Carbon Cycling + Flashcards
Carbon Dioxide
- carbon sinks: decrease in CO2 in the atmosphere
- carbon sources: increase in CO2 in the atmosphere
- Carbon is found in both the abiotic and biotic parts of an ecosystem
- Autotrophs produce most of the carbon found in organisms.
- Autotrophs transform carbon dioxide into more complex carbon-based compounds, such as glucose.
- The concentration of carbon dioxide present in our atmosphere is 0.04% or 400 ppm (parts per million)
- Carbon dioxide can combine with water to produce carbonic acid, which is an unstable compound that dissociates in water as hydrogen and hydrogen carbonate (bicarbonate) ions. This can make the water more acidic as the hydrogen ions that are released reduce the pH.
- In an aquatic ecosystem, carbon is present in the form of carbon dioxide and hydrogen carbonate ions.
- Land plants absorb carbon dioxide through their stomata, which are pores found on the underside of their leaves. However, aquatic plants absorb dissolved carbon dioxide into their leaves from the environment. The carbon dioxide is then used to make carbohydrates and other carbon compounds
- autotrophs take up and give off oxygen during photosynthesis, allowing for the existence and survival of heterotrophs.
- both autotrophs and heterotrophs respire and produce carbon dioxide
- in winter, the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increases as the plants are dormant; plants produce less oxygen and take up less carbon dioxide as they lose their leaves. However, in summer, as plants have more leaves, they are able to produce more oxygen and take up more carbon dioxide, so the concentration of carbon dioxide decreases in the atmosphere.
- the rate of photosynthesis increases in warmer seasons and decreases in colder seasons.
- Certain bacteria (e.g. Escherichia, salmonella) ferment orgnaic matter into CO2 and other products:
- convert orgniac matter into alchohol, hydrogren and CO2
- convert alcohol into CO2, hydrogen and acetic acid
Methane and Peat Formation
- methane is a carbon molecule which is produced in anoxic conditions and can oxidise into carbon dioxide and water
- produced from organisms that live in anaerobic conditions (organisms that live in the absence of oxygen) by methanogenic achaeans
- peat is partially digested organic matter than forms in acidic, water-saturated soil. It contains large amounts of carbon and can be compressed into coal over time
- Peat forms in waterlogged, acidic and anoxic conditions where saprotrophic organisms cannot survive
- For peat to form, conditions should prevent degradation. The two required conditions are:
- Low pH or acidic condition
- anoxic condition or absence of oxygen.
- anaerobic vs anoxic:
- anoxic is used to describe environments without oxygen
- anaerobic refers to organisms that are able to survive without oxygen
- Uses of peat:
- As a substitute for firewood for cooking and heating
- To increase the moisture holding capacity of the soil (that is rich in sand particles) in horticulture
- To increase the water infiltration rate of soils rich in clay particles
- To acidify soils for specific pot plants.
- methanogens are archaea that are anaerobic organisms that obtain energy through the synthesis of methane from CO2 and H2 or acetate.
- Archaea (a type of prokaryote) - Methanogenic
- produces CO2 from methane and hydrogen (called methanogenesis)
- in the atmosphere, methane is oxidized into carbon dioxide and water (release of CO2 result of methanogenesis)
Decomposition of Organic Matter
- fossil fuels are organic matter that has been compressed over time to form coal, oil and gas
- the carbon trapped in fossil fuels is released into the atmosphere through combustion, which is a process of burning, which releases carbon dioxide from organic material
- Reservoirs for carbon
- biomass
- fossilised remains
- atmosphere, sediments and sedimentary rocks
- coal is formed in wetlands
- formed from deposits of peat buried under other sediments
- through partial decomposition in the bottom of lakes and oceans, oil and gas are formed
- oil and natural gas is formed in mud
- the decomposed matter is compressed and heated, producing liquid carbon compounds or gases.
Calcium Carbonate
- when calcium carbonate is fossilized, it becomes limestone
- Calcium carbonate is an important source of carbon in the environment, as it makes up the shells and exoskeletons of various animals and can eventually become porous sedimentary rocks like limestone.
- found in reef-building corals or molluscs made of calcium carbonate
- calcium carbonate dissolved in acid, but not basic (alkaline) solutions
- as most of our oceans are alkaline, it is the perfect environment to create sedimentary rocks such as limestone
- examples of carbon reservoirs on Earth
- sedimentary rocks, e.g. limestone deposits
- calcium carbonate shells
- the atmosphere
- fossil fuels
- carbon dioxide dissolved in oceans
- The process that takes place to move carbon from one form to another
- photosynthesis, which changes co2 in the atmosphere into carbon compounds in plants
- consumption, which moves carbon into the food chain
- fossilization/lithification, which compresses carbon into rocks, fossils or fossil fuels
- combustion and respirations, which releases carbon back into the atmosphere
Volcanic Activity
- over time, Earth's crustal plats move and collide, causing rock to melt under the extreme heat and pressure, producing CO2
- the volcanic eruptions release CO2 build-up
Carbon Cycle
Reservoir/Sink→a place where a certain element, such as carbon, has accumulated or pooled.
