Velopharyngeal-nasal Function & Speech Production
Skeletal Superstructure
- pg 120 textbook
- temporal bone
- nasal bone
- alveolar process
- maxillary bone
- mandible
- styloid process
- mastoid process
- zygomatic bone
- nasal choana
- vomer
The Pharynx
- extends from base of skull to cricoid cartilage in front and to 6th cervical vertebra in the back
- pharynx is an oval tube, larger side to side than front to back
- connective tissue predominates at the top
- muscle predominates at the bottom
- continues w/esophagus at lower end
- 3 cavities
- nasopharynx
- hard palate is lower boundary
- oropharynx
- between hard palate and hyoid bone
- contains palatine tonsils and lingual tonsils
- laryngopharynx
- between the hyoid and base of cricoid cartilage
- faucial isthmus
- narrow opening between velum and the tongue and between anterior faucial pillars
Velum
- velum means “curtain”
- consists of soft palate and uvula
- covered w/connective tissue
- Muscle fibers are most numerous in the middle portion; scarce at the front and back
Nasal Cavities
also called nasal fossae
2 chambers separated by nasal septum
septum is cartilage at front, bone at back
floor is hard palate
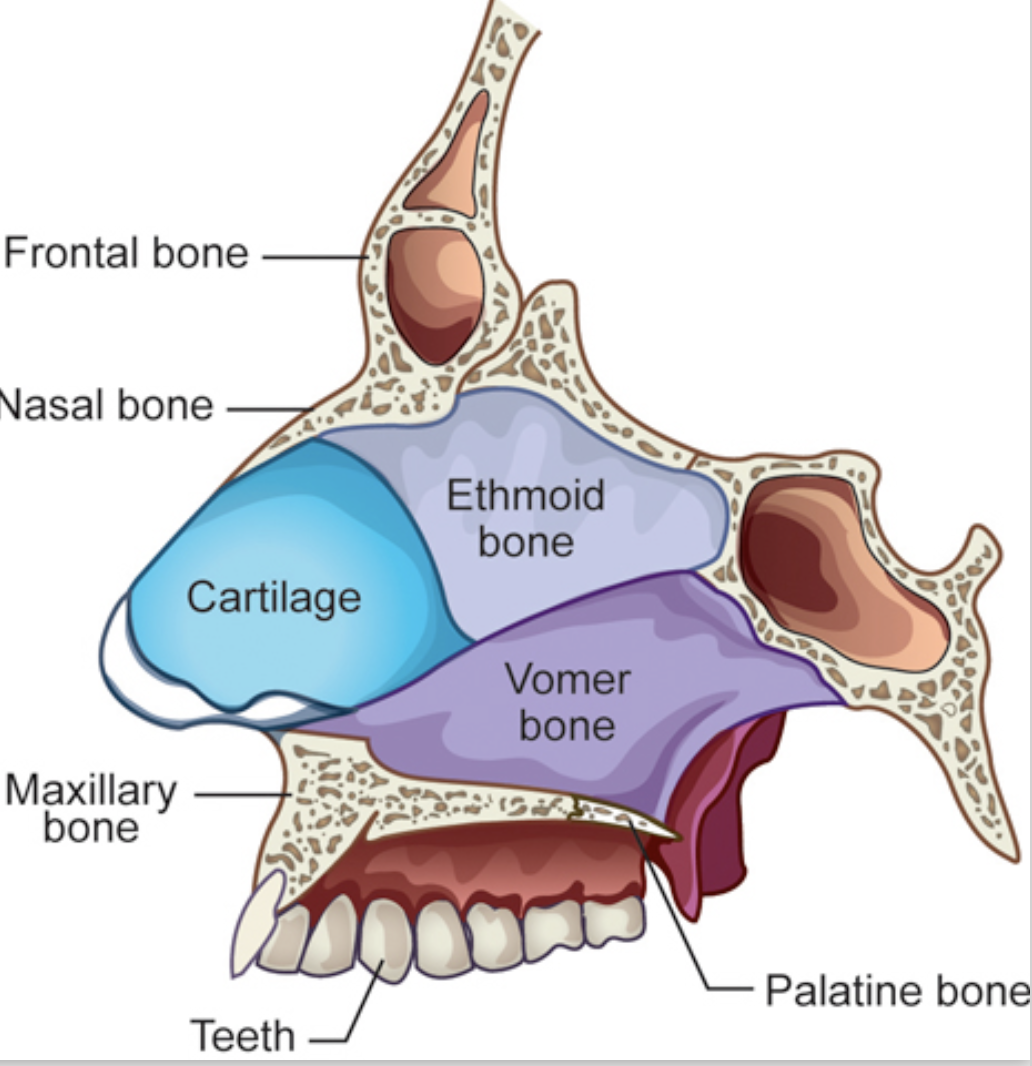
lateral walls are made up of conchae
- conchae - curled and convoluted bone
nasal vestibule at fornt
rich blood supply
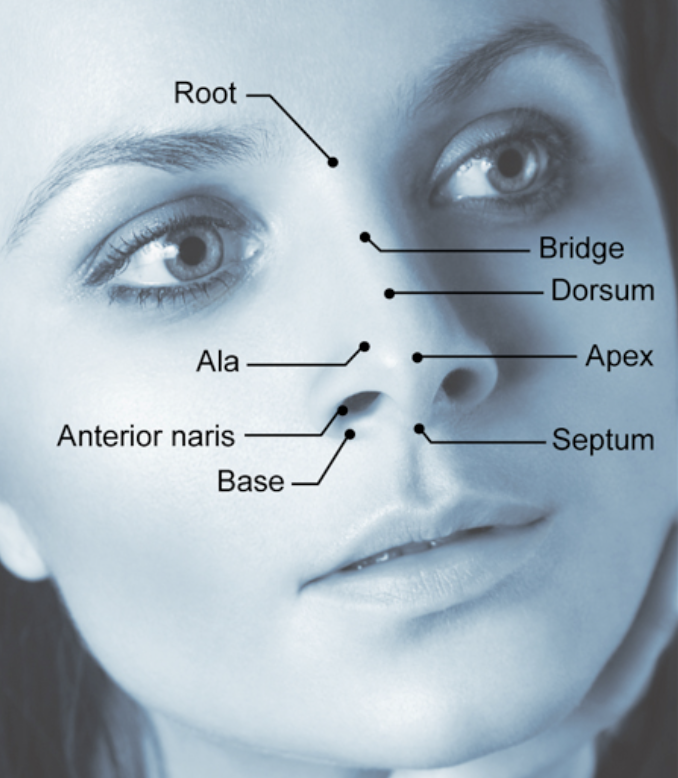
The Outer Nose
root
bridge
dorsum
ala
apex
anterior naris
base
septum
Forces
- passive
- recoil of muscles, cartilages, and connective tissues
- surface tension
- gravity
- aeromechanical forces
- active
- muscles of pharynx
- muscles of velum
- muscles of outer nose
Muscles of Pharynx
The constrictors
- function: pull pharyngeal walls inward and forward to constrict pharyngeal tube
- Superior constrictor
- originates at front of pharyngeal tube and inserts into median raphe of posterior pharyngeal wall
