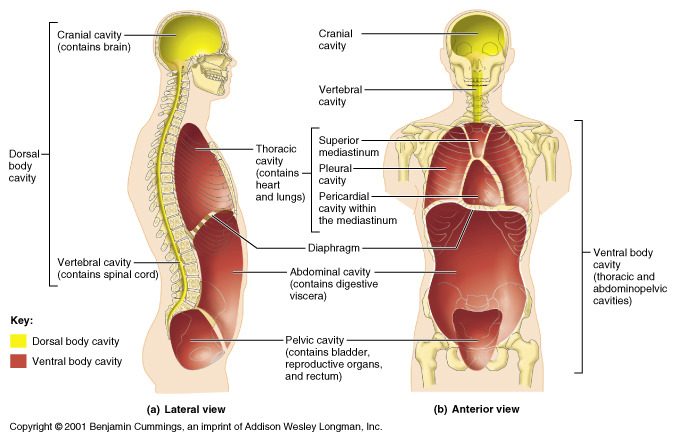
Abdominopelvic cavity(both pelvic and abdominal together)
Pleural cavity refer to right and left lung
Mediastinum in the middle between lung, houses heart and other structures
Abdominal Quadrants
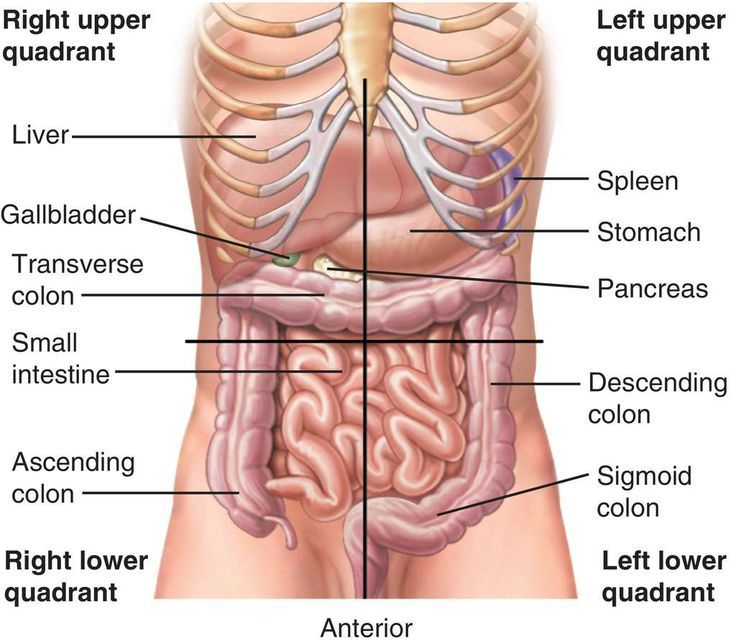 anatomical left and right is when your left and right flipped
anatomical left and right is when your left and right flipped
Directional terms
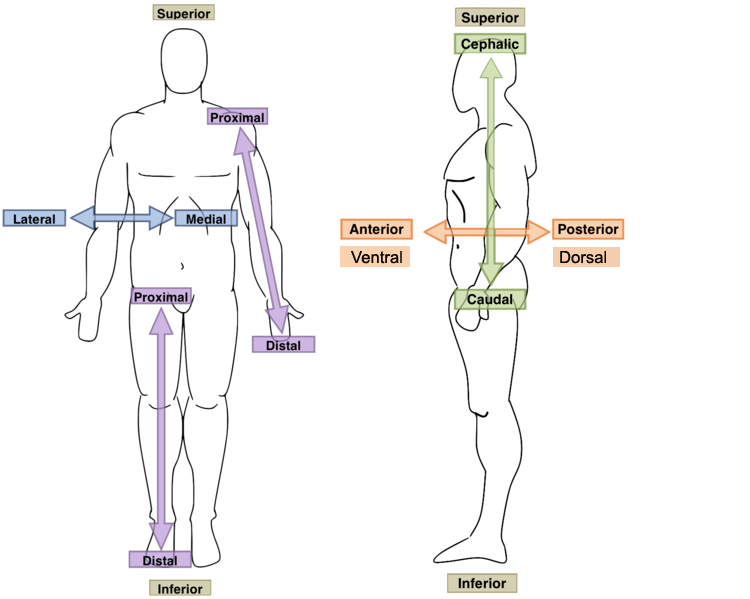
Superior and Inferior: above and below
Medial and lateral: closer to the midline and further from midline
Anterior and posterior: front and back
Proximal and distal: closer and farther
Superficial and deep: on the surface and deep within the body skin has superficial and deeper layers
Ventral and dorsal: often used with anterior and posterior
Afferent and efferent: carrying towards center and carrying away from center
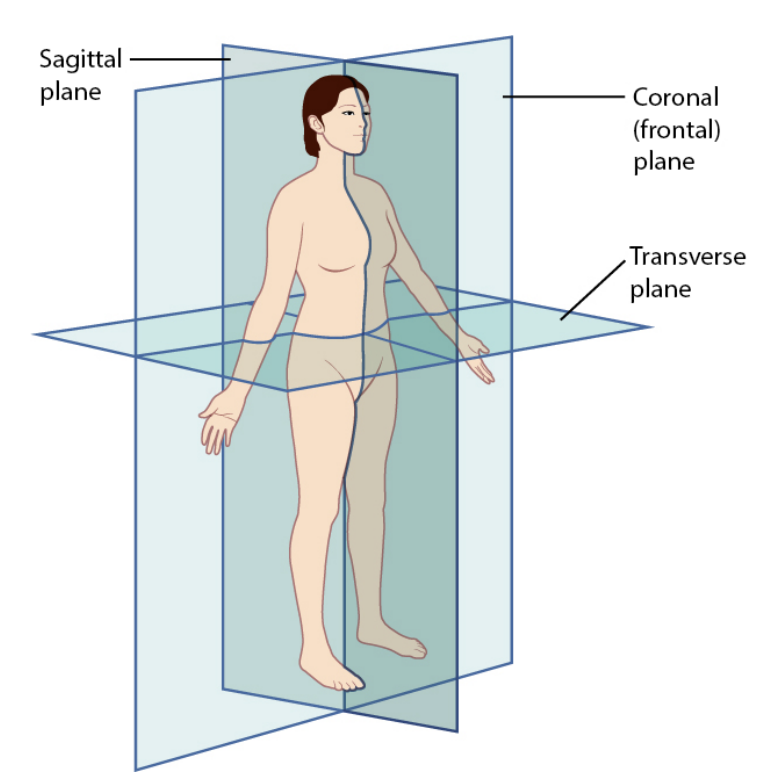
Frontal Plane: runs lengthwise, side to side, divides body into anterior and posterior(front and back)
Sagittal plane: runs through middle from front to back, divides body into left and right
Transverse: runs crosswise, divides body into upper and lower parts