Organic Lecture 2/19
Review
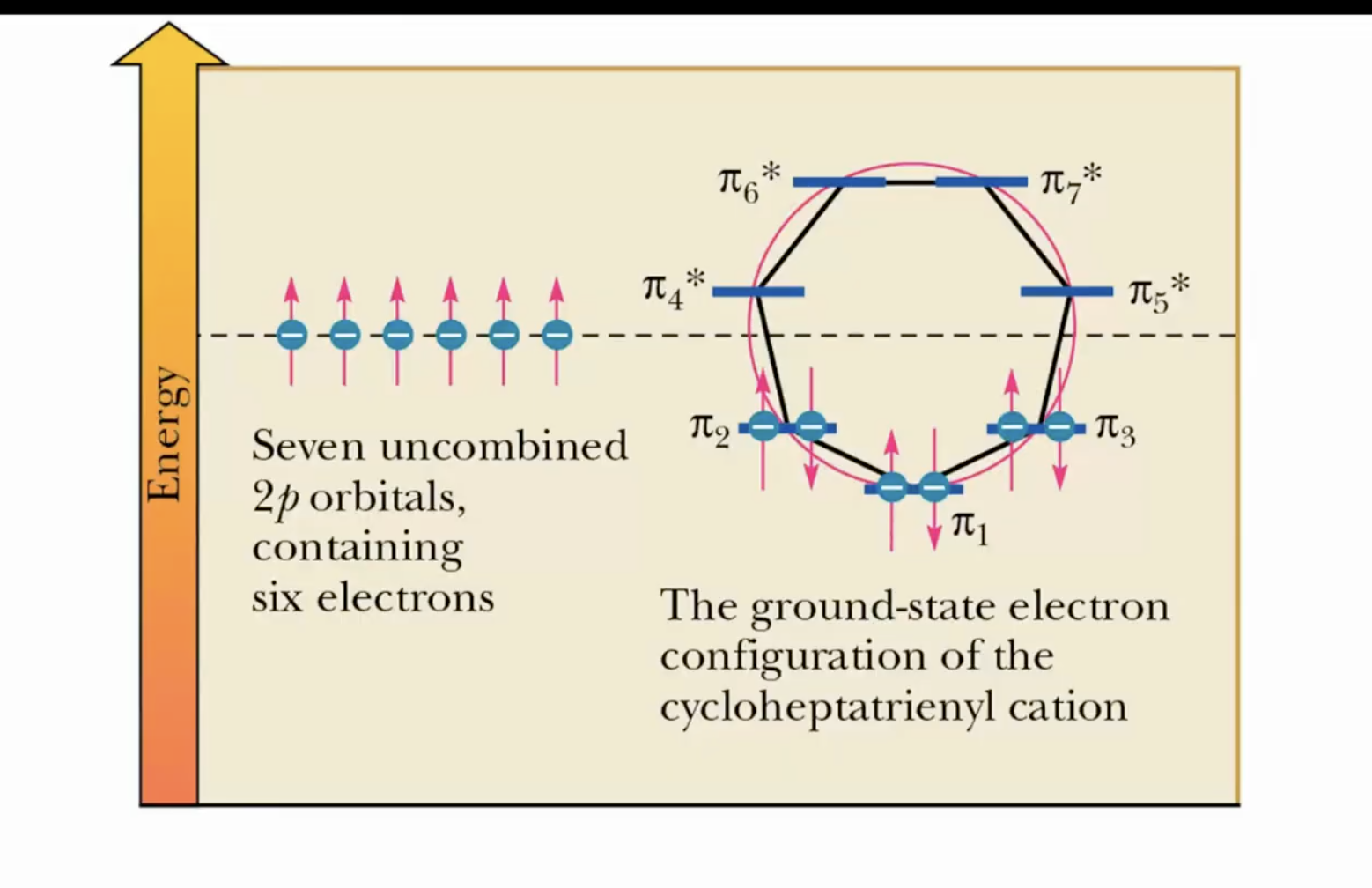
Cycloheptatriene: one that’s aromatic is the cation because of 4n+2 electrons, satisfying Huckel’s rules.