- middle constrictor
- inferior constrictor
- consists of 2 parts
- thyropharyngeus (upper)
- cricopharyngeus (lower)
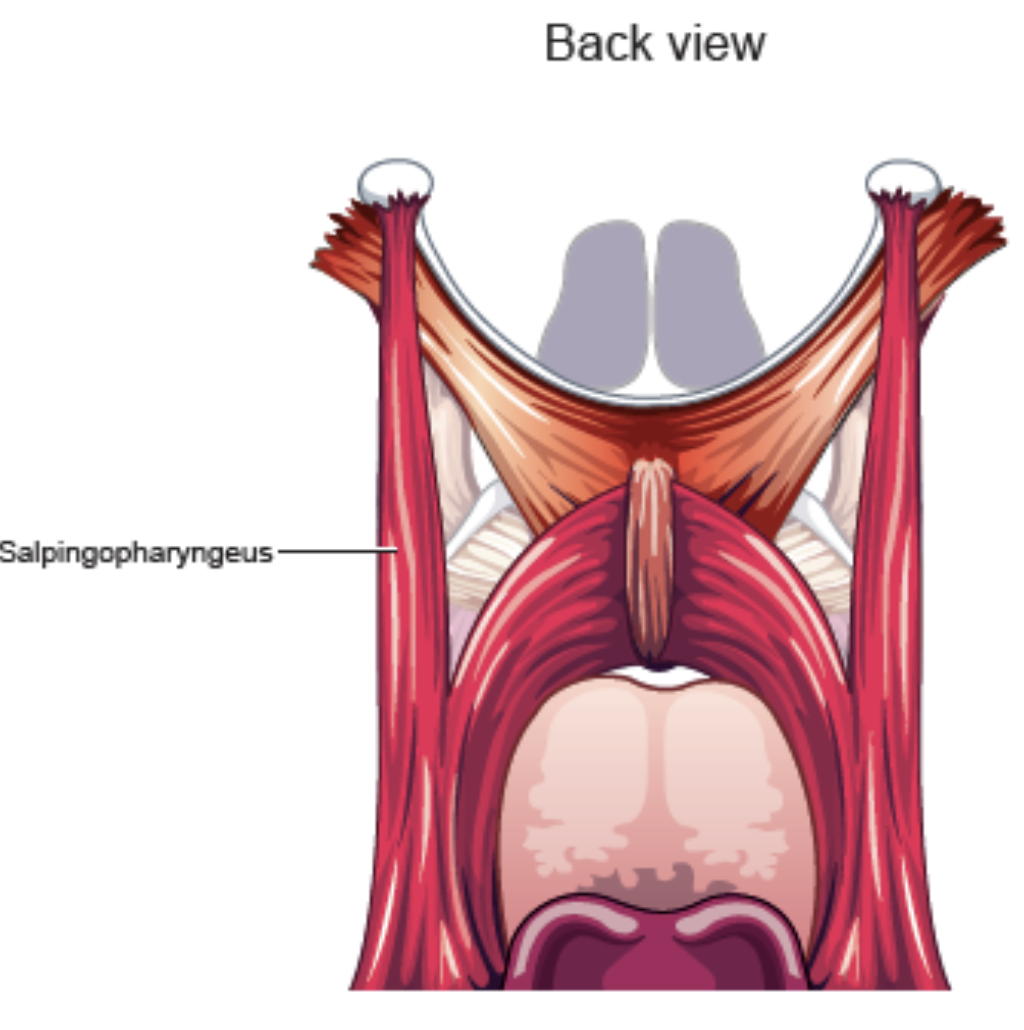
Salpingopharyngeus
function: pulls lateral pharyngeal walls upward and inward
origin: near lower border of pharyngeal orifice of auditory tube
insertion: lateral pharyngeal wall
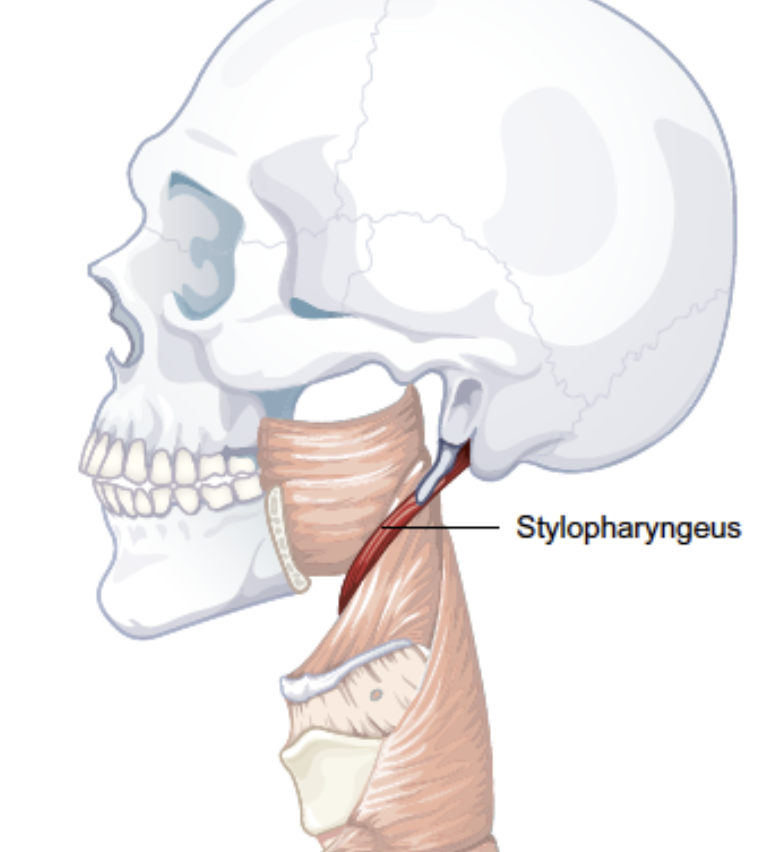
Stylopharyngeus
Function: pulls up on pharynx and pulls lateral walls outward (widens pharynx)
Origin: styloid process
Insertion: lateral pharyngeal wall and thyroid cartilage
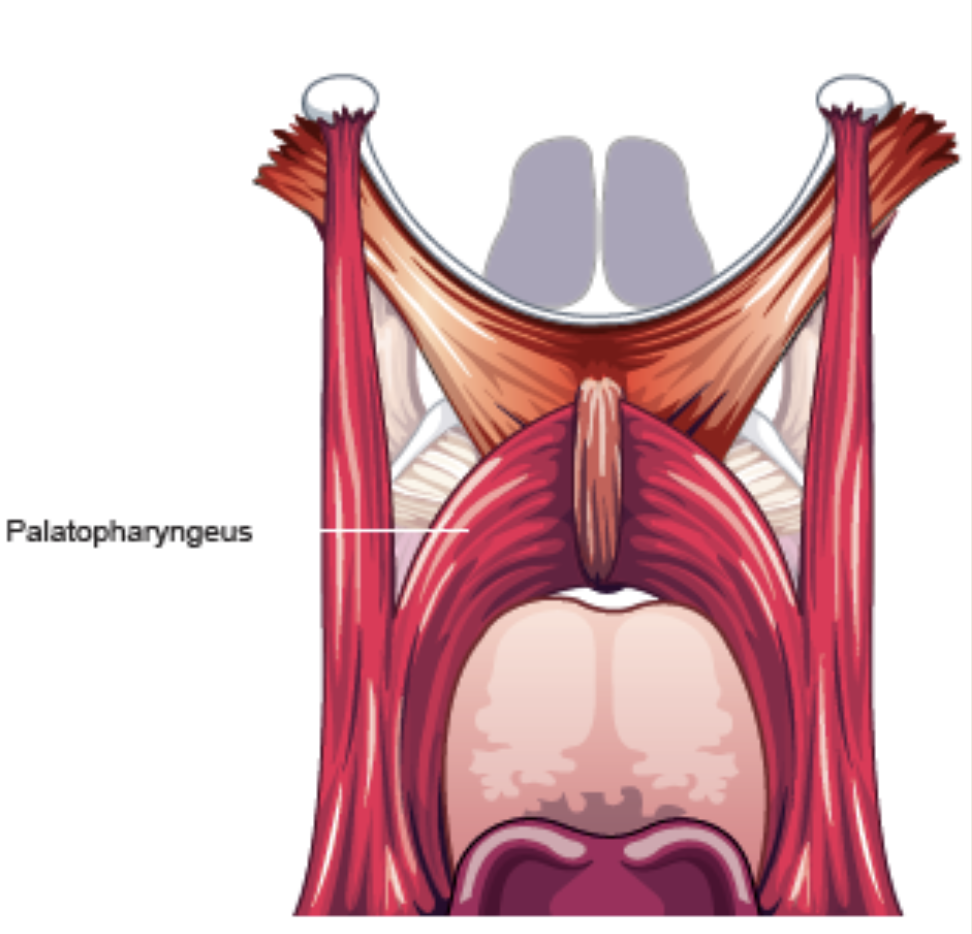
Palatopharyngeus
Function: pulls inward on upper pharyngeal walls and upward on lower lateral pharyngeal walls (with velum fixed)
Origin: soft palate
Insertion: lower lateral wall of pharynx and thyroid cartilage
Muscles of the velum
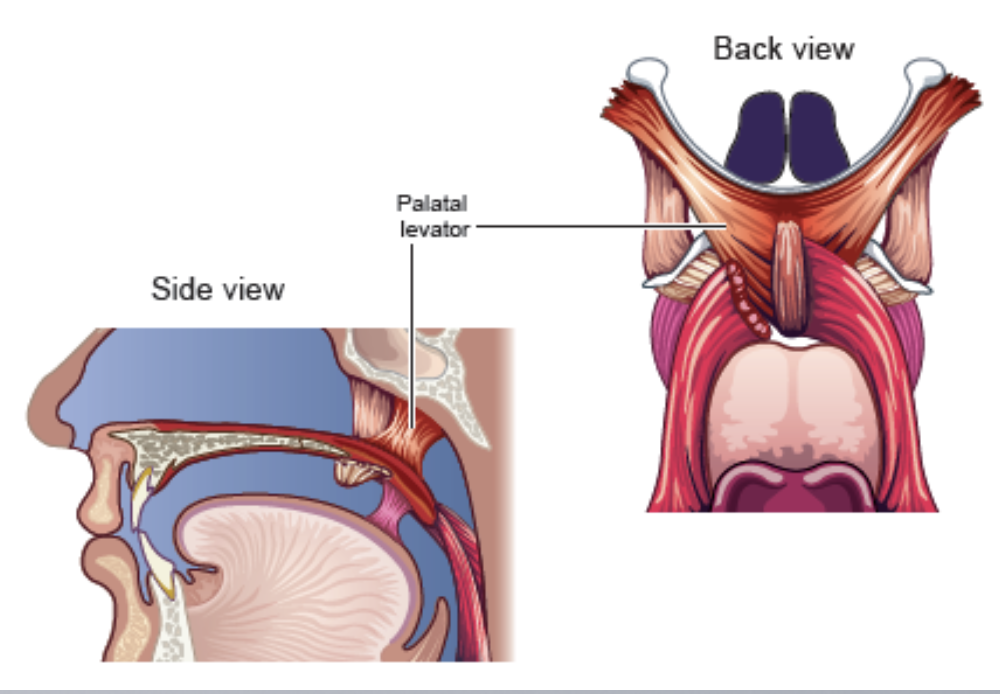
Palatal Levator (levator veli palatini)
- function: draws the velum upward and backward
