8.3 Liver and Gall Bladder
Liver Functions
The liver is crucial for many metabolic activities, including:
Carbohydrate metabolism:
Stores glycogen.
Lipid metabolism:
Stores fats.
Protein metabolism:
Synthesizes most plasma proteins.
Storage of vitamins and minerals:
For example, stores Vitamin A.
Detoxification:
Breaks down toxic substances such as alcohol.
Nutrient processing:
All nutrients, except fats, from the gastrointestinal tract are conveyed to the liver via the portal vein.
Bile secretion:
Important for digestion of fats.
Liver Structure
The liver is the largest organ in the body, comprising about 2% of body weight:
Average weight:
Females: ~1400 g
Males: ~1800 g
Palpation:
Only the inferior margin (thin edge) is palpable in a healthy individual.
Anatomical structures:
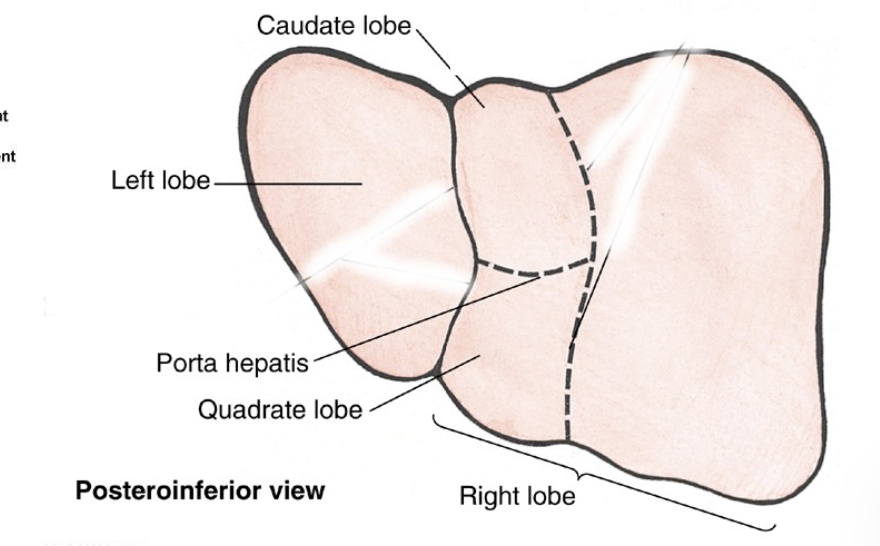
Divided into 4 lobes:
Right lobe (larger)
Left lobe
Caudate lobe
Quadrate lobe
Falciform ligament:
Attaches the liver to the anterior wall, divides left, right
Bare area:
Part of the liver with no peritoneum covering.
Lobular structure:
Functional units are lobules. Each lobule contains acini, which are ellipsoid areas of hepatocytes.
Blood Supply to the Liver
Porta Hepatis (hilum) - door through which blood vessels, nerves and
ducts enter and leave the liver, contains
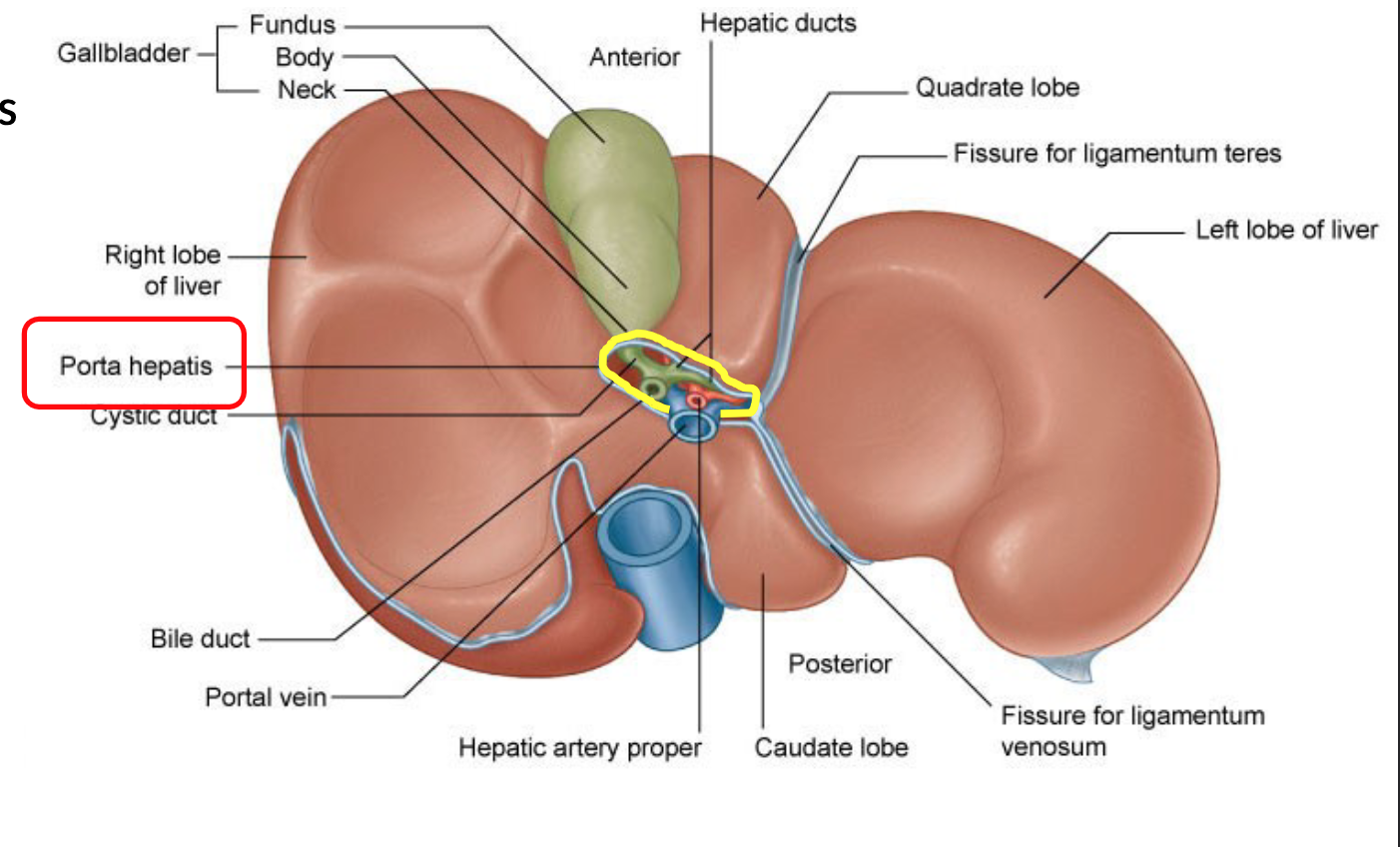
Dual blood supply:
Portal Vein:
Carries 70% of blood to the liver.