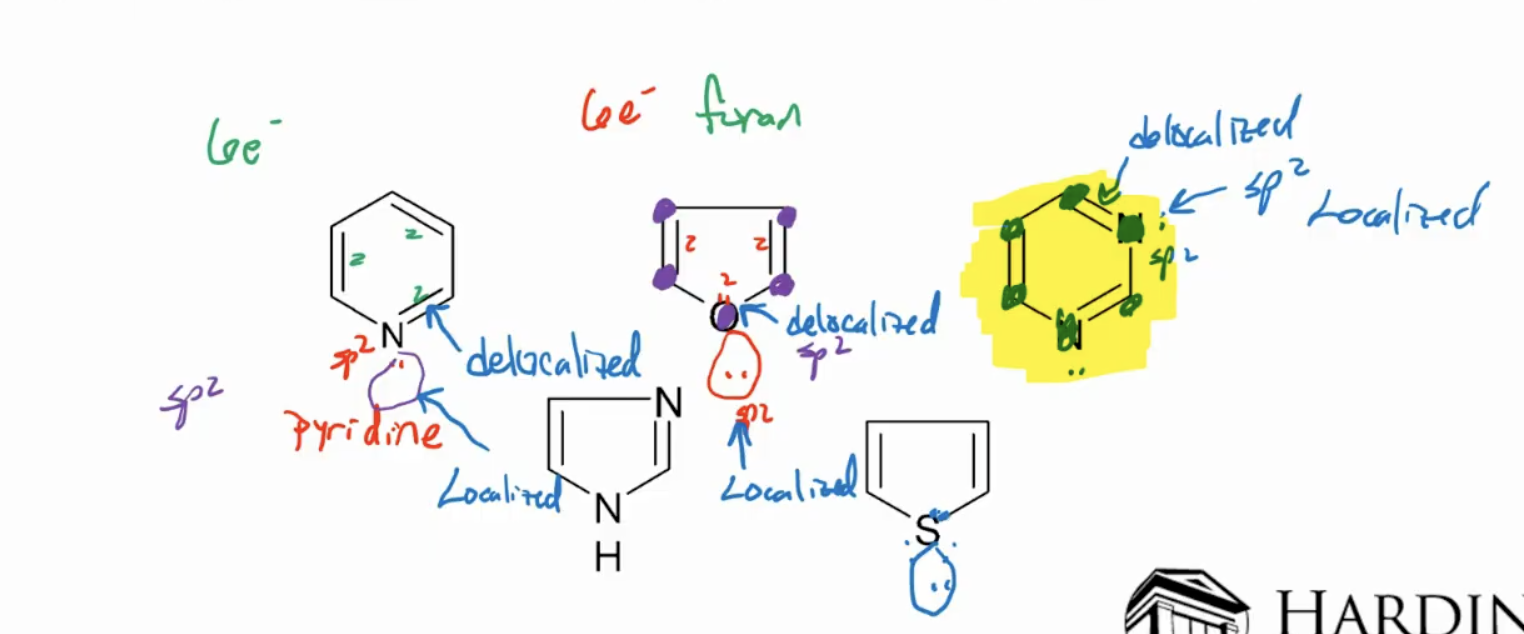
Heterocycles can be aromatic as well: can re-hybridize to make aromatic.
Making benzene ring: 3 acetylenes, Cu or Fe, and heat
Reaction of Arenes
Generally unreactive, but if they do react it will happen via substitution. Require harsh conditions because of how stable an arene is.