Flux→the process that moves an element from one reservoir/sink to another
lithosphere→the portion of the Earth that consists of the crust and upper mantle
Hydrosphere→the portion of the Earth that consists of water including oceans, leakes, ponds and rivers
Biota→the portion of the Earth that consists of living organisms
Atmosphere→the layer of gases surrounding the Earth
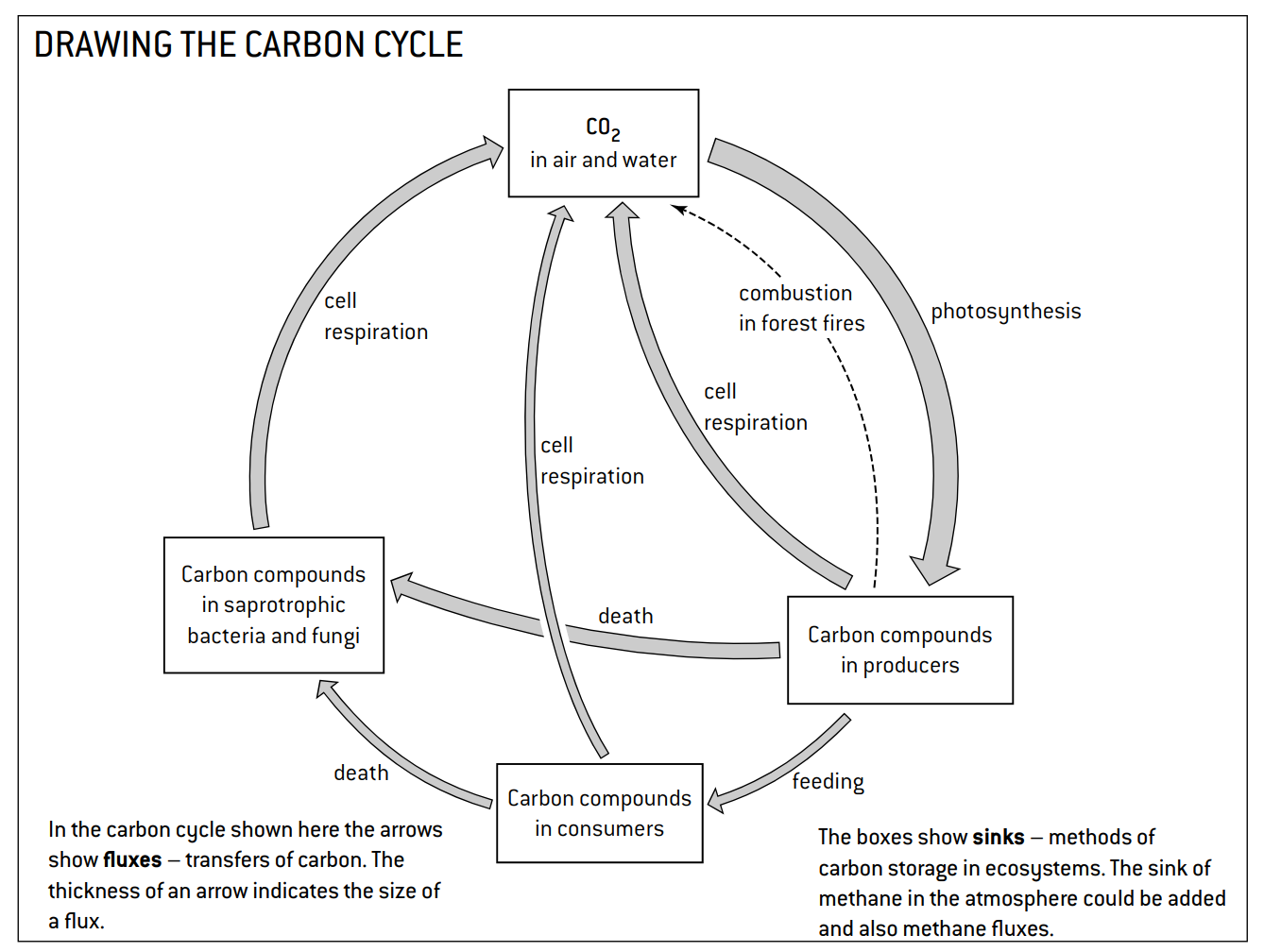
Which process/flux decreases the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere?→photosynthesis
What is formed when carbon dioxide combines with water?→carbonic acid
During which process in some living organisms is inorganic carbon from the atmosphere used to build organic carbon-based compounds?→photosynthesis or carbon fixation
Which type of organism feeds on dead organisms whilst respiring to release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere?→decomposers
Limestone rock is made up of a high proportion of calcium carbonate deposits. What type of rock is limestone?→sedimentary rock
\
\
\