Deoxygenated blood with nutrients from the gastrointestinal tract.
Hepatic Arteries:
Carry 30% of oxygenated blood to the liver.
Branch from the celiac trunk.
Venous Drainage:
Blood is drained from the liver via hepatic veins into the inferior vena cava (IVC).
Lymphatics and Nerves
The liver produces a major portion of lymph in the body (around 40% of thoracic duct lymph originates here) via lymphatic vessels
Nerve supply: hepatic nerve plexus
Parasympathetic: Vagus nerve (CN X)
Sympathetic: Splanchnic nerves.
Gallbladder Functions
The gallbladder:
Stores and concentrates bile( fluid used for digestion).
Releases bile to emulsify fats during digestion.
Anatomy of the Gallbladder
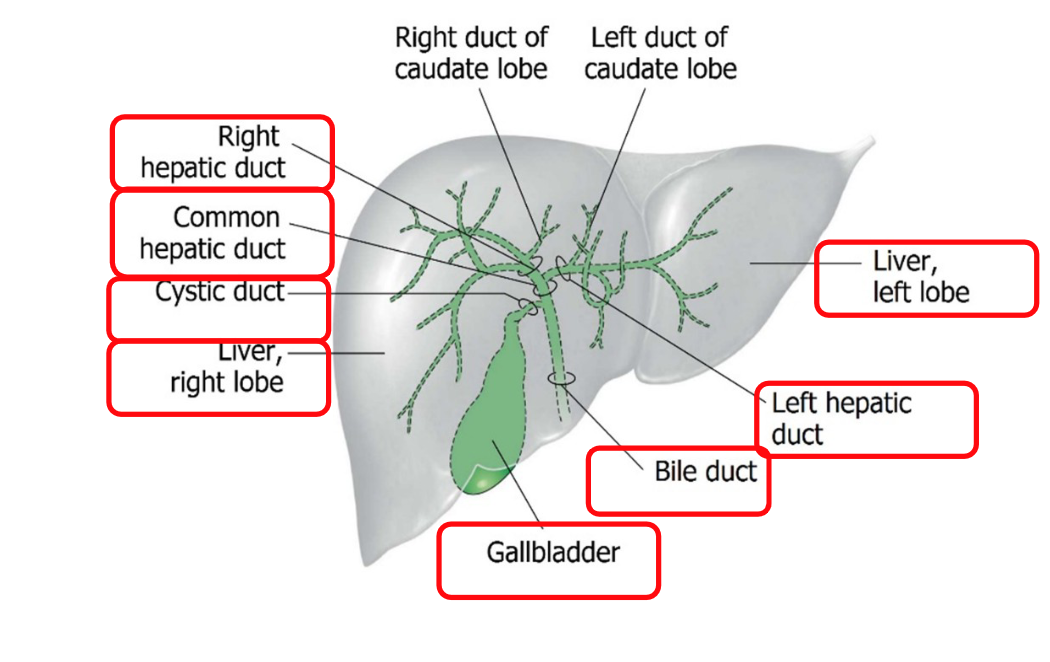
The gallbladder is connected to the liver by a system of ducts:
Right and Left Hepatic Ducts ➜ Common Hepatic Duct ➜ Cystic Duct ➜ Gallbladder
Bile flows from the gallbladder to the duodenum.
Blood Supply and Lymphatics of the Gallbladder
Most blood supply comes from the cystic artery (a branch of the right hepatic artery which arises from the common hepatic artery).
Venous drainage:
Directly into the liver via short venules.
Lymphatics drain into cystic lymph node of Lund located in the Calot triangle.
Innervation of the Gallbladder
Innervation is from:
Right phrenic nerve: Sensory function.
Hepatic branch of the right vagus nerve: Parasympathetic innervation.
Celiac plexus: Sympathetic function.
Surgical impacts:
Procedures such as vagotomy can lead to gallbladder dysfunction, causing formation of gallstones and potential cholecystitis.
Summary of Key Points
The liver's roles include metabolism, vitamin storage, substance breakdown, and bile production.
The gallbladder functions to concentrate and store bile.
Liver anatomy features 4 lobes with a hilum (porta hepatis) and a dual blood supply from the portal vein and hepatic arteries.
Liver lobes are made of functional units (lobules) containing acini, which are critical for liver function.
Bile produced by the liver travels through ducts to the gallbladder, then to the duodenum as needed for fat digestion.