The Network Layer
IP
IP Address- 32 bit/4 byte long numbers made of four octets. Each octet normally represented in decimal numbers.
Belong to networks, not the devices attached to those networks
Each Octet = 8 bits
Dotted-decimal notation
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
Dynamic IP Address-
Sometimes reserved for clients
Static IP Address- must be configured on a node manually
In some cases, static IP addresses are reserved for servers and network devices.
IP Address Classes
IP address can be split into 2 sections:
Network ID
Host ID
Address class system- a way of defining how the global IP address space is split up
3 primary address classes:
Class A- where the first octet used for the network ID, last three are for the host ID (1:3)
Class B- where the first two octets are used for the network ID and the last two octets are for the host ID (2:2)
Class C- first three octets are for the network ID and last octet is for host ID (3:1)
Classless inter-domain routing (CIDR)
Data Link Layer
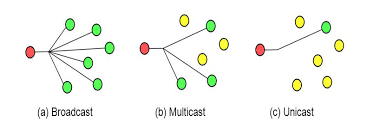
Unicast, Multicast, & Broadcast
Unicast- receive one receiving address
signified by a 0 in the first octet of a destination address. It means the ethernet frame is intended for ONLY the destination address
Multicast- sends data from single source to multiple recipients on the network at the same time
Broadcast- send/transmit by means of radio, television or by streaming over the internet