Palatal tensor (tensor veli palatini)
- function: opens the auditory tube
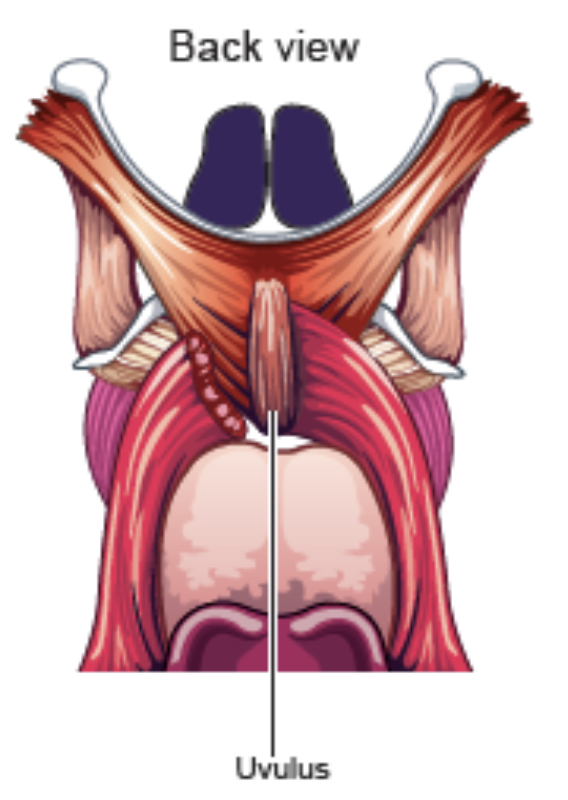
Uvulus
- function: shorten, lift, increase bulk of velum
- only intrinsic muscle of the velum
Glossopalatine
- function: pulls downward and forward on the velum (with tongue fixed)
- Origin: side of tongue
- insertion: lower surface of palatal aponeurosis
Pharyngopalatine
- function: pulls downward and backward on velum (with pharynx fixed)
- origin: lower lateral wall of pharynx and thyroid cartilage
- insertion: runs through posterior faucial pillar and inserts into soft palate and superior constrictor muscle
Muscles of the Outer Nose
- Levator labii superioris alaeque nasi
- function: draws the ala upward and enlarges the naris
- origin: frontal process and infraorbital margin of maxilla
- insertion: divides with one part inserting into upper lip and the other into cartilage of nasal ala
- Anterior nasal dilator
- function: enlarges the naris
- origin: lower edge of lateral nasal cartilage
- insertion: deep surface of the skin near the outer margin of the naris on the same side
- posterior nasal dilator
- function: enlarges the naris
- origin: nasal notch of maxilla and sesamoid cartilages of the outer nose
- insertion: into the skin near the alar cartilage along outer naris on the same side
- nasalis
- function: constricts the naris
- origin: maxilla
- insertion: aponeurosis
- depressor alae nasi
- function: draw outer nose down, decrease naris aperture (constricts naris)
- origin: fossa of maxilla
- insertion: back part of ala
Movements of Velopharyngeal-nasal apparatus
- movements of pharynx
- lengthening/shortening by vertical movements of larynx
- inward/outward movements of lateral pharyngeal walls
- forward/backward movements of posterior pharyngeal walls
- forward/backward movements of velum, tongue, and epiglottis
- movements of the velum