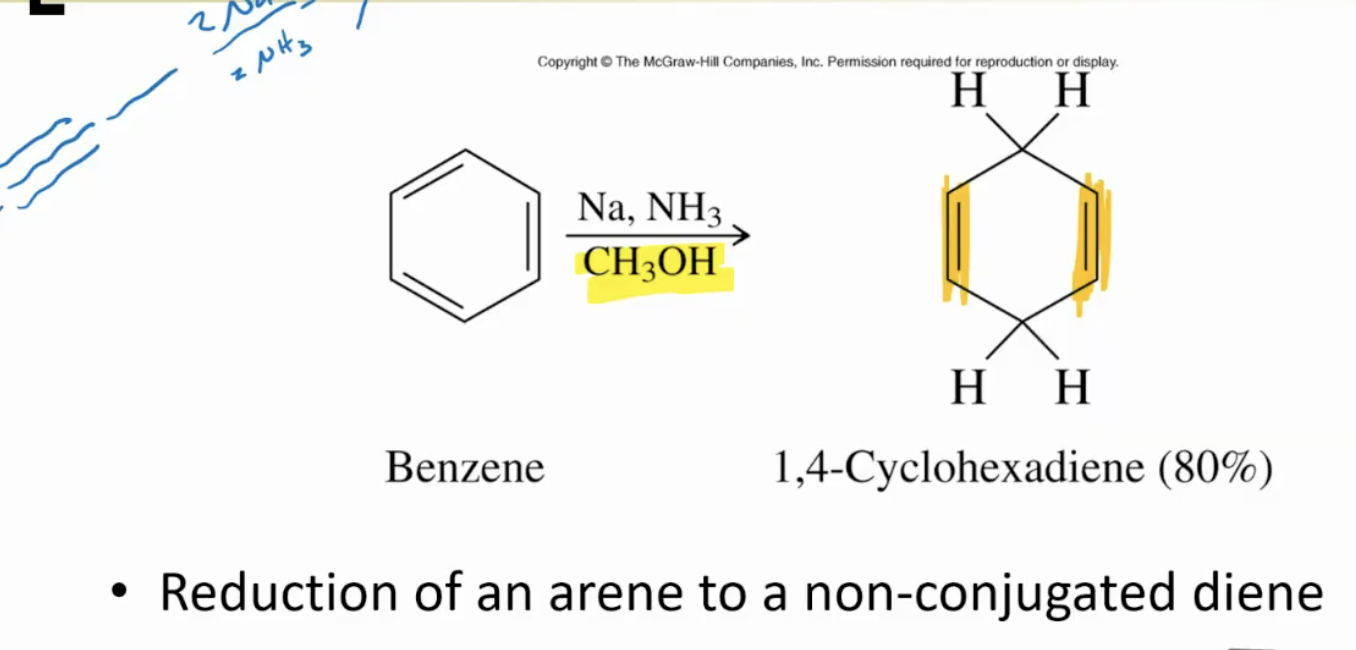
Birch reduction: convert benzene into non-conjugated diene. Uses Na, NH3 and CH3OH.
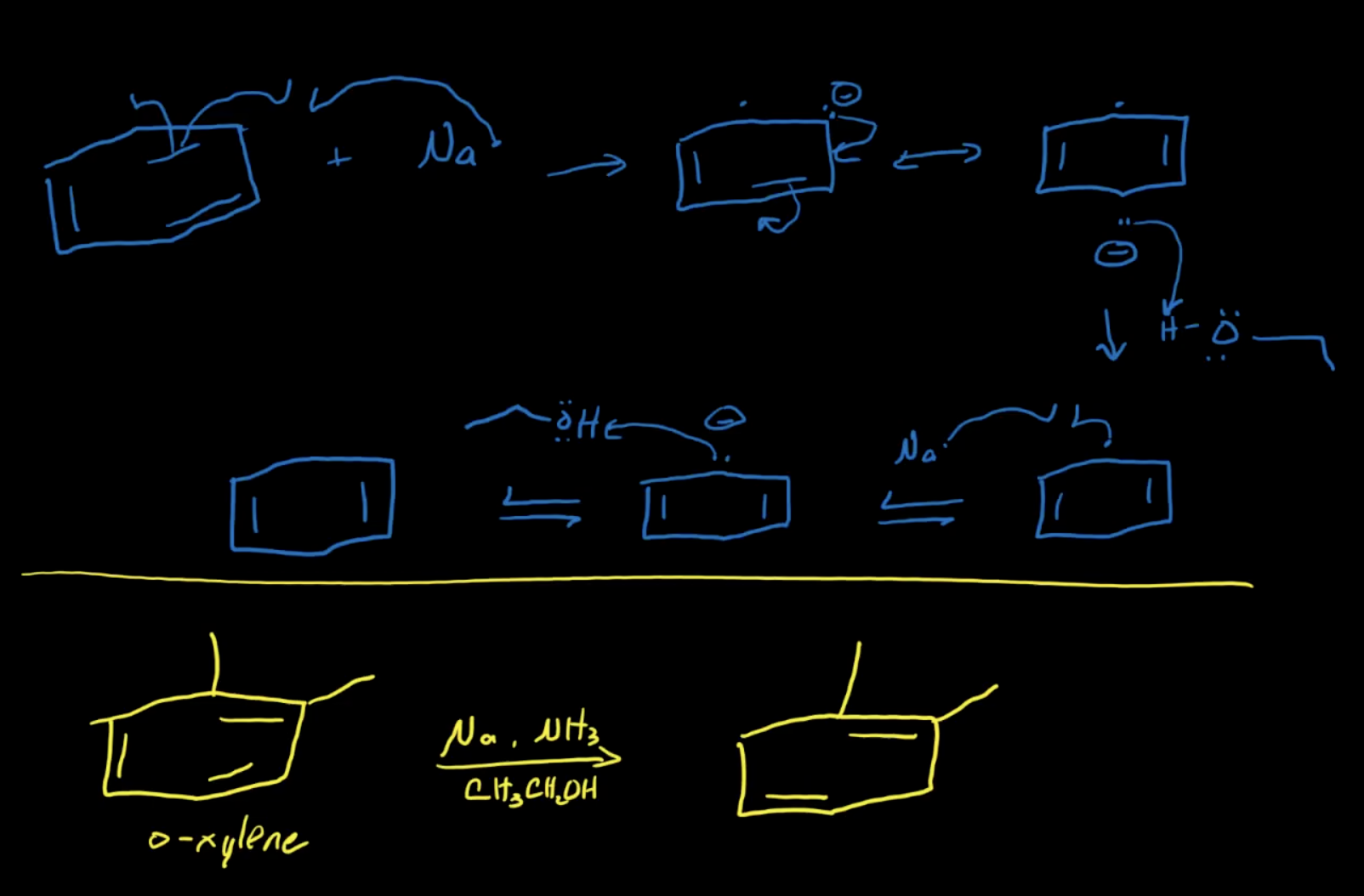
Mechanism of Birch Reduction
