Chapter 3: Metals and Acids
Metals and Oxygen
Many metals will react with oxygen from the air to produce a metal oxide.
Often, they will need to be heated before they can react
Metal | Reaction with Oxygen |
|---|---|
magnesium | burns vigorously |
zinc | burns less vigorously |
iron | burns |
lead copper | does not burn, when heated an oxide layer is formed on the surface. |
gold | no reaction |
Metals and Water/Steam
Very reactive metals like sodium will react with cold water to produce a metal hydroxide and hydrogen gas. An example of this is = sodium + water → sodium hydroxide + hydrogen 2Na(s) + 2H2
Other metals like magnesium only react with steam, and produce a metal oxide and hydrogen. An example of this is = Mg(s) +H2O(g) → MgO(s) +H2(g)
Magnesium can be reacted with steam using a setup which uses a glass tube, with a magnesium ribbon and a mineral wool soaked in water inside, which is clamped and heated with a Bunsen burner.
State Symbols
Symbol equations have letters in brackets after each substance.
These tell you the state of matter of each substance, and are called state symbols: (s) = solid, (l) = liquid, (g) = gas, (aq) = dissolved in water
H2O(s) is ice,
H2O(l) is water
H2O(g) is steam
NaCl(aq) is sodium chloride (table salt) dissolved in water.
Metals and Acids
If a metal reacts with an acid, it produces a salt and hydrogen gas.
All acid compounds have hydrogen in them.
When the hydrogen is replaced by a metal, the compound is called a salt.
For example, sulfuric acid has the formula H2 SO4 so copper sulfate has the formula CuSO4 – it is a salt because the copper has taken the place of the hydrogen in sulfuric acid.
The three main acids are hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, and nitric acid.
Metals can react with all of these acids to produce a salt and hydrogen gas.
Examples-
copper + hydrochloric acid → copper chloride + hydrogen
iron + sulfuric acid → iron sulfate + hydrogen
magnesium + nitric acid → magnesium nitrate + hydrogen
Testing for Hydrogen gas
The gas produced when reacting a metal and a salt can be collected in an upturned test tube, and a test is performed to check that the gas is hydrogen.
Insert a lit splint into the upturned test tube – if the gas is hydrogen, there will be a squeaky ‘pop’ sound.
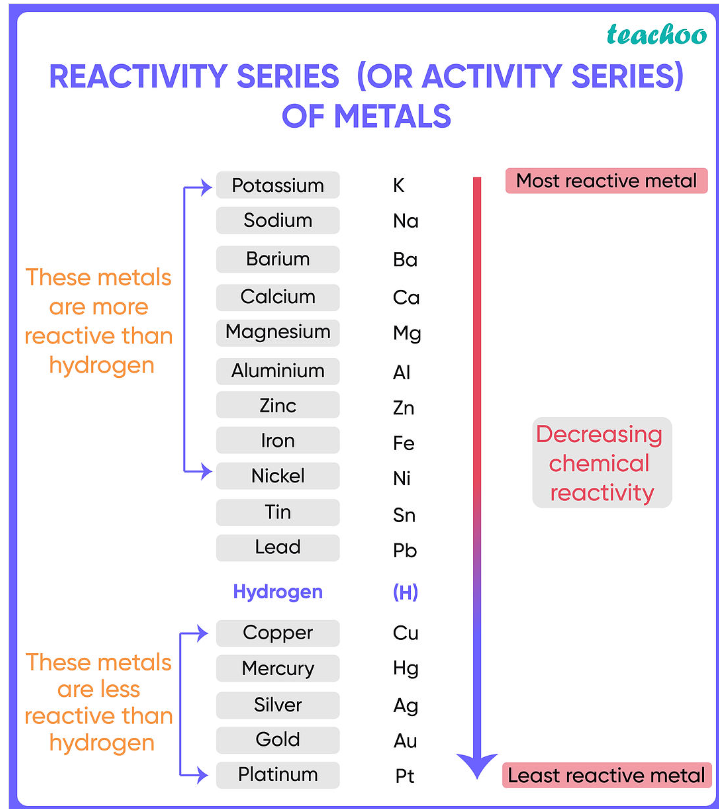
Reactivity
A displacement reaction occurs when a more reactive element takes the place of a less reactive element in a compound.
In metals, this means that the more reactive metal will become a compound, and the less reactive one an element.
The Reactivity Series