Nervous system and neurons
Central nervous system | It receives sensory information from the PNS (body), and transfers motor information back to the PNS (body). |
Brain | It regulates and guides all other parts of the nervous system. It helps to maintain our bodily functions, such as breathing. Receives information from the outside world from our senses, and then coordinates an appropriate response. |
Spinal cord | A long, cable like ladder of nerve fibres from the base of our brain to the lower back. It passes sensory information via afferent neurons up to the brain, and transmits motor information via efferent neurons down from the brain to the PNS (body). |
Neocortex (cerebral cortex) |
|
Autonomic nervous system | Communicates between the CNS and organs, glands, and muscles to make sure our vital organs are working without conscious awareness. It controls unconscious responses. |
Peripheral nervous system | Sends sensory information to the CNS (brain) and receives motor information from the CNS (brain). |
Somatic nervous system | It transmits sensory information from our eyes, ears, and nose towards our CNS. After that it transmits motor messages from our brain via our spinal cord, to help initiate voluntary movement. Controls conscious responses. |
Sympathetic nervous system | It prepares the body for action to help deal with a potential threat. It helps to activate the fight/flight/freeze response in emergencies. |
Parasympathetic | Helps to counterbalance the affects of the sympathetic nervous system, and returns the body back to its normal levels of functioning. |
Enteric nervous system | It controls the communication between our gut and brain, and controls our digestive tract, which is made up of organs that food and liquids travel through when they are swallowed. 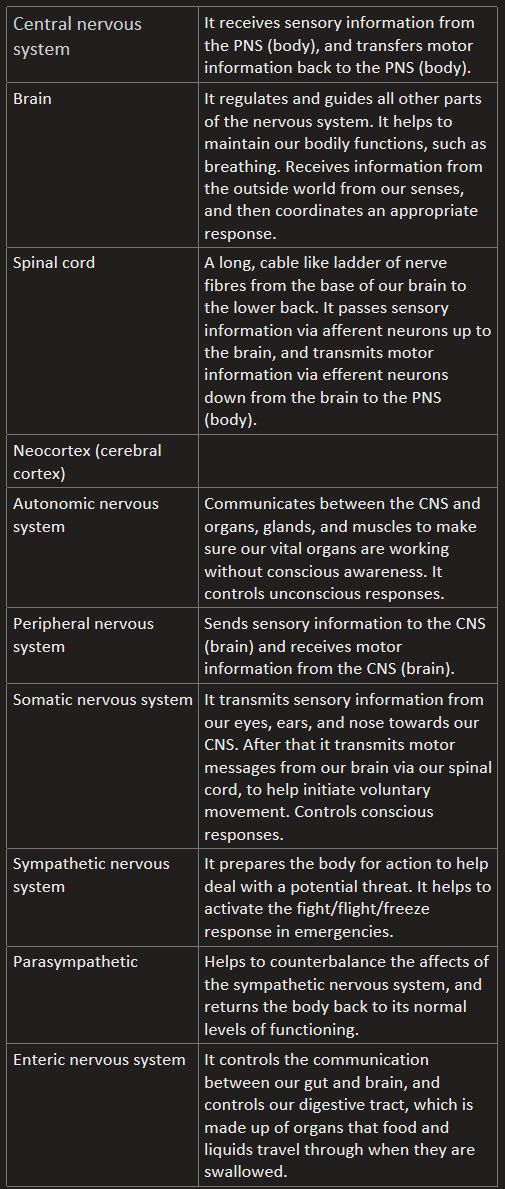 |