-always forms more stable alkene, more substituted
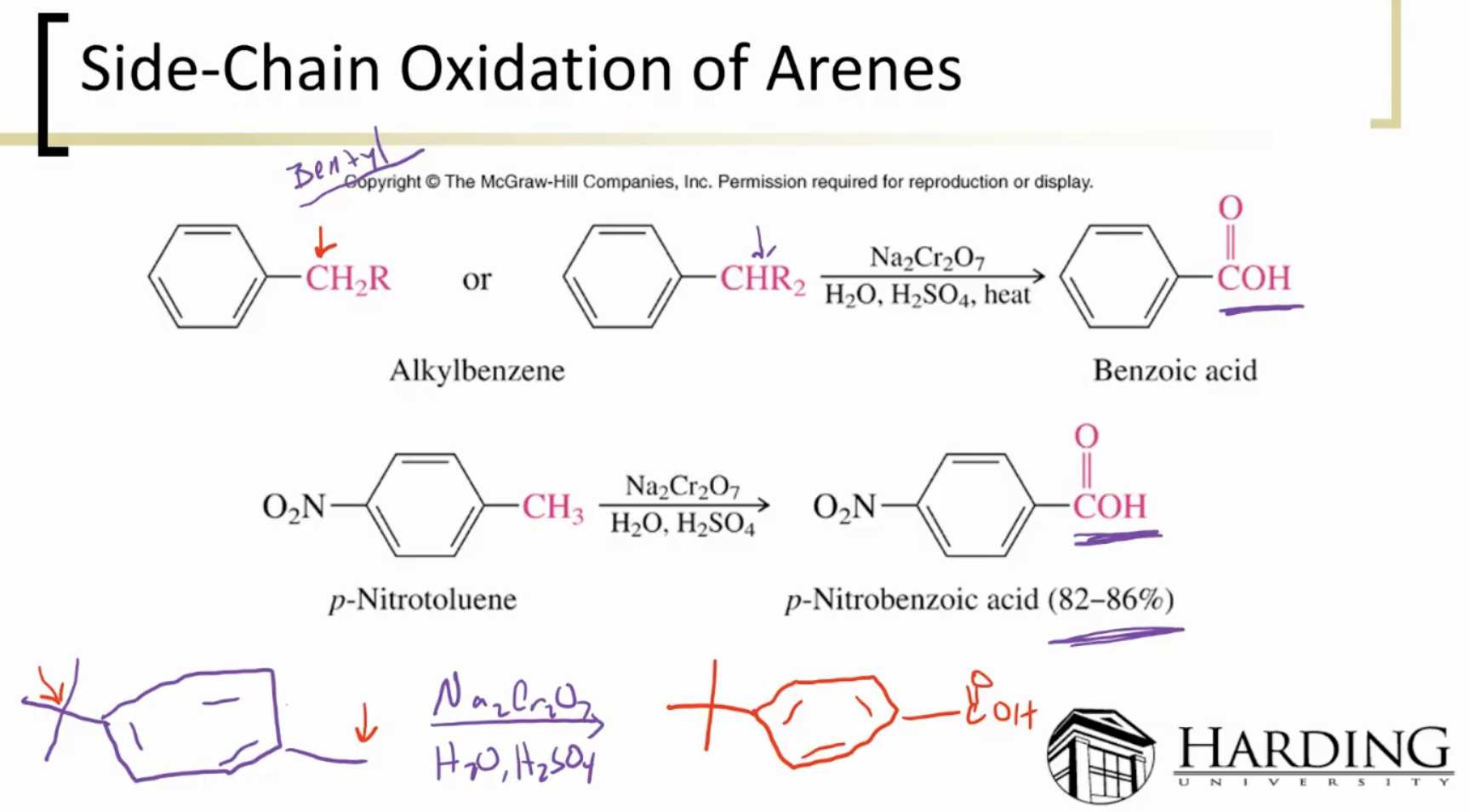
Oxidized Arenes:
Usually resistant to oxidation because nothing can be pulled off. Much rather go through combustion.
