2.1 - economical developments
Gustav Stresemann
- Party: DVP which was centre right
- Roles: chancellor 1923 and foreign minister 1923-1929
- His number one priority was the stabilization of the economy
Stabilization of the currency
- ending passive resistance which encouraged new relations
- issuing a new currency: the rentenmark in november 1923, this replaced the reichmark. the exchange rate was 1 rentenmark:1trillion reichmark
- Balancing the budget : expenditure was cut, taxes raised and 300,000 civil servants were let go.
- Stresemann stabilized the economy by introducing a new currency to abolish the old one.
Dawes plan
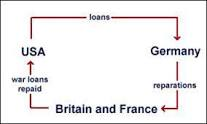
- it was an attempt to fix the reparation problem
- it was a temporary fix
- proposed on April 1924 and agreed in September 1924
- repayment stayed the same 1 billion marks for the first 5 years and 2.5 billion for the rest
- infinite amount of time to repay it
- loaned 800 million marks from the USA which couldn’t even pay for the first payment.
The Young Plan
- proposed on august 1929 agreed in January 1930
- amount was to be reduced by 20% Germany was to pay 2 billion marks per year, 2/3 of which could be postponed each year
- some thought it wasn’t a big enough reduction and postponement meant that they would constantly remain in debt
- payed over 59 years to end in 1988, but people were worried that the economy would never recover
- loans available by american, coordinated by JP Morgan, this meant that Germany became dependent on American success. This meant that the American depression would effect them heavily.
To what extent did the economy recover?
- foreign investment as others gained confidence inn the country
- overall in 1924-28 the economy did improve
- improved industry
- standard of living increased and wages increased
- inflation kept low
- working class benefited
Limits
- not recovered from the war
- shortage of credit material based on the availability of loans
- uneven recovery chronologically and across different parts of the economy