Chemistry
Acids + Bases
Acids | Bases |
Properties:
| Properties:
|
Acids
Acids are corrosive substances - they react with solid substances ‘eating them away‘
Some acids like sulphuric acid are used in car batteries. Sulphuric acid is also dangerously corrosive
Some acids are safe to even taste like the ones in fruit and vinegar
Strong acids are able to react to their full extent with other substances, while weak acids do not.
The word acid comes from the latin word ‘acidus’ meaning sour.
Bases
Some bases are very corrosive especially caustic soda (sodium hydroxide)
Bases that can be dissolved in water are called alkalis
Similar to acids bases can be strong or weak
The strength of an acid or base can be measured by the pH scale.
Strong acids:
| Weak acids:
|
Strong Bases:
| Weak Bases:
|
How do you tell if a substance is an acid or a base?
Acid base indicators are substances that can be used to tell whether a substance is an acid or a base.
They react with acids and bases producing different colour in each
1 commonly used indicators:
Litmus - turns red in acid and blue in a base
Bromothymol blue - turns yellow in acid and blueish purple in a base
Universal indicator - a mixture of indicators and it changes colour as the strength of an acid or base changes.
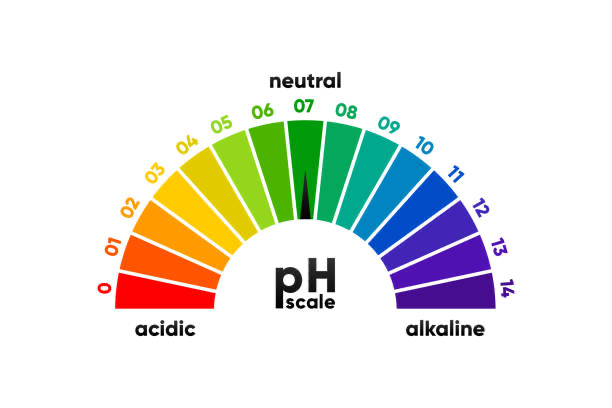
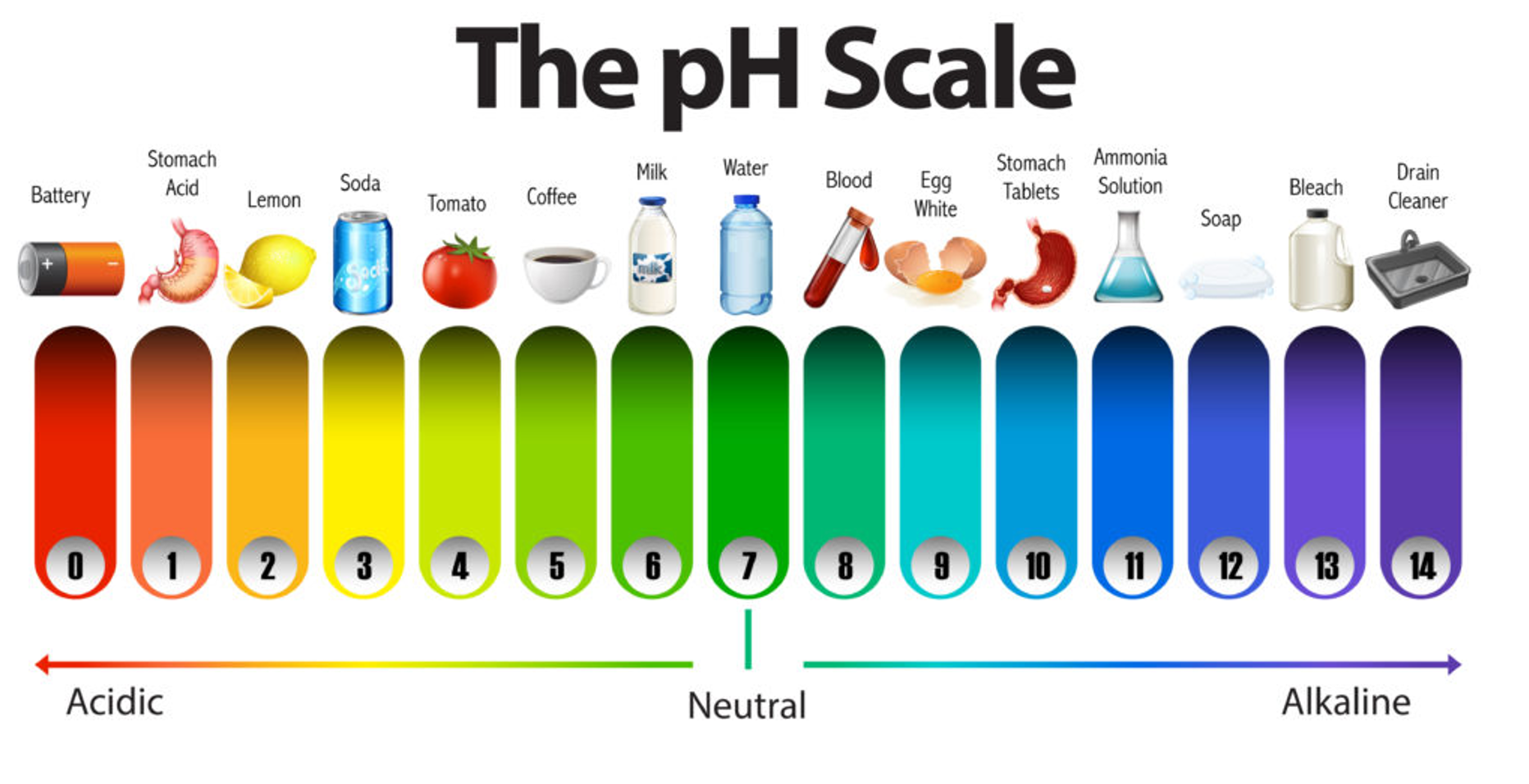
The pH scale
You can describe how acidic or basic a substance is by using the numbers on pH scale
The pH scale ranges from 0-14
Low pH numbers (less than pH 7) mean that the substance is acidic
High pH numbers (more that pH 7) mean that the substance is basic
If a substance has a pH of 7, it is said to be neutral - neither acidic not basic
Pure water is an example of a neutral substance
The pH scale also measures whether an acid or base is strong or weak
A strong acid has a very low pH (pH 0 or 1)
A strong base has a very high pH (pH 14 or 15)
Neutralisation
When an acid and a base react to eachother, the products include water and a salt a reaction like this is called a nautralisation
Neutralisation reactions are also used to cooking and to keep swimming pools and spas clean
To neutralise means to stop something from having an effect.
To stop the properties of acids from having an effect, a base can be added to it.
To stop a bas from having an effect, an acid can be added.
acid + base → water + salt