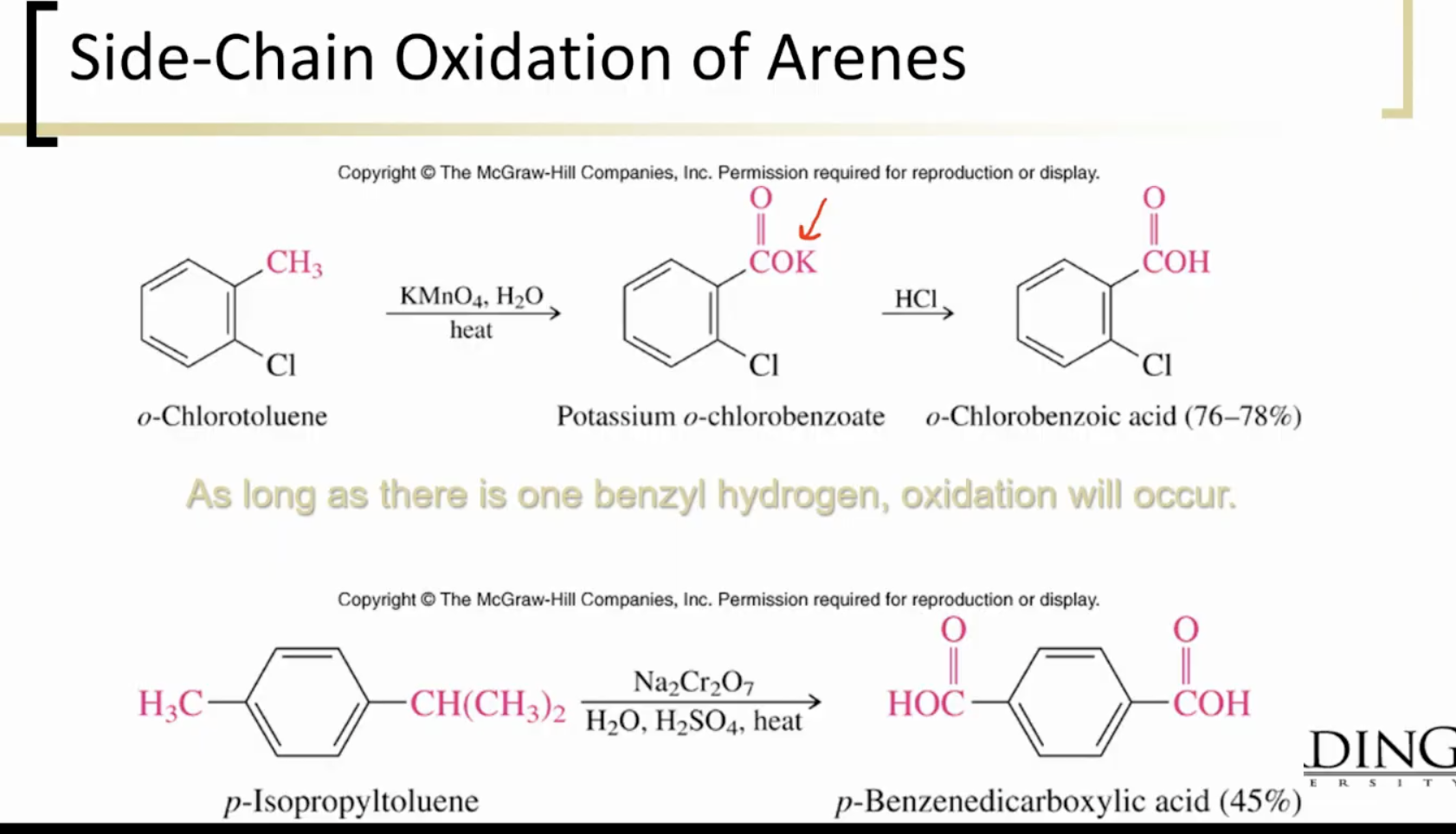
Side Chain Oxidation: needs at least one benzylic hydrogen
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitutions (EAS):
The electrophile has to be ridiculously unstable for the pi bond on aromatic to come grab it.
Mechanism: generate electrophile (fast), form carbocation(slow), then regeneration of aromaticity(fast)
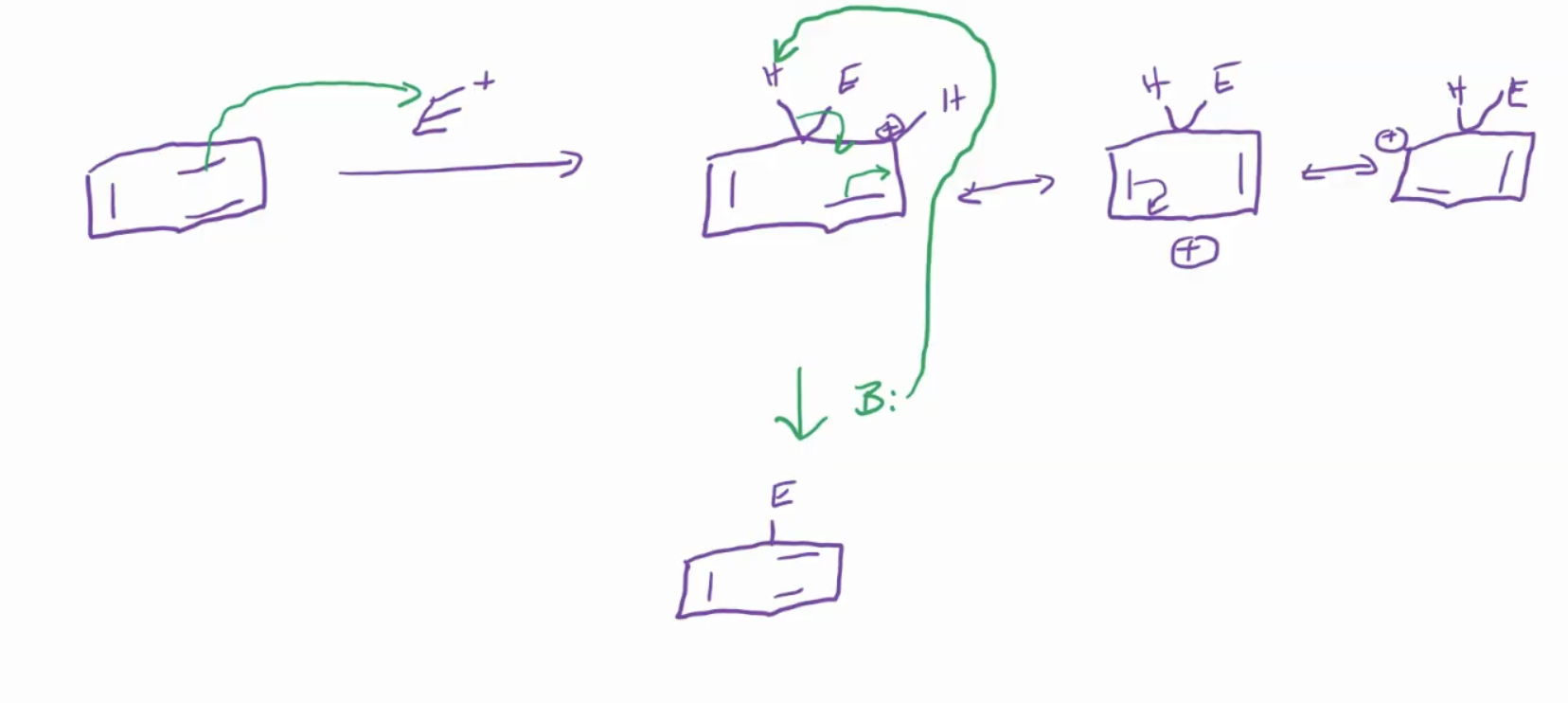
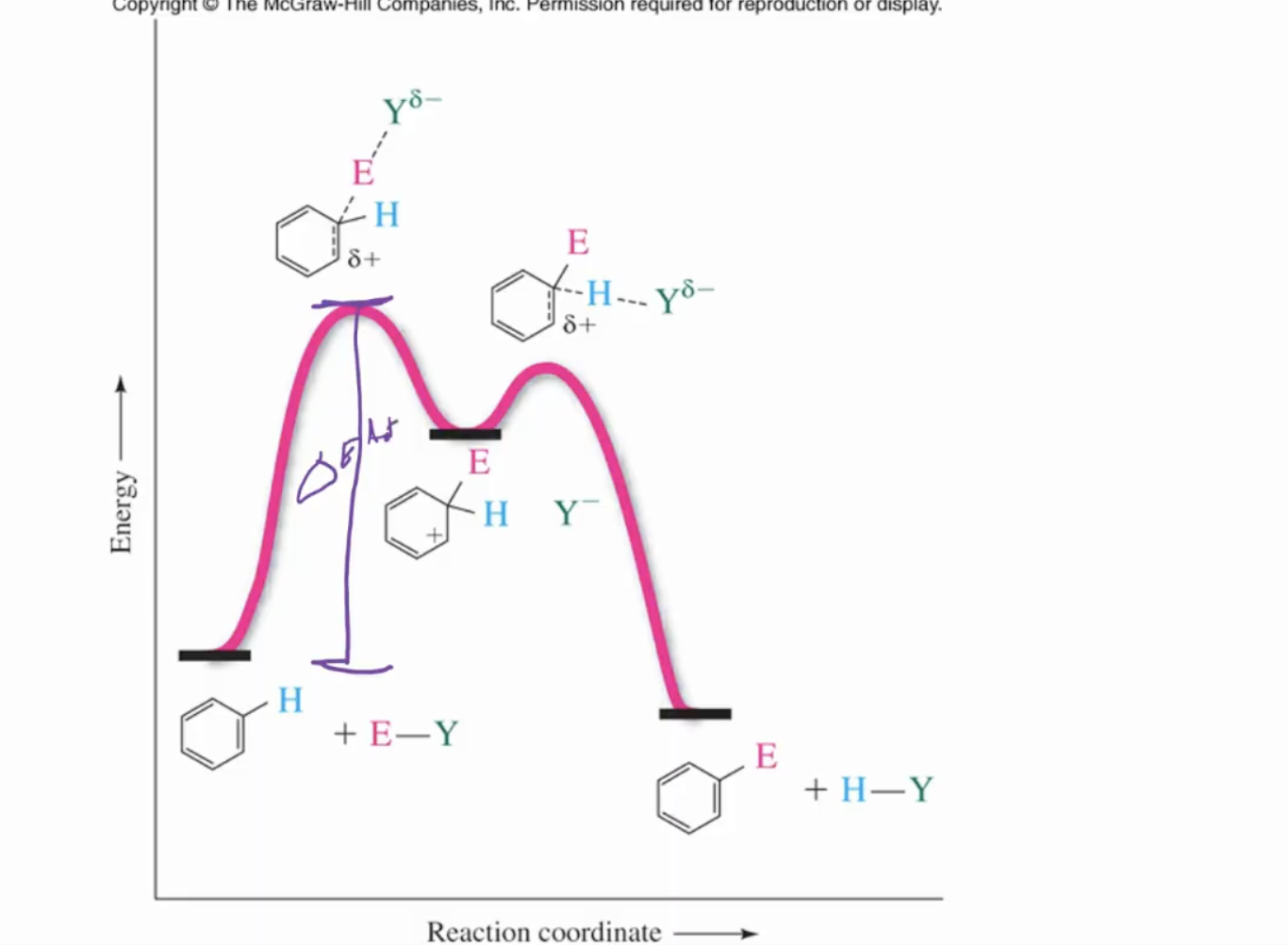
Electrophiles to use: Cl+, NO2+, C+(CH3)3, and SO3
Halogenation of Arenes:


 Knowt